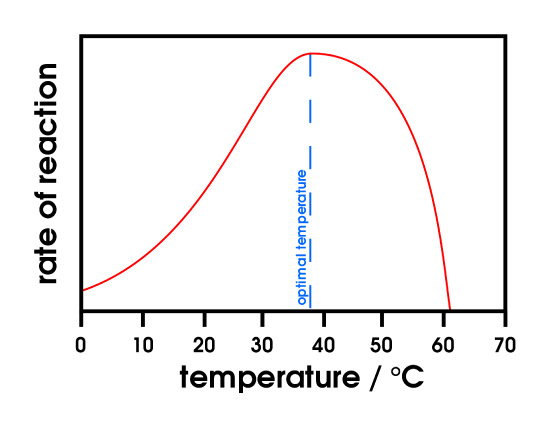
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions in living cells. They are essential for the proper functioning of cells and are involved in a wide variety of biological processes, such as digestion, metabolism, and synthesis. The activity of enzymes is affected by a number of factors, including temperature, pH, and substrate concentration. One important factor that can influence enzyme activity is the concentration of the enzyme itself.
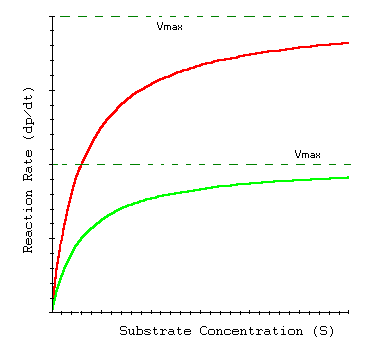
As the concentration of an enzyme increases, the rate of the reaction it catalyzes also increases. This relationship is known as the reaction rate law. The rate of an enzymatic reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the enzyme, up to a certain point. This point is known as the maximum reaction rate, or Vmax. At the Vmax, the enzyme is saturated with substrate, and any further increase in enzyme concentration will not result in an increase in reaction rate.
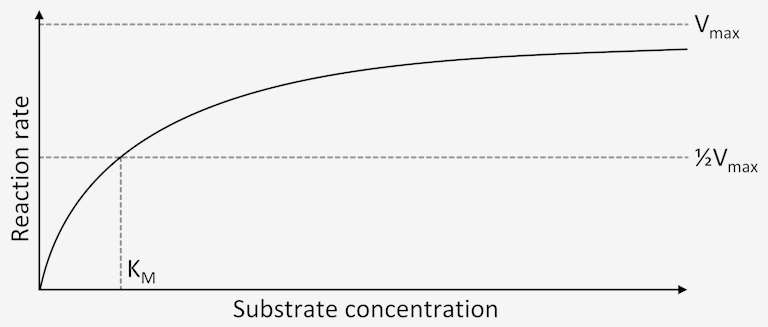
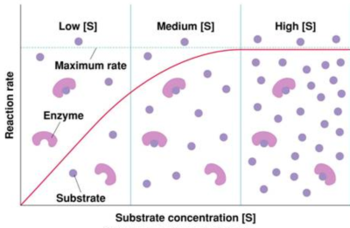
The effect of enzyme concentration on enzyme activity can be demonstrated using a standard assay called the Michaelis-Menten curve. This curve plots the reaction rate (rate of product formation) against the substrate concentration. At low substrate concentrations, the reaction rate is directly proportional to the substrate concentration. As the substrate concentration increases, the reaction rate increases until it reaches the Vmax. At substrate concentrations above the Vmax, the reaction rate plateaus and remains constant, as the enzyme is already saturated with substrate.
The effect of enzyme concentration on enzyme activity can be explained by the concept of active sites. Each enzyme has a specific active site that binds to a particular substrate. The active site is where the chemical reaction takes place. As the concentration of the enzyme increases, there are more active sites available to bind to the substrate, resulting in an increase in the reaction rate. However, once all of the active sites are occupied by substrate, the reaction rate reaches a maximum and cannot increase further.
In summary, the concentration of an enzyme has a direct effect on its activity. As the concentration of the enzyme increases, the rate of the reaction it catalyzes also increases, up to a certain point. At substrate concentrations above the maximum reaction rate, the reaction rate plateaus and remains constant. Understanding the effect of enzyme concentration on enzyme activity is important in the fields of biochemistry, medicine, and industry, as it allows researchers to optimize enzyme activity for various applications.