In the Odyssey, omens play a significant role in the story as they provide hints and clues about the future events that will unfold. These omens can take many forms, including dreams, bird sightings, and natural phenomena.
One of the most prominent omens in the Odyssey is the dream that Odysseus has while he is held captive on the island of Calypso. In this dream, an eagle with a dove in its claws tells him that he must leave Calypso and return home to Ithaca. This dream serves as a sign that Odysseus' long journey is finally coming to an end and that he will soon be reunited with his loved ones.
Another important omen in the Odyssey is the sight of a pair of eagles fighting over a hare. This omen is interpreted by the suitors as a sign that they will soon be victorious in their quest to win Penelope's hand in marriage. However, the eagles are actually a sign that Odysseus is on his way home and will soon reclaim his throne from the suitors.
There are also several instances of natural omens in the Odyssey, such as the appearance of a rainbow, which is seen as a sign of good fortune. Similarly, the sight of a shooting star is seen as a positive omen, indicating that a new era of peace and prosperity is about to begin.
Overall, the omens in the Odyssey serve as an important narrative device, helping to foreshadow future events and add a sense of mystery and suspense to the story. They also highlight the role of the gods in the lives of the characters, as it is believed that the gods are responsible for sending these signs and predicting the future.
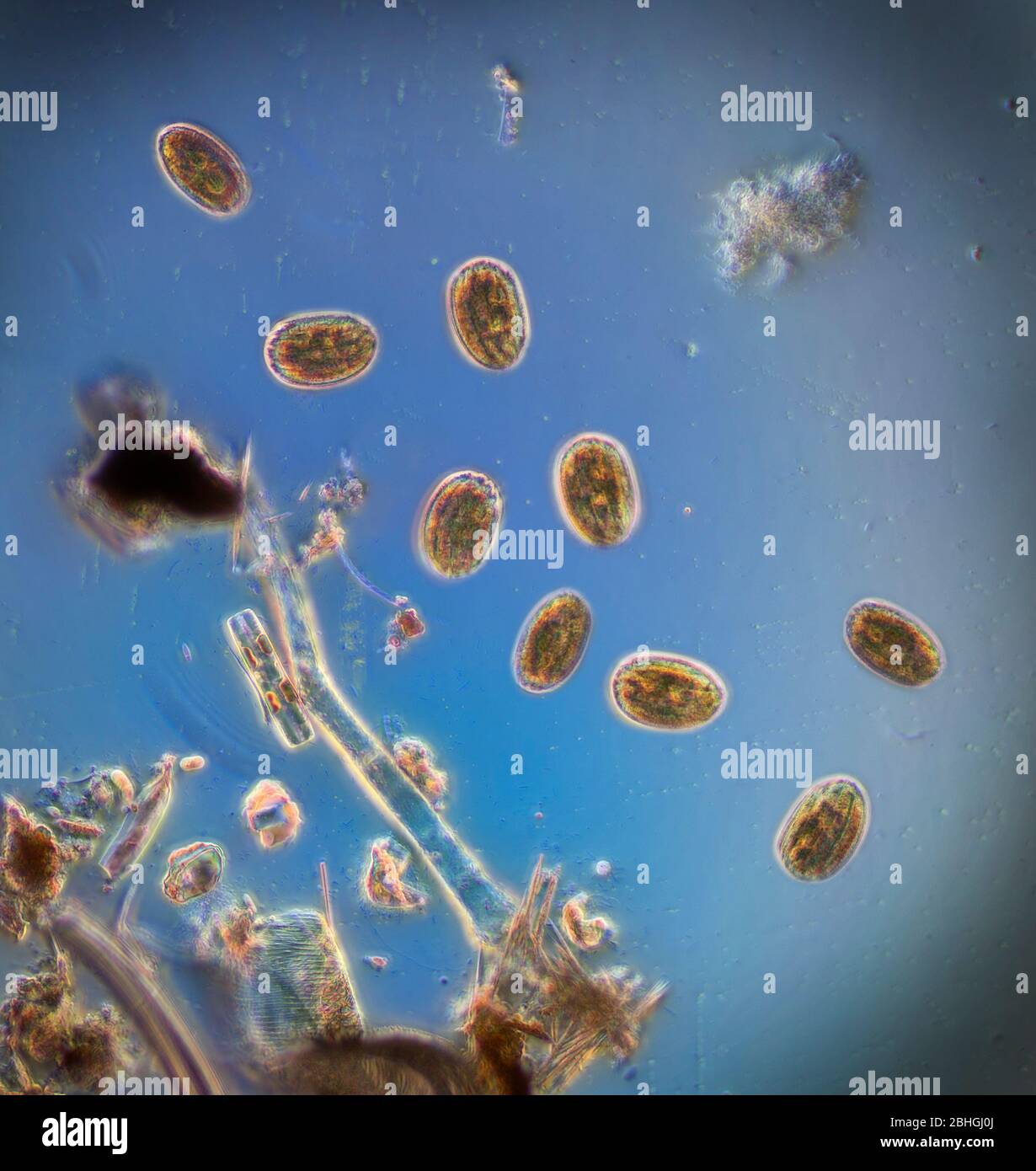
PHYSIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF TETRAHYMENA VORAX.
They were washed three times in sterilized, deionized water. Phenotypic switching in polymorphic Tetrahymena: a single-cell Jekel and Hyde. Once it is released from the cells, the chelate functions as a paracrine ligand that induces microstomal to macrostomal differentiation in Tetrahymena vorax. It has been shown that the iron chelate is most active at lower pH values than higher pH levels Ryals et al. This whole process takes about 12 hours at 30°C, but even longer than this at cooler temperatures. However, chromosome duplication had not taken place, as indicated by the wild-type ploidy and the normal quantity of other genes on the same chromosomes.
The Feeding Behavior Of The Protist Known As Tetrahymena Vorax Case Study Solution and Analysis of Harvard Case Studies

The experiments were performed at room temperature 21—23°C. This model is consistent with coordination potential between hypoxanthine and uracil, however, several other structures are possible. At the end of the incubation period, the cells were quickly but gently mixed with formaldehyde to a final concentration 0. It has been suggested that the formation of food vacuoles is induced by the mechanical action of captured particles Tetrahymena pyriformis incubated with polystyrene latex particles and natural food particles bacteria accepted the polystyrene latex particles as readily as the bacteria, and acid phosphatase appeared normally in the vacuoles The non-selective phagocytosis seen in microstomes changes to a highly selective process during the transformation to macrostomes. The mechanoreceptor potentials and the associated Ca 2+ spikes also seem to be linked to the prey-capturing behaviour of macrostome cells. However, the cell also tended to follow the outline of the obstacle simply by continued forward swimming.
How does Tetrahymena feed?

After reading the case and guidelines thoroughly, reader should go forward and start the analyses of the case. Phagocytosis and the formation of food vacuoles are essential processes involved in the growth and development of Tetrahymena thermophila populations. Specifically, chromatographic analysis has revealed that ferrous iron, hypoxanthine, and uracil are the chemicals in stomatin responsible for triggering the morphological change. A bioassay has been developed to test the inductive qualities of stomatin preparations. There were also some differences in swimming behaviour in the two morphs. Initially, fast reading without taking notes and underlines should be done.
Tetrahymena vorax (Kidder et al.) Kidder

The aim of this study was to compare the susceptibility to infection with Tetrahymena of five different ornamental fish species from two different super orders. These results indicate that macrostome T. Species in genus Species in this genus include. CRC Press, LLC Boca Ratan, Florida. Retrieved Dec 30 2022 from Tetrahymena vorax is a fresh water polymorphic ciliated protist. The experimental saline solution was prepared following the method of Dryl -1,respectively. While the actual number of unique chromosomes are unknown, the number is thought to be around 187 in the MAC, and 5 in the MIC.
Tetrahymena

The cell then swims forward again, the prey is in a digestive vacuole DV 6. The tetrahymena organism is present in almost all tanks feeding on bacteria in the water. Upper panels display the various positions of the glass needle used to stimulate the cells. The germline nucleus contains 5 pairs of chromosomes which encode the heritable information passed down from one sexual generation to the next. It is at this junctional zone that several hundred fusion pores form, allowing for the mutual exchange of protein, RNA and eventually a meiotic product of their micronucleus. In the experiments, we used T.







