The evolution of human skin color answers. The Evolution of Human Skin Color 2022-12-17
The evolution of human skin color answers
Rating:
6,1/10
917
reviews
The evolution of human skin color is a fascinating topic that has long been the subject of scientific study and debate. The variation in skin color seen among humans is the result of adaptations that occurred over time as our ancestors migrated to different parts of the world and faced different environmental pressures.
One of the primary factors that has influenced the evolution of skin color is the amount of sunlight that an individual is exposed to. In regions with high levels of sunlight, such as equatorial Africa, the skin of early humans evolved to be darker in order to protect against the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Darker skin contains higher levels of the pigment melanin, which absorbs UV radiation and helps to prevent DNA damage and skin cancer.
As humans migrated to regions with lower levels of sunlight, such as Europe and Asia, the selection pressure for dark skin decreased. In these environments, lighter skin became advantageous because it was able to produce more vitamin D when exposed to sunlight. Vitamin D is essential for the absorption of calcium, which is necessary for strong bones. Lighter skin also reflects more sunlight, which can help to keep the body cool in hot environments.
In addition to the adaptive value of lighter skin, there is also evidence that the evolution of skin color may have been influenced by sexual selection. In some cultures, lighter skin is considered more attractive, and individuals with lighter skin may have had an advantage in attracting mates.
Overall, the evolution of human skin color is a complex process that has been shaped by a variety of factors, including the need to protect against UV radiation, the production of vitamin D, and sexual selection. Understanding the evolution of skin color can help us to better appreciate the diversity of human cultures and the ways in which our ancestors adapted to different environments.
Evolution of human skin color

Based on this information, write a hypothesis for where in the world you would expect to find human populations with darker or lighter skin pigmentation i. Case teaching notes are protected and access to them is limited to paid subscribed instructors. Researchers found that among people of African ethnicity, there is very little variation in MC1R alleles; almost everyone has the allele associated with the darker skin trait. After humans were dispersed from the Tower of Babel, the emigrating populations would have encountered vastly different environments. American Journal of Human Biology, 31 4 , e23272. What is the primary UV Index value of your state on thi particular day in September? American Journal of Human Biology, 30 5 , e23170.
Next
Evolution of Skin Color Flashcards

Running time: 18:58 min. American Journal of Cultural Sociology. The colours of humanity: The evolution of pigmentation in the human lineage. Jablonski explains that melanin, located in the top layer of human skin, absorbs UV radiation, protecting cells from the damaging effects of UV. We recommend that the net result of IPD is immediate absorption or spreading of UVR photons at a surface level within the skin, therefore saving some damages to deeper layers. Answers will vary depending on location.
Next
the evolution of human skin color case study answers

These traits are known as adaptations. Pigment Cell and Melanoma Research, 34 4 , 707-729. The phenomenon of skin lightening: Is it right to be light? For Jablonski, passing on this understanding of human skin color is what she wishes is an action towards better understanding within humankind. These are a few questions that form the basis for what Penn State anthropologist Nina Jablonski calls an explanatory framework of the evolution of skin pigmentation in modern human beings. Human skin pigmentation, migration and disease susceptibility. Within as well as in between populace genetic differences are used to characterize the distribution of alleles in 5 genes related to skin shade around the world. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 139 4 , 451-461.
Next
2022 UPDATED!!! THE EVOLUTION OF HUMAN SKIN COLOR BY ANNIE ANSWER KEY

This details aids us recognize the basis of the biogeographic circulation of skin shades. Up until that point, Jablonski was known for her work in primatology and research on Old World monkeys. Genetics determines the type of melanin i. The evolutionary response, Jablonski says, was a loss of pigmentation. The images in Figure 2 show that the size and number of melanosomes, and the amount of melanin, are different in people with different skin colors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112 26 , 8052-8057.
Next
The Evolution of Human Skin Color. Penn State
It means that there is selection against that trait. The simplest explanation for the similarity in the sequences is that the gene was inherited from a common ancestor in all the species. This is very similar to the MC1R variation seen or not seen! Sex Roles, 78, 255-271. More darkly pigmented people have more of the brown-black eumelanin, and the more eumelanin, the darker the skin. Up until that factor, Jablonski was known for her operate in primatology as well as research study on Vintage monkeys.
Next
Evolution of Human Skin and Skin Pigmentation

Find your approximate location on the map. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 319 4 , H906-H914. As a recap, it is useful to compare the patterns of UVR at the equator and within the tropics to those outside of the tropics. Translational Behavioral Medicine, 10, 234—243; Jablonski, N. They typically include a summary of the case, teaching objectives, information about the intended audience, details about how the case may be taught, and a list of references and resources. Otherwise, the implication would be that some humans are more highly evolved than others! Scientific knowledge is based on empirical evidence.
Next
Skin Color and Natural Selection

The A allele evolved and spread among European populations, but not in Asian populations, so some other genetic pathway for forming light skin must have evolved. British Journal of Dermatology, 181 5 , 916-931. Journal of Applied Physiology, 125 4 , 1232-1237. Thus, populations found in equatorial areas will have the darkest skin most eumelanin and populations at higher latitudes will have lighter skin least eumelanin. UV light was a solid consider the development of skin color; darker skin protects cell centers from UV damage. Through the progressive disclosure of data, students learn about are the factors that may have exerted pressure on the evolution of this trait.
Next
The Evolution of Human Skin Color

American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 175 2 , 437-447. Nina Jablonski walks us through the evidence that the different shades of skin color among human populations arose as adaptations to the intensity of ultraviolet radiation in different parts of the world. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 107 Supplement 2 , 8962-8968. Photosynthesis of vitamin D3 in the skin depends upon the solar zenith angle, which changes with period, latitude, as well as time of day, as well as is more regulated by the quantity of pigment and density of the skin Mawer and Davies, 2001; Lips, 2006. Social and affective touch in primates and its role in the evolution of social cohesion.
Next
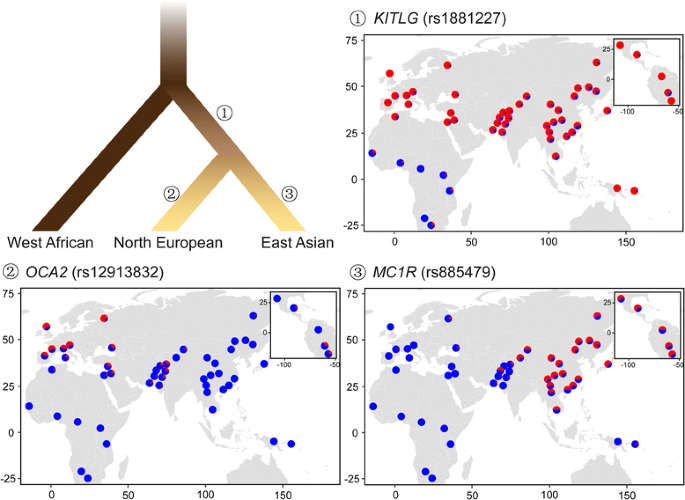
The evolution of human skin and skin color. It all began in the early 1990s when Jablonski began exploring gaps in the literature about the evolution of human skin and skin color. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 372 1724. Remind students that the film mentioned that a person's skin color is determined by the type and amount of melanin in their skin. To become a paid subscriber, purchase a subscription Teaching notes are intended to help teachers select and adopt a case.
Next

The evolution of human skin colouration and its relevance to health in the modern world. Student responses may vary about whether the findings support their hypothesis from question 5. Evidence from different disciplines can inform what makes a human trait beneficial or harmful in a particular environment. Melanin is a natural sunscreen that prevents the breakdown of certain essential biomolecules in particular, the B vitamin folate, and DNA , while permitting enough UVR to enter the skin to promote the production of essential vitamin D. And this evolution has implications for our health. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Here there was selection for lighter skin which let more UV radiation through for vitamin D synthesis.
Next








