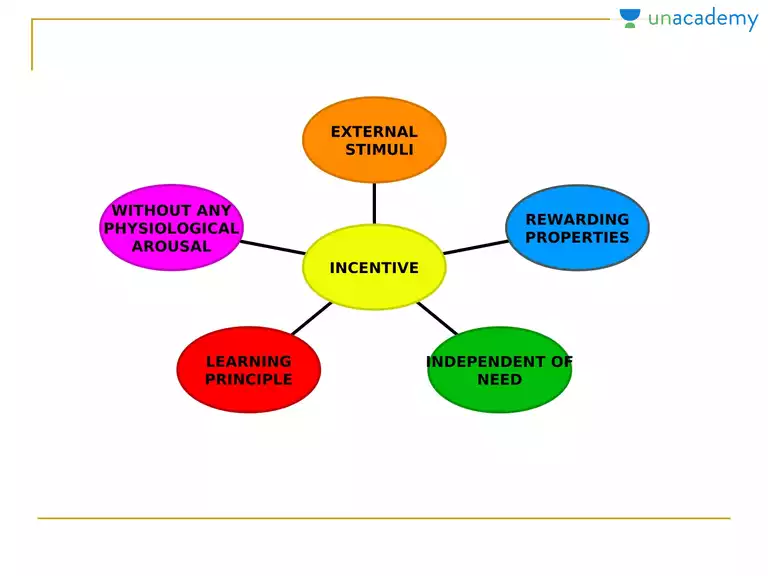
The incentive theory of motivation suggests that behavior is driven by the desire to gain rewards or avoid punishments. According to this theory, people are motivated to perform certain actions because they expect to receive a reward or avoid a punishment as a result.
One of the key proponents of the incentive theory was psychologist B.F. Skinner, who argued that people are motivated to perform a behavior because they expect a positive outcome or consequence. This could be something tangible, such as money or a prize, or it could be something intangible, such as praise or social approval.
For example, a student might be motivated to study for a test because they expect to receive a good grade, which could lead to academic success and future opportunities. Similarly, an employee might be motivated to work hard because they expect to receive a promotion or raise as a result.
The incentive theory also incorporates the concept of punishment, which is a negative consequence that is used to discourage undesirable behavior. For example, a parent might use punishment to discourage a child from misbehaving, such as taking away privileges or imposing a punishment, in order to discourage the child from repeating the undesirable behavior.
One of the strengths of the incentive theory is that it can help to explain why people engage in certain behaviors and how they can be motivated to change their behavior. By understanding the rewards or punishments that are associated with a particular behavior, it is possible to design incentives that can encourage people to engage in desirable behaviors or discourage them from engaging in undesirable behaviors.
However, the incentive theory has also been criticized for its emphasis on external rewards and punishments and its lack of consideration for internal factors that may influence motivation, such as personal values and interests. Additionally, the use of punishment as a means of motivation has been controversial, with some arguing that it can be abusive or ineffective in promoting long-term behavior change.
Overall, the incentive theory of motivation is an important perspective on how people's behavior is influenced by the rewards and punishments that they expect to receive. While it is a useful tool for understanding and influencing behavior, it is important to also consider other factors that may contribute to motivation and to use rewards and punishments in a responsible and ethical manner.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2795385-what-is-intrinsic-motivation-5afb187443a1030037f0b2a0.png)




