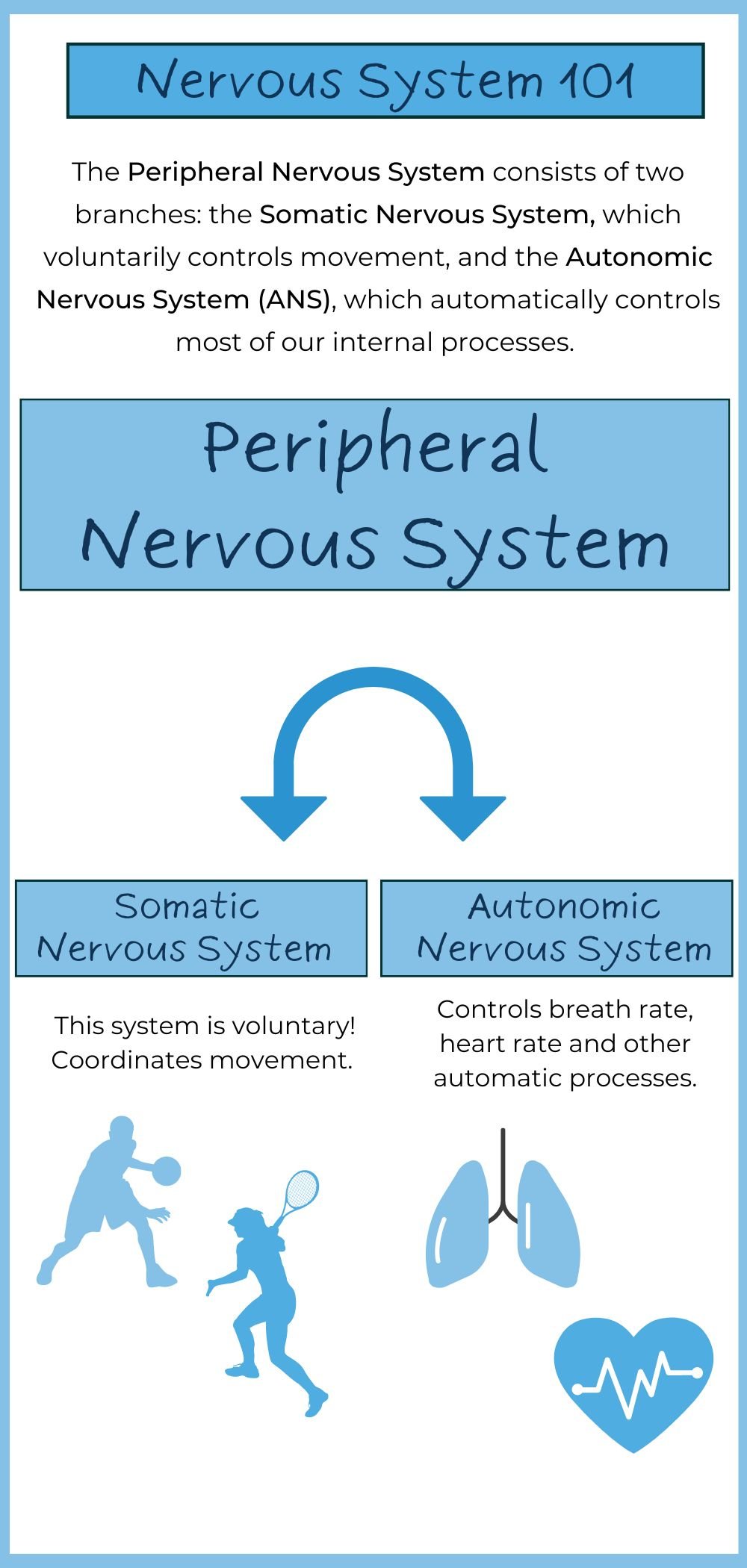
The autonomic system is a complex network of nerves and hormones that controls the body's unconscious actions, such as digestion, heart rate, and breathing. While it is often thought of as being separate from the nervous system that controls voluntary movement, the autonomic system actually plays a crucial role in enabling and regulating voluntary movement.
The autonomic system is divided into two branches: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for activating the body's "fight or flight" response, while the parasympathetic nervous system helps the body rest and digest. Both of these systems work together to maintain homeostasis, or balance, within the body.
One way that the autonomic system affects voluntary movement is by regulating blood flow and oxygen delivery to the muscles. During physical activity, the sympathetic nervous system increases heart rate and blood pressure to ensure that the muscles have an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients. On the other hand, the parasympathetic nervous system slows down heart rate and blood pressure after physical activity to allow the body to recover.
In addition to regulating blood flow, the autonomic system also plays a role in the function of the muscles themselves. The sympathetic nervous system stimulates the release of hormones such as adrenaline and noradrenaline, which can increase muscle strength and endurance. These hormones can also increase the body's overall metabolic rate, which can help to fuel the energy demands of voluntary movement.
Another way that the autonomic system affects voluntary movement is through the control of sweat production. During physical activity, the sympathetic nervous system activates sweat glands to help regulate body temperature and prevent overheating. Sweating is an important way for the body to dissipate heat and maintain a stable internal temperature, which is necessary for optimal muscle function.
In conclusion, the autonomic system plays a vital role in enabling and regulating voluntary movement. From regulating blood flow and oxygen delivery to the muscles, to controlling sweat production and hormone release, the autonomic system helps to maintain homeostasis within the body and ensure that the muscles have the necessary resources to function optimally.
Does the autonomic system control voluntary movement?
These nerves carry signals from the five senses to the head, neck, and tongue. The sympathetic nervous system supplies nerves to the abdominal and pelvic visceral organs, as well as hair follicles, sweat glands, and more. Vitamin deficiencies, especially vitamin B12, can damage your autonomic nervous system. Both Again, heart rate variability becomes a relatively sensitive and non-invasive measure of autonomic nervous system activity. What part of the nervous system is described as a regulating function of body parts associated with involuntary body movements? Your clammy and tremulous hands attempt to grasp the wheel. Think of the sympathetic nervous system as revving up all bodily functions that are critically important for immediate survival while downregulating the bodily functions that are less critical.
Autonomic Nervous System: What It Is, Function & Disorders
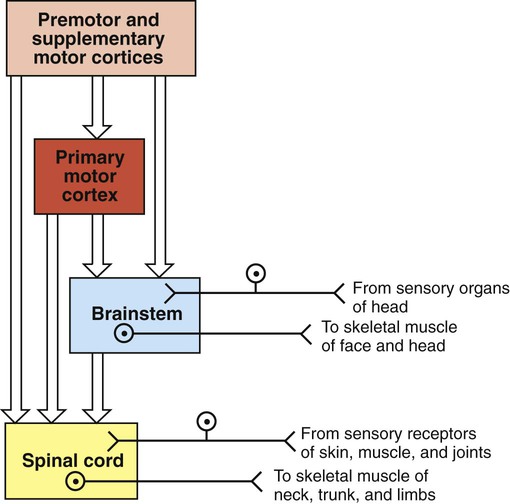
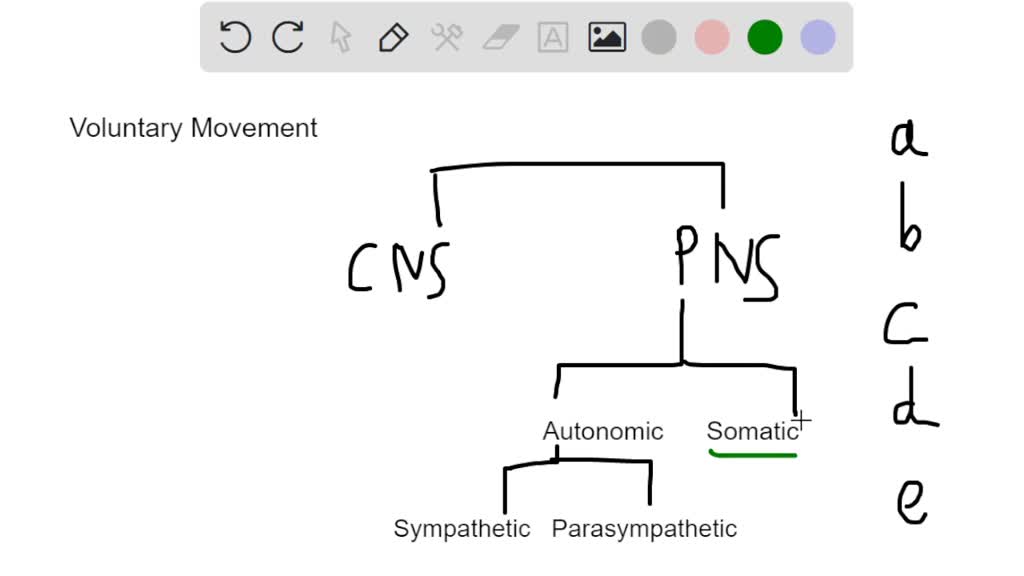
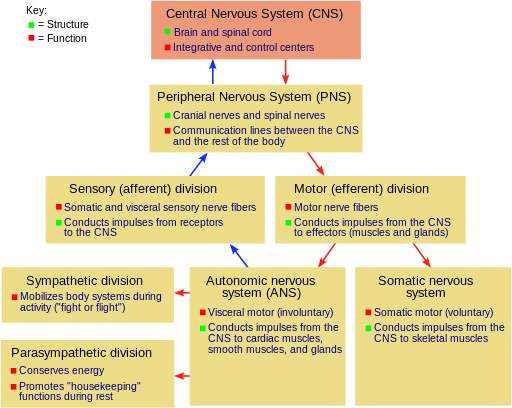
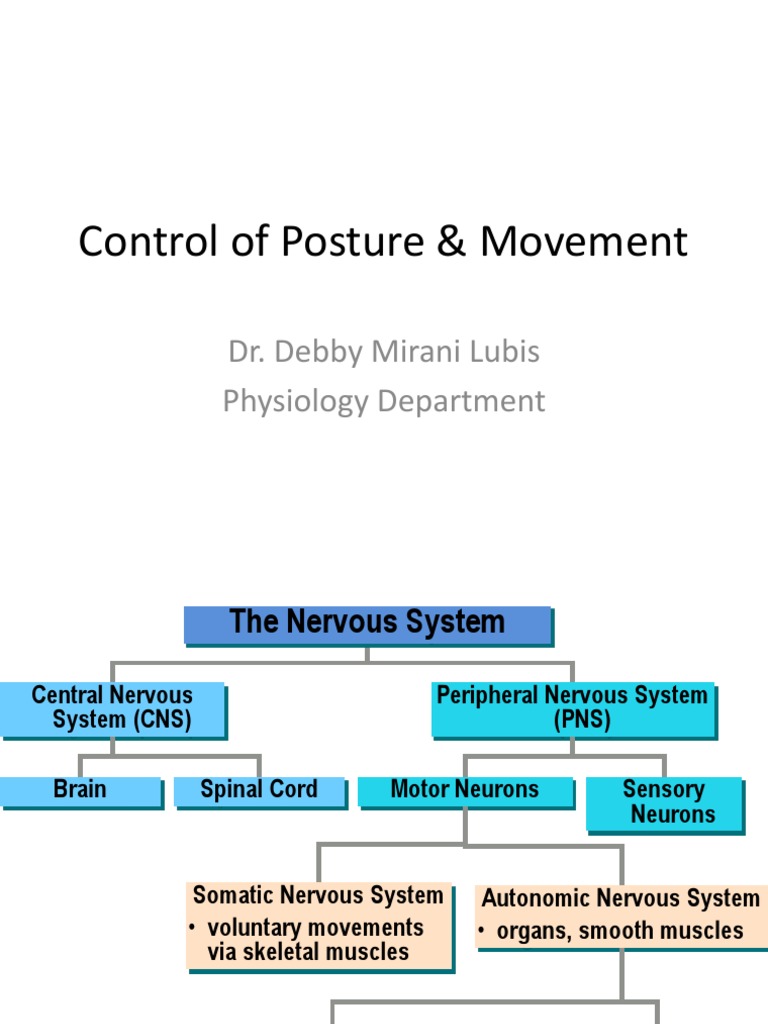
A spinal cord, which is located in the brain, governs the muscles. The sympathetic division is responsible for "fight or flight" responses such as increased heart rate, dilated pupils, and sweating. Most nerves release norepinephrine, but those that signal to the sweat glands release acetylcholine. Adams and Victor's Principles of Neurology, 11e. The role of each division is described below. Motor, or efferent, fibers transmit orders from the CNS to the body to generate a response. Other dysautonomias include digestive malfunction, heart or lung control issues, and other malfunctions involving systems which are typically under the control of the subconscious.
Does the autonomic nervous system control voluntary movement?
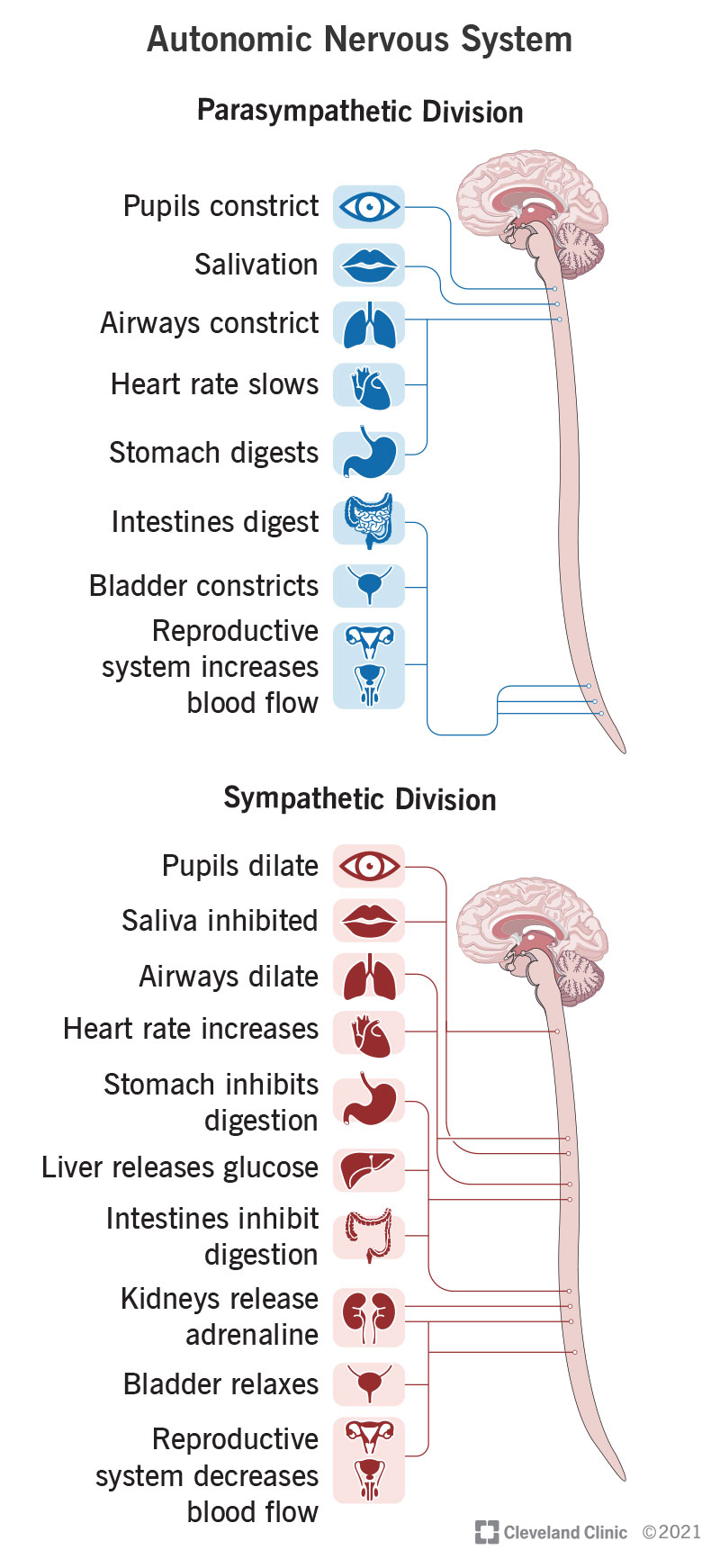
Postganglionic Parasympathetic Neurons Similar to the sympathetic nervous system, an action potential is generated through the postganglionic parasympathetic neuron once preganglionic acetylcholine binds to postganglionic nicotinic cholinergic receptors. Although the majority of autonomic nervous system reactions are involuntary, they can interact with the somatic nervous system, which controls voluntary movements. Your nervous system helps you regulate your voluntary and involuntary actions, as well as thinking, communicating, and memory. Autonomic afferent nerves are common to the entire system, they do not differentiate into sympathetic or parasympathetic. Autonomic disorders have many different causes. Although most of the autonomic nervous system responses are involuntary, they can integrate with the somatic nervous system, which is responsible for the voluntary movements. It is not diagnosed if it is caused by a general medical condition.