The linear model of innovation. The Linear Model of Innovation: The Historical Construction of an ... 2023-01-06
The linear model of innovation
Rating:
9,6/10
455
reviews
The linear model of innovation is a conceptual framework that explains the process of innovation as a linear, step-by-step progression from idea generation to commercialization. It is often used to describe how new products or technologies are developed and brought to market.
According to the linear model, the process of innovation begins with idea generation, which is the process of coming up with new ideas for products or technologies. This can be done through a variety of methods, such as brainstorming sessions, market research, or customer feedback.
Once an idea has been generated, it must be refined and developed into a more concrete concept. This typically involves conducting market research to determine the feasibility and potential demand for the product, as well as identifying any potential challenges or obstacles that may need to be addressed.
Once a concept has been developed, it is time to move on to the prototyping phase. This involves creating a physical or digital prototype of the product or technology, which can be tested and refined. This phase is critical to the success of the product, as it allows the team to identify and address any issues or problems before the product is mass-produced.
The final step in the linear model of innovation is commercialization, which is the process of bringing the product or technology to market. This typically involves manufacturing and distributing the product, as well as marketing and promoting it to potential customers.
One of the main advantages of the linear model of innovation is that it provides a clear, step-by-step framework for the development and commercialization of new products or technologies. It is also a useful tool for identifying potential bottlenecks or roadblocks in the innovation process, and for developing strategies to overcome them.
However, the linear model of innovation also has its limitations. It assumes that innovation is a linear, predictable process, which may not always be the case. In reality, the innovation process can be complex and unpredictable, and may involve multiple iterations and refinements before a product or technology is ready for commercialization.
Overall, the linear model of innovation is a useful framework for understanding the process of innovation, but it is important to recognize that it is just one model among many, and that real-world innovation may not always follow a linear path.
Models of Innovation: The History of an Idea
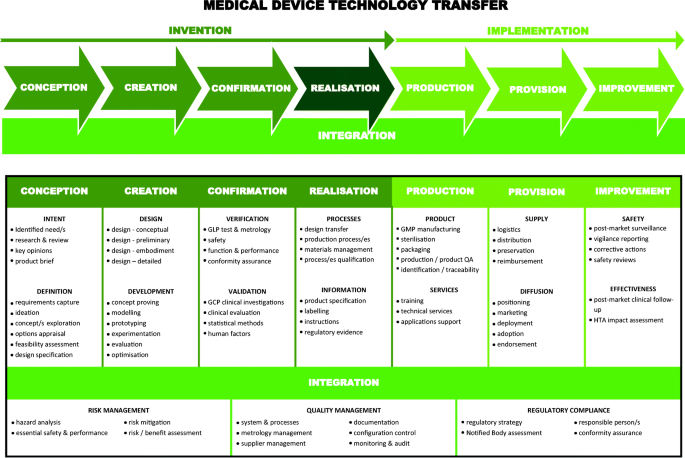
According to the third generation model, an idea originates from creativity, customer feedback or basic research. After the product is verified, then you can plan for market launch and production start-ups. The process of innovation is related to business strategies that make a company competitive. From a social point of view, the conceptions both of Sef and of innovationism incorporate a purely instrumental valuation of science. Although Sef includes among basic science's benefits to society its contribution to the competitiveness of private enterprises, it does not exclude the possibility that such benefits may reach society in ways external to the market system.
Next
SciELO

It will then consider the implications of the research on a medium The Invention Of An Invention Innovation It is imperative to distinguish between invention and innovation. Besides, the model presents less risks when innovation. Long before this historians of science and technology, as well as historians more generally had recognized that the realities of the innovative process were far more complex than this simplistic view" Freeman, 1996, p. To my mind, the number of well documented cases of serendipity of the type at issue is sufficient to justify the investment in basic research, even from a purely instrumental point of view. Godin, The New Economy: What the Concept Owes to the OECD.
Next
The Linear Model of Innovation: The Historical Construction of an Analytical Framework

Godin, Are Statistics Really Useful? An example is Ryanair, a budget airline which has successfully copied the no-frills service model of Southwest Airlines. The purpose for the interaction and collaboration is so as to gain greater potential from real time information processing. Introduction This paper is a fragment of a larger research project that I have been working on for some time. Market need—Development—Manufacturing—Sales The linear models of innovation supported numerous criticisms concerning the linearity of the models. The acknowledgement of the cultural value of science as a factor in the legitimation of public financing of basic research leads to the question of criteria to be adopted for the distribution of resources. The model was usually taken for granted. So all of these firms Why Innovation Is An Tool For Generating Value And A Source Of Competitive Advantage production and productivity " Oslo Handbook, 2005 , where innovation is the necessary tool for generating value and a source of competitive advantage.
Next
Linear model of innovation

However, to fully understand and implement business strategies, it is crucial to understand the process of innovation. Godin, The Obsession for Competitiveness and its Impact on Statistics: The Construction of High Technology Indicators. There are more ways to innovate than these four. That prescription is of course not imposed once and for all, as if by a decree. That basic science has some innovation potential - or, in other words, that it contributes to some extent to the creation of innovations - is not denied by even the most radical innovationists. Their role was to determine whether the set objectives for the stage had been met.
Next
The Linear Model of Innovation

Thus each stage would be successive and conditioned by the previous one. The public financing of scientific research, provided in accordance with neoliberal principles, is an action of the state that promotes commodification - in this case the commodification of science in the programmatic dimension -; it is therefore a manifestation of the market interventionist view. The gate assesses the innovative idea in terms of finances, market and technology. Such is the case with the most influential model in STS-STI: the linear model of innovation. So if a mathematician, or a chemist, or even a physiologist, were to tell me that the driving force is his work had been the desire to benefit humanity, then I should not believe him nor should I think the better of him if I did. The autonomy of the scientific community in the determination of the programme of research is exercised in this way, i. These companies use mainly incremental innovation with in-house applied research and development.
Next
[PDF] The Linear Model of Innovation

Adaptations of Farmer Field Schools FFS are being implemented and monitored in most of the field sites for a number of practices, like seed multiplication, post-harvest technologies and soil and water management. In that context, i. Process of Innovation The theory, known as innovation, highlights how a company can innovate its offerings and services to grow its business and compete in the market. For as long as that system is not established, economic liberals must and will unhesitatingly call for the intervention of the state in order to establish it, and once established, in order to maintain it. It is stealthy in nature since newer tech will often be inferior to existing market technology. Godin, The Measure of Science and the Construction of a Statistical Territory: The Case of the National Capital Region NCR.
Next
Basic Science and Technological Innovation: the linear model and its limits » IRIS

Lastly, during diffusion, the innovation starts to be copied by others. Internal systems must grow with the company. Firstly, the innovator invents something. Shortcomings and failures that occur at various stages may lead to a reconsideration of earlier steps and this may result in an innovation. The reference to applications was necessary as a crucial element in the legitimizing argument for the concession of public funds to basic science, but for that purpose there was no need for a sophisticated model of the passage from basic to applied science: the conception of science as the ultimate source of technological advances was sufficient. The Linear Model of Innovation is an early model of innovation that suggests technical change happens in a linear fashion from Invention to Innovation to Diffusion. Alumnus of the Brazilian School of Internet Governance.
Next
The Linear Model of Innovation: The Historical Construction of an ...

The important thing is to find the type s that suit your company and turn those into success. His research and policy interests are anthropology of the State, privacy and data protection, science and technology studies, platform governance and encryption policy. In this book, Benoît Godin examines the emergence and diffusion of the three most important conceptual models of innovation from the early twentieth century to the late 1980s: stage models, linear models, and holistic models. It is innovation that is to build a new successful product or a theory which will be accepted by people in the market. IBM, General Motors, Northern Telcoma, and 3M all use this model in all their innovations. As evidence of the applicability of the Linear Model of Innovation to modern day innovation, there has also been the introduction of the Farm-level Applied Research Methods Programme for East and Southern Africa, a regional collaborative initiative of five core countries, which are: Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia and Zimbabwe. Therefore, we cannot assume that innovations are a modern day process.
Next
Linear Model of Business Innovation

The airplane, for example, was not the first mode of transportation, but it is revolutionary as it allowed commercialized air travel to develop and prosper. At an intermediate level, there is grosso modo a limited amount of funds for financing the research carried out in public and private universities and research institutions, distributed by sponsoring agencies. The market interventionist view acknowledges that the conditions for the operation of the free market as the organizing principle in society do not come about naturally, but require the engagement of the state in several types of action, like the creation of markets for as yet non commodified categories of goods, the conversion of various forms of property rights into private property rights, the suppression of rights to the commons, the elimination of alternative indigenous forms of production, etc. Godin, Taking Demand Seriously: OECD and the Role of Users in Science and Technology Statistics. In spite of the advances in the domain of Intellectual Property Rights, scientific knowledge still functions as a public good: with a few exceptions, it is not protected by patents, and copyrights do not provide income for its producers - i. They assume different forms in different sectors of social life, and sometimes one, sometimes the other prevails. They are continually being invented, with one author developing many versions of the same model over time.
Next
Linear Model of Innovation
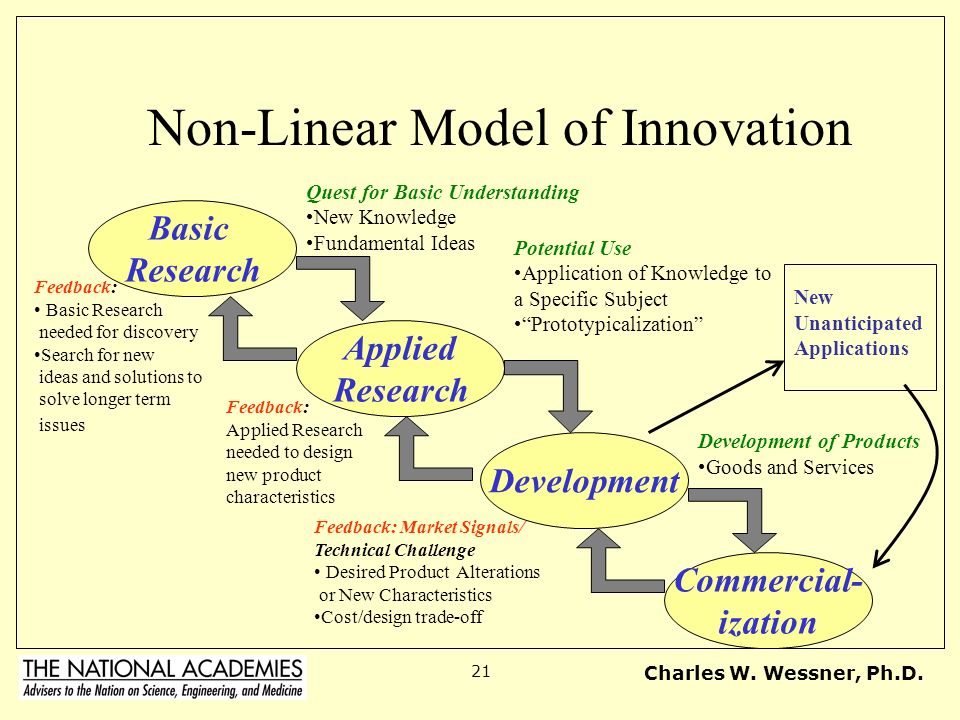
Godin, Neglected Scientific Activities: The Non Measurement of Related Scientific Activities. The conclusion is that, with due reservations, the defense of basic science grounded on the Principle of Serendipity has some validity, and helps to legitimate its financing by the state. Stokes 1997 is one of the authors who deny the presence of the LMI in Sef although not interpreting the misattribution as resulting from an anachronism. Industrial Relations Research Association, Champaign: Illinois, pp. According to the model, there is a simple sequence of steps going from basic science to innovations - an innovation being defined as an invention that is profitable.
Next








