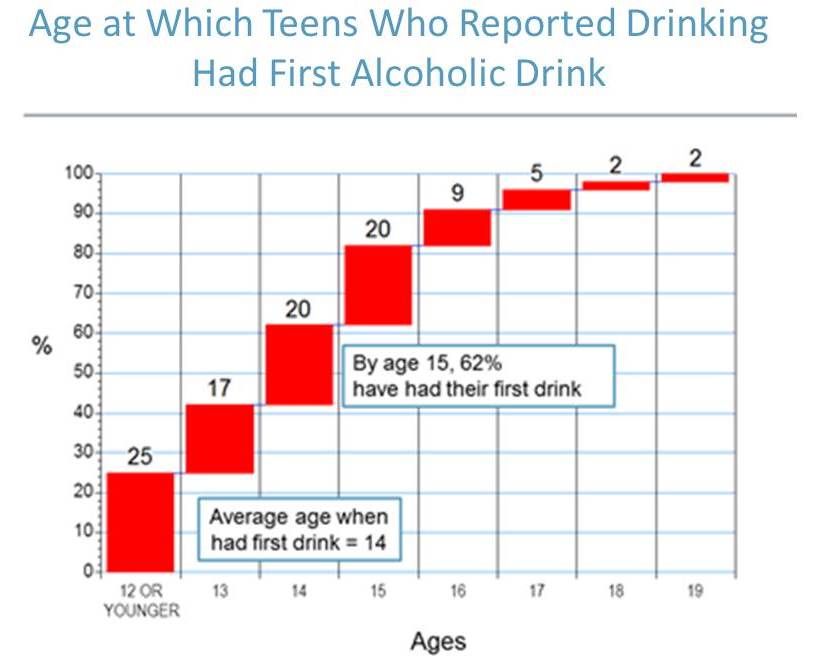
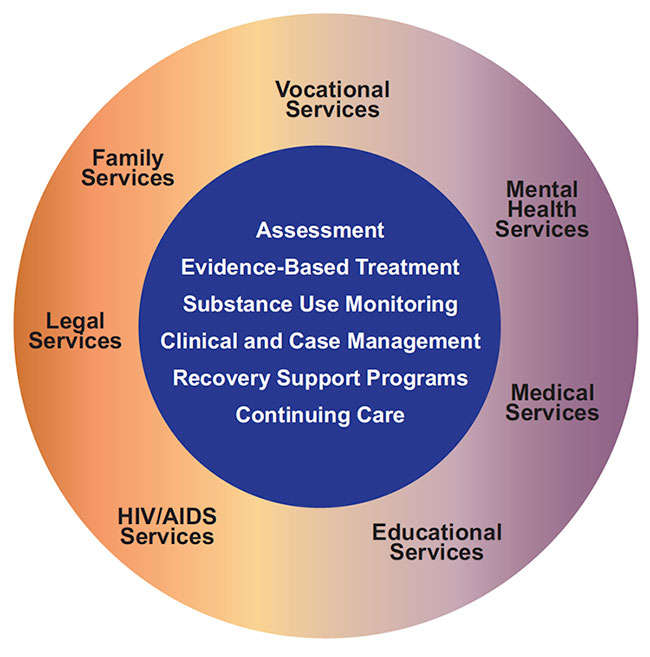
Teenage drug abuse is a significant problem that affects communities across the United States. According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), approximately 10% of teenagers in the US have used an illicit drug in the past month. This problem not only has the potential to cause harm to the individual teenager, but it can also have negative consequences for their family, school, and community.
There are a variety of factors that can contribute to teenage drug abuse. One of the most common is peer pressure, as many teenagers feel pressure to fit in with their friends and may use drugs in order to do so. Other contributing factors can include mental health issues, such as depression or anxiety, a lack of parental supervision, and a lack of access to positive role models or activities.
The consequences of teenage drug abuse can be severe. It can lead to physical health problems, such as organ damage and addiction, as well as mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety. Drug abuse can also lead to criminal behavior and legal problems, and can interfere with school and work performance.
There are several ways in which we can address the issue of teenage drug abuse. One approach is to educate teenagers about the risks and consequences of drug use. This can be done through school programs and community initiatives that provide information about the dangers of drug abuse. Another approach is to provide support and resources for teenagers who are struggling with drug abuse. This can include access to counseling and treatment programs, as well as support from friends and family.
In conclusion, teenage drug abuse is a significant problem that affects communities across the United States. It is important to address this issue through education and support, in order to help teenagers avoid the negative consequences of drug abuse and lead healthy and productive lives.
Teenage drug abuse is a significant problem that affects millions of adolescents in the United States. It is a public health concern that can have serious consequences for both the individual and society. This paper will explore the causes and consequences of teenage drug abuse, as well as discuss potential prevention and treatment methods.
One of the main causes of teenage drug abuse is the influence of peer pressure. Adolescents are often surrounded by peers who engage in risky behaviors, and they may feel pressure to fit in or be accepted by their peers. This can lead them to experiment with drugs or continue using them even if they know it is harmful.
Another cause of teenage drug abuse is a lack of parental supervision and involvement. When parents are not present or actively engaged in their child's life, adolescents may be more likely to engage in risky behaviors, including drug use. This is especially true for teens who come from homes with a history of drug abuse or where drugs are easily accessible.
The consequences of teenage drug abuse can be severe and long-lasting. Substance abuse can lead to physical and mental health problems, such as addiction, brain damage, and mental illness. It can also interfere with academic and social functioning, and increase the risk of accidents and injuries. In addition, drug abuse can lead to legal problems and damage relationships with friends and family.
Preventing teenage drug abuse requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the root causes of the problem. This may include educating teens about the dangers of drug use, providing support and guidance to at-risk teens, and implementing policies and programs that promote healthy behaviors.
Treatment for teenage drug abuse typically involves a combination of therapies, such as individual and group counseling, support groups, and medication-assisted treatment. Treatment can be provided in a variety of settings, including outpatient clinics, residential programs, and hospitals.
In conclusion, teenage drug abuse is a significant problem that has serious consequences for both the individual and society. To effectively address this issue, we need to address the root causes of the problem and provide appropriate prevention and treatment options.