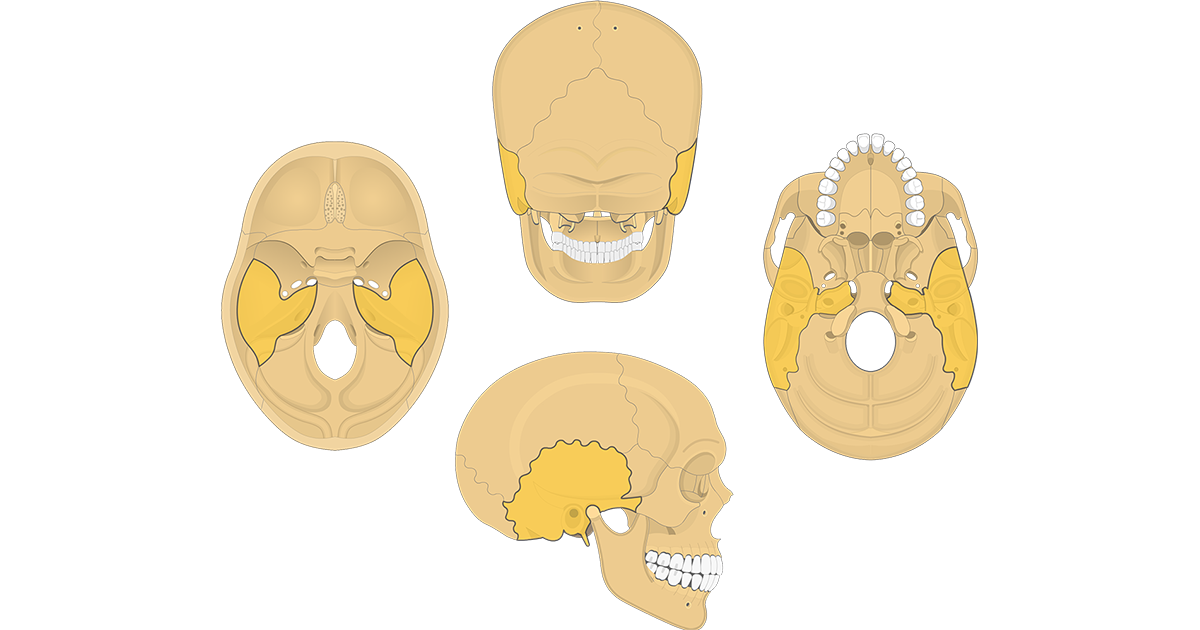
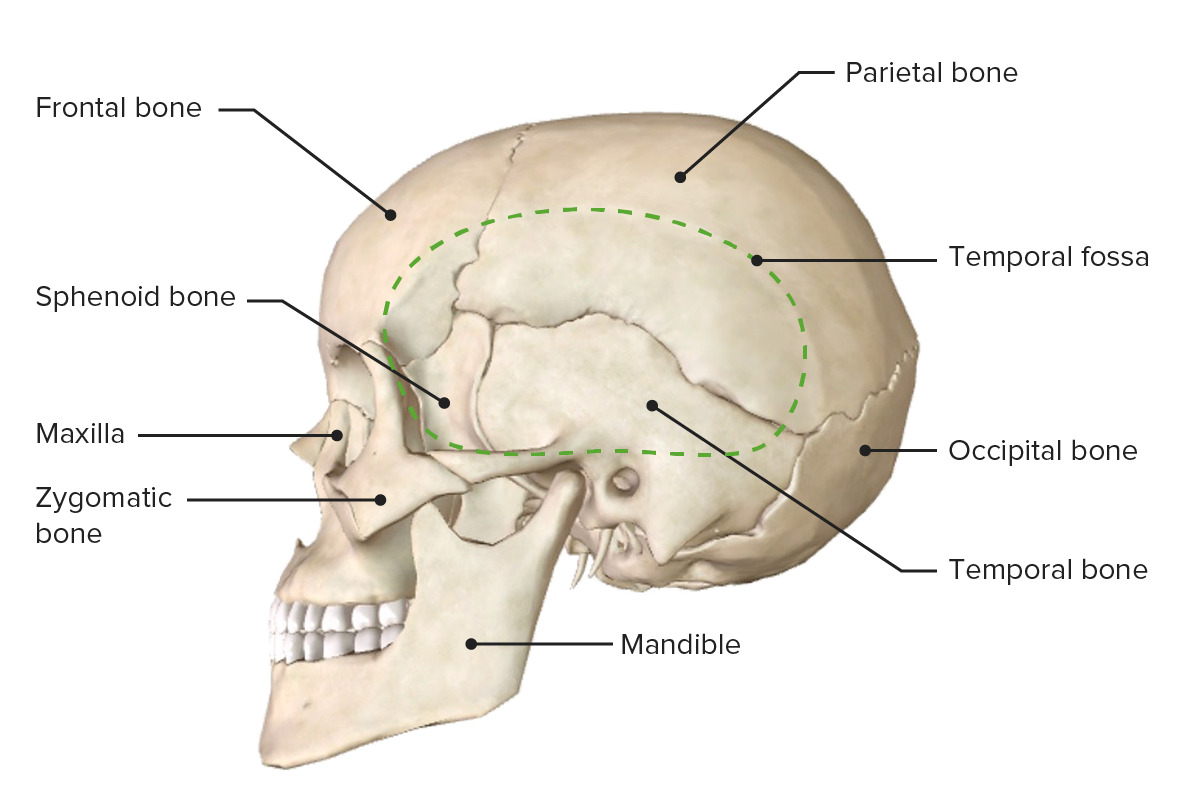
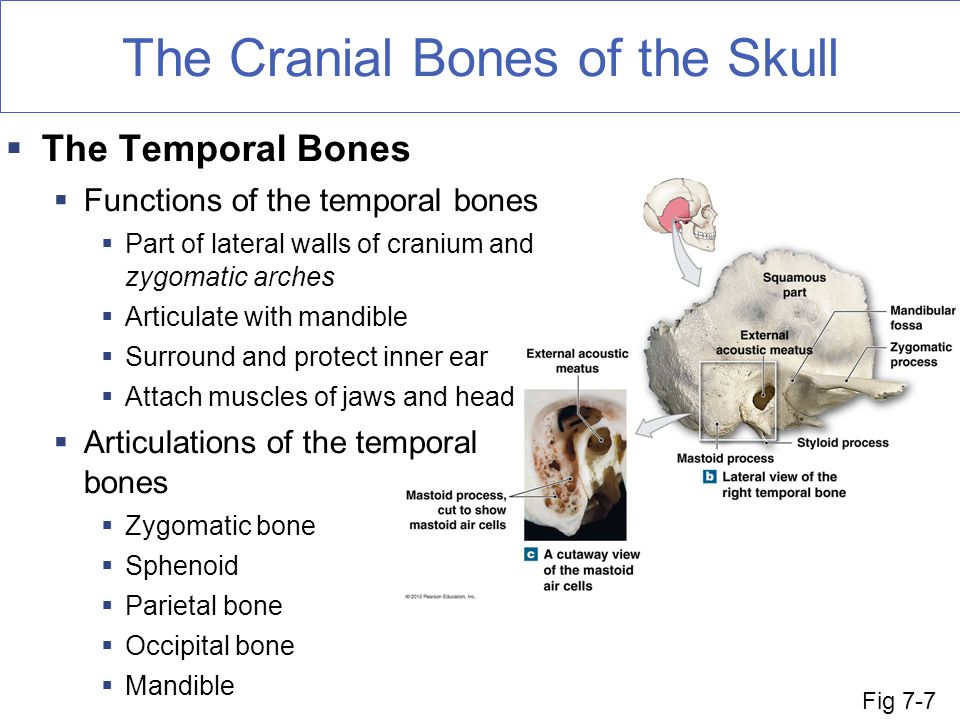
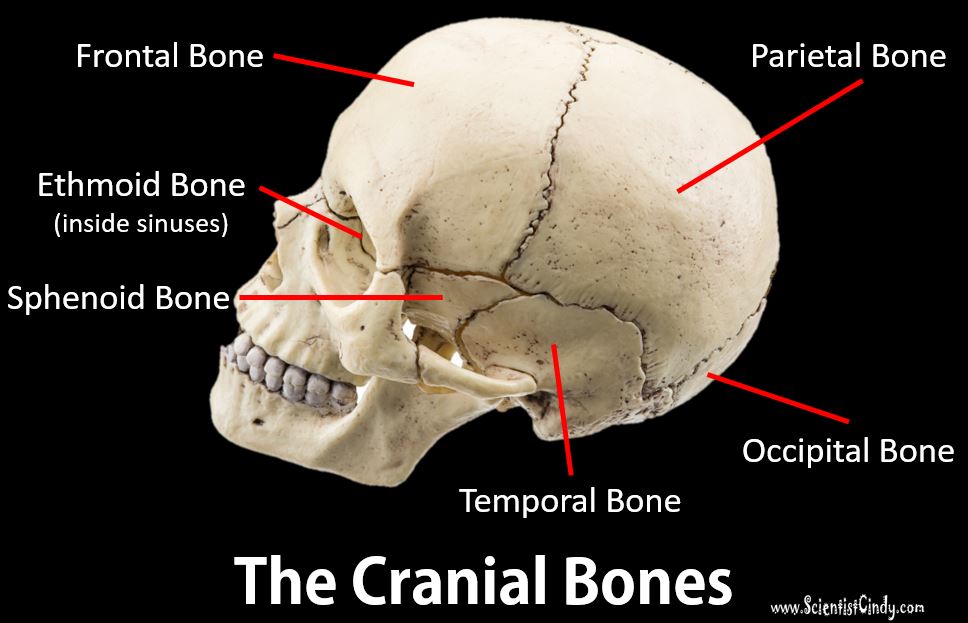
The temporal bones are a pair of bones located on either side of the skull, behind the ears. These bones have several important functions in the body.
First and foremost, the temporal bones serve as protective structures for the brain. They contain the auditory tubes, which allow for the passage of sound waves to the inner ear, and the auditory ossicles, which are small bones that transmit sound waves from the eardrum to the inner ear. The temporal bones also house the structures that are responsible for balance, including the vestibular system and the vestibulocochlear nerve.
In addition to their role in hearing and balance, the temporal bones also serve as attachment points for several muscles. These muscles, including the temporalis and masseter muscles, are responsible for chewing and facial expressions.
The temporal bones also contain the zygomatic arch, which is a bony arch that spans across the cheek and is important in the movement of the lower jaw. The zygomatic arch is formed by the zygomatic process of the temporal bone and the zygomatic process of the cheekbone.
Finally, the temporal bones contain several important blood vessels and nerves, including the internal carotid artery and the middle meningeal artery, which provide blood to the brain, and the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for sensation in the face.
In summary, the temporal bones are essential for several important functions in the body, including hearing, balance, facial expression, and the supply of blood and nerves to the brain. They play a vital role in the overall function and health of the body.
Infections of the Temporal Bone

One can feel the zygomatic process by touching just under the eye and moving toward the ear. It forms a bony mass between the sphenoid and occipital bones within the cranial cavity. The contraction of its anterior fibers moves the mandible dorsocranially elevation. Treatment for temporal lobe damage will vary depending on what types of secondary effects the individual is experiencing. Notably, fractures can also lead to leaking of cerebral spinal fluid. Ligaments and joint capsule Synonyms: Superior and inferior synovial membranes of temporomandibular joint, Synovium of temporomandibular joint , The joint capsule originates from the borders of the mandibular fossa, encloses the articular tubercle of temporal bone and inserts at the neck of mandible above the pterygoid fovea, which is a depression on the anterior surface of the neck. It then enters the foramen lacerum, transits the pterygoid canal and enters sphenopalatine fossa through the vidian canal.
Temporal Lobe Function

Lobes of the Brain The brain as a whole can be divided into three main parts: the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brainstem. Sound enters the ear canal and makes the tiny bones ossicles inside the ear vibrate. A narrow bony projection, called the styloid process, extends downwards and anteriorly from the inferior surface of the tympanic part. Depending on the extent of the tumor, radiation sometimes has to be performed as well. This hollow partially encloses the internal acoustic meatus and the Synonyms: Meckel's groove, Impressio trigemini ossis temporalis The ridge is limited posteriorly by the arcuate eminence, which is raised superiorly by the superior semicircular canal. We hope this article helped you understand the potential outcomes of temporal lobe damage and how to approach recovery.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-5356410071-2f406d60bf76433fb276382a83cfcd4c.jpg)