The dorsal root ganglia (DRG) are a group of small, spherical structures located along the spinal cord. They are an essential component of the nervous system and play a key role in the transmission of sensory information from the body to the brain.
The DRG consist mainly of sensory neurons, which are specialized cells that are responsible for detecting changes in the external and internal environment of the body. These neurons have long, thin processes called axons, which extend from the DRG and travel to the brain or other parts of the body. When sensory neurons detect a change in their environment, they generate an electrical signal called an action potential, which travels along the axon and is transmitted to the brain or other parts of the body.
The DRG are crucial for the perception of pain, temperature, touch, and other sensations. They also play a role in the reflexes that help us maintain balance and coordination, such as the reflexes that help us maintain our posture and avoid falling.
The DRG are located near the spinal cord and are connected to it by a series of nerve fibers called afferent fibers. These fibers carry sensory information from the body to the brain, where it is processed and interpreted. The DRG also contain a small number of motor neurons, which are specialized cells that transmit signals from the brain or spinal cord to muscles and other organs.
In addition to their role in sensory and motor functions, the DRG are also involved in the regulation of inflammation and the immune response. They contain a variety of immune cells and signaling molecules that play a role in the body's response to injury and infection.
Overall, the DRG are an essential component of the nervous system, and their proper functioning is crucial for the perception of sensory information and the maintenance of reflexes and coordination. Any dysfunction or damage to the DRG can lead to sensory and motor deficits, as well as a range of other problems.
Dorsal Root Ganglion

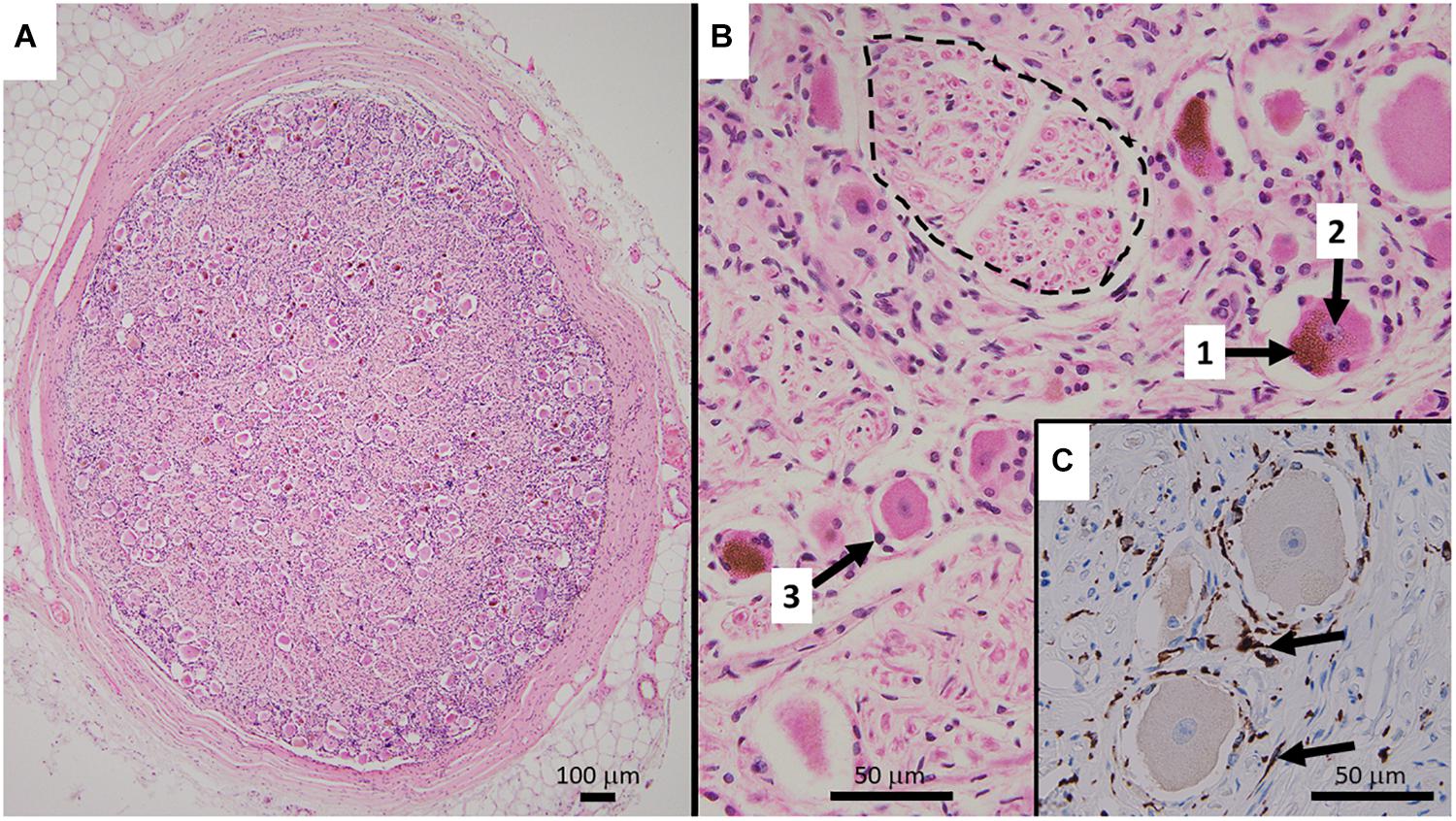
The cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglion serve as the first relay center and the processing center of this information. However, it has been shown that these neural bodies are indeed active participants in the regulation of this signaling process. Histology Upon histological examination, dorsal root ganglion is seen as a basophilic structure distinct from the surrounding highly eosinophilic nerve fibers. D It provides mainly sensory anesthesia. In the case that the virus is reactivated, shingles occur. The sensory impulses generated in the periphery pain, touch, temperature changes activate the peripheral processes of the spinal ganglion neurons.
Ganglia: Definition, location, function

It forms the sensory arm of the reflex arc required to carry out the reflex action. A pseudounipolar neuron consists of a cell body bearing one short This article will discuss the + Show all Key facts about the dorsal root ganglion Definition Collection of neuronal cell bodies of sensory neurons that transmit sensory impulses Structure Cell bodies of pseudounipolar neurons, satellite glial cells Blood supply Radicular arteries branches of vertebral artery C1-C7 , deep cervical artery C7-T1 , posterior intercostal arteries T1-T11 , subcostal artery T12 and lumbar arteries Function Transmission of sensory neural signals to the central nervous system from the peripheral nervous system Synonyms: Dorsal root ganglion, Spinal sensory ganglion , The term ganglion refers to a cluster of the neuronal cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. Function Here is more about the function of ganglia in the body. Cell bodies of motor neurons d. Being in the brain, they are part of the central nervous system, not the peripheral nervous system, as other ganglia are. The satellite cells are the smaller cells seen in the periphery of the actual neurons.
chapter 13 spinal cord Flashcards

Bill contracts a viral disease that destroys cells in the posterior gray horns in his spinal cord. The posterior root expands to form the ganglia as soon as it leaves the spinal cord. Treasure Island FL : StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan-. You touch it anyway, producing a pain sensation in your fingers, a withdrawal of your hand, and an auditory comment of what you are thinking. All the posterior roots of spinal nerves contain a ganglion. Synonyms: Sympathetic chain, Sympathetic ganglia , Sympathetic chain ganglia, also known as paravertebral ganglia, are the autonomic ganglia of the SNS. We will also discuss the functions and clinical conditions associated with the dorsal root ganglion.