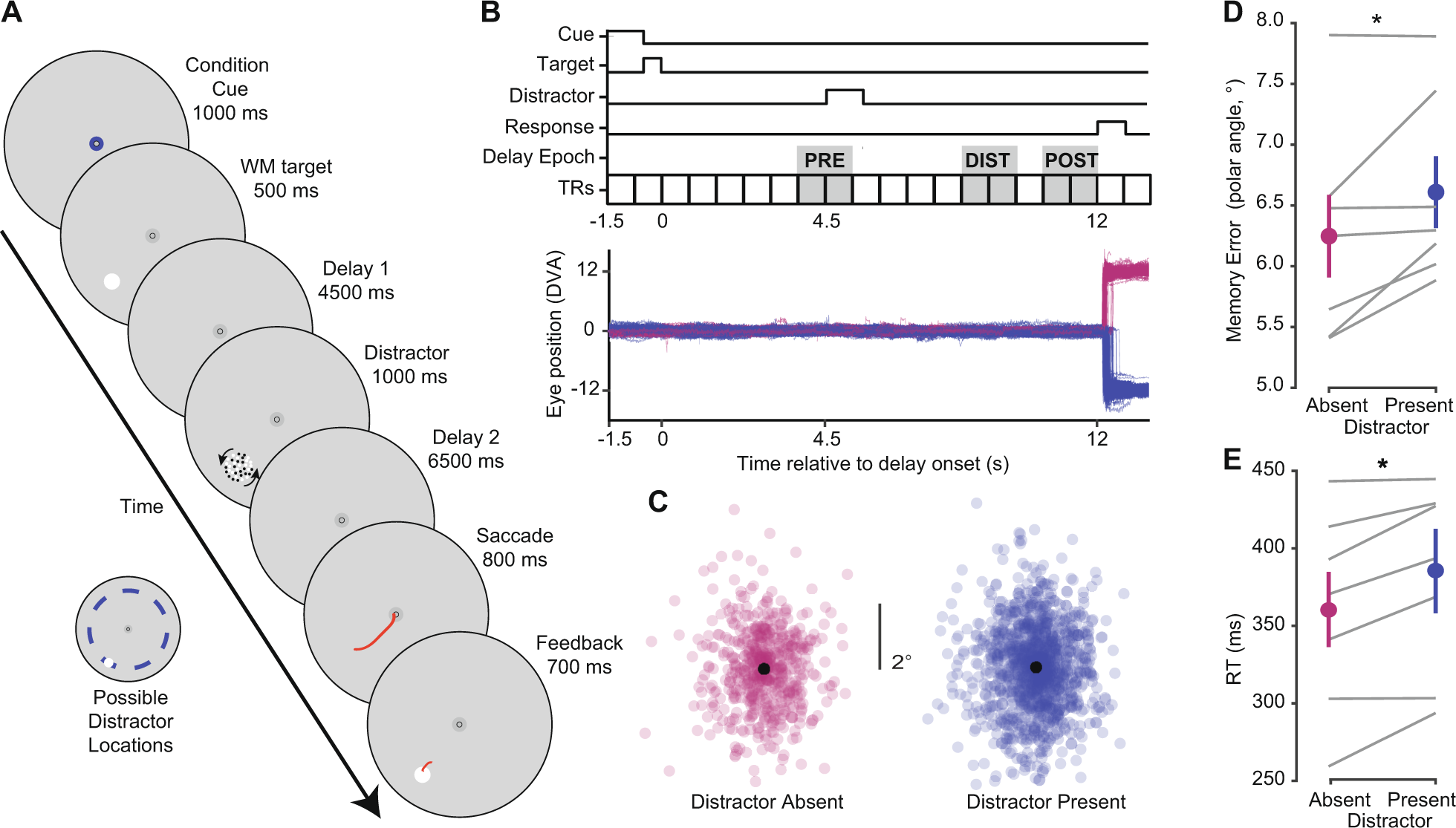
The activation information mode (AIM) model is a theory of how the brain processes information and how it is related to consciousness. It was developed by Bernard Baars, a cognitive neuroscientist, in the 1980s and has since been widely studied and discussed in the field of psychology.
According to the AIM model, the brain processes information in two different modes: the unconscious mode and the conscious mode. The unconscious mode is responsible for automatic processes, such as reflexes and basic perceptual processing, while the conscious mode is responsible for more complex cognitive processes, such as decision making and problem solving.
One key aspect of the AIM model is the concept of "global workspace," which refers to a shared, conscious space where information from various sources is integrated and can be accessed by different cognitive processes. Information in the global workspace is considered "activated," meaning it is currently being actively processed and is available for use in decision making and other cognitive tasks.
The AIM model suggests that the brain has limited capacity for processing activated information and that this capacity is a key factor in determining our level of consciousness. When we are fully conscious, the global workspace is fully activated and we are able to process a large amount of information at once. On the other hand, when we are unconscious or in a state of reduced consciousness, such as during sleep or under the influence of drugs, the global workspace is less activated and we are able to process less information.
The AIM model has been influential in the study of consciousness and has led to a better understanding of how the brain processes and integrates information. It has also been used to explain various phenomena, such as the role of sleep in memory consolidation and the effects of different drugs on consciousness.
Overall, the activation information mode model provides a framework for understanding the relationship between brain function and consciousness, and has contributed significantly to our knowledge of the complex processes underlying mental activity.
What Is Activation in Psychology?

These two ways are: Definition Photons and waves Term When light waves enter the eye, they first pass through the Definition cornea Term Which of the following is true about cones? A girl learns that whenever her brother shares his cookie with her, her mother gives him a piece of candy. He hopes they will learn not to eat the sheep. Which of the following statements is NOT true according to the neurocognitive perspective on dreaming? Also, they reveal our desires and fears. Term A humanistic psychologist would be interested in which of the following research studies? Consciousness-Your awareness of everything that is going on around you and inside your own head at any given moment, which you use to organize your behavior including your thoughts, sensations, and feelings. Many parts of the brain baffle scientists, but a specific aspect of the mind that is fascinating and puzzling is dreams and their functions.
Intro to Psych and Behaviour Chapter 5 Flashcards
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/iStock-524160718-59566dfd3df78c4eb629ed75.jpg)
A major reason being that only the dreamer can experience and retell the dream. In 'Introductory Lectures on Psycho-Analysis,' he wrote: 'Though the number of symbols is large, the number of subjects symbolized is not large. A creativity B self-awareness C consciousness D intelligence C consciousness To treat your sleep problem you are told that you should not nap, you should set your alarm clock to wake up at the same time each day, and you should get out of bed if you cannot sleep. Using your bed for sleeping, and only for sleeping, helps train your body to sleep there with less difficulty. Other than that, dreams are meaningless. This is an example of a Definition negative correlation. A heroin B alcohol C cocaine D marijuana B alcohol Tommy desperately wants to quit smoking.
PSYC1030
D She was having a non-REM dream that was more like fleeting sleep images. A Dement B James C Freud D Jung A Dement Mary is having insomnia. This find contradicts the classic Freudian theory of a driving force behind all dreams. Definition the brain and the spinal cord. This phenomenon is called Definition All of the above a monocular cue, a pictorial depth cue, linear perspective Term What term do psychologist use to designate our personal awareness of feelings, sensations, and thoughts? C The animal comes to the laboratory a tabula rasa, or "blank slate,"and can be taught anything with the right conditioning. When you ask him how he made it through, he says, "I had eidetic imagery.
What does the activation information mode model suggests?
Term The point at which a person can detect a stimulus 50 percent of the time it is presented is called the Definition Absolute threshold Term An automobile manufacturer has decided to add a little bit of horsepower to its cars. Definition They amplify the vibrations of the ear drum. When the topic of punishment is discussed, what is one outcome of punishment the expert is likely to note for the parents to consider? Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP -A device that delivers a continuous stream of air under mild pressure. A psychogenic drug B stimulant C narcotic D depressant B stimulant What is the largest single preventable cause of premature death in the United States? C There have been cases in which sleepwalking was a successful murder defense. D All of the statements are not true. C Her son must always model the behavior immediately. A drugs that slow down activity in the central nervous system B drugs capable of influencing perception, mood, cognition, or behavior C drugs that speed up activity in the central nervous system D drugs derived from the opium poppy that relieve pain and produce euphoria B drugs capable of influencing perception, mood, cognition, or behavior A newspaper advertisement describes a book that offers interpretations of dreams.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/iStock-524160718-59566dfd3df78c4eb629ed75.jpg)