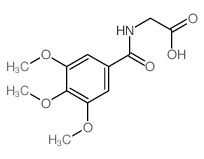
Tetraphenylcyclopentadienone, also known as TPCP, is a chemical compound commonly used as a starting material in the synthesis of organic compounds. It is a yellow solid with a molecular formula of C24H20O and a molecular weight of 312.41 g/mol.
The Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for TPTP provides important information about the safe handling and use of the compound. The MSDS includes information on the physical and chemical properties of TPTP, as well as its potential health and environmental hazards.
One of the physical properties of TPTP listed on the MSDS is its melting point, which is reported to be between 118-120°C. The compound is also reported to be soluble in a variety of organic solvents, including ethanol, acetone, and chloroform.
The MSDS also provides information on the potential health hazards of TPTP. The compound is classified as a skin and eye irritant, and can cause skin irritation and redness upon contact. Inhalation of TPTP can also irritate the respiratory tract and cause coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing. Ingestion of TPTP can cause nausea, vomiting, and gastrointestinal irritation.
The MSDS also includes information on the environmental hazards of TPTP. The compound is not readily biodegradable and can accumulate in the environment. It may also be toxic to aquatic life if released into water.
It is important to handle TPTP with care and to follow proper safety guidelines when working with the compound. This includes wearing protective clothing and equipment, such as gloves, goggles, and a lab coat, and working in a well-ventilated area. It is also important to properly store TPTP and dispose of it according to local regulations.
In conclusion, the Material Safety Data Sheet for TPTP provides important information on the safe handling and use of the compound. It is important to follow proper safety guidelines when working with TPTP to minimize the potential health and environmental hazards associated with the compound.