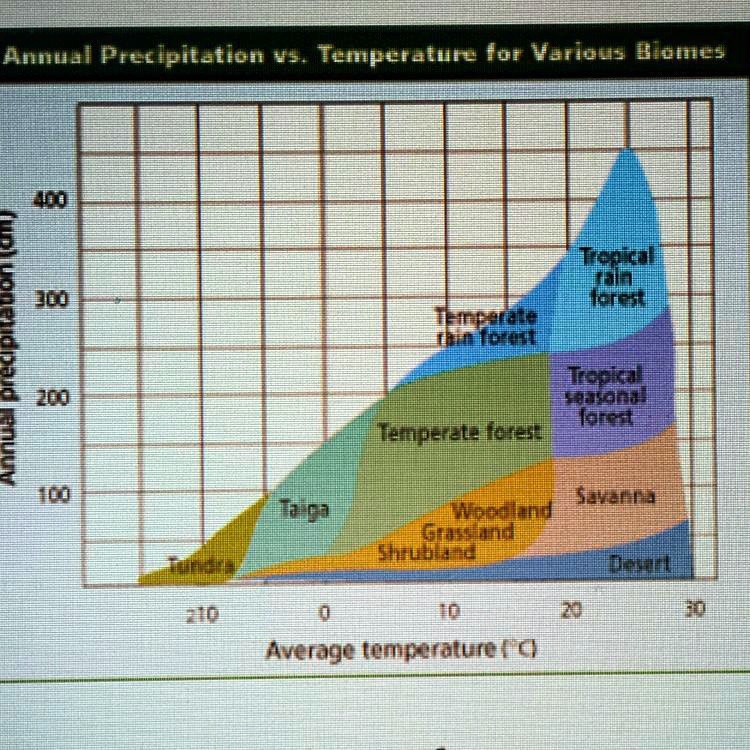
The taiga, also known as the boreal forest, is a vast region of coniferous trees that stretches across North America and Eurasia. It is characterized by long, cold winters and short, cool summers, and is home to a diverse array of plant and animal life. One of the most important factors that shapes the taiga ecosystem is the amount of rainfall it receives.
Rainfall in the taiga is generally low, with annual totals ranging from about 20 to 40 inches (50 to 100 cm). This is due in large part to the fact that the taiga is located in the subarctic and polar regions of the Northern Hemisphere, which experience some of the lowest levels of precipitation on Earth. The taiga also experiences a high degree of evapotranspiration, as the long, cold winters and short, cool summers result in relatively low rates of evaporation from the ground and vegetation.
Despite the low overall levels of rainfall in the taiga, it is an important factor in shaping the ecosystem. The trees of the taiga are adapted to survive in this environment, with thick, waxy leaves that help to conserve moisture and prevent excessive water loss. The roots of these trees are also able to reach deep into the soil in search of moisture, allowing them to thrive even in dry conditions.
The distribution of rainfall within the taiga also plays a significant role in shaping the ecosystem. In some areas, the taiga receives more rainfall due to the influence of nearby bodies of water, such as lakes and oceans. These areas are often characterized by more lush, diverse vegetation and a greater variety of plant and animal life. On the other hand, areas of the taiga that are further inland and away from these bodies of water tend to receive less rainfall and have a more sparse, less diverse vegetation.
Overall, the amount of rainfall in the taiga plays a critical role in shaping its ecosystem. Despite the low levels of precipitation in this region, the trees and other plants of the taiga have adapted to thrive in this environment, and the distribution of rainfall has a significant impact on the diversity and abundance of plant and animal life.