A government is a system of institutions and practices that are put in place to manage and regulate the affairs of a state or community. Governments are responsible for maintaining order, protecting citizens and their property, and providing for the common good. They also play a key role in shaping the policies and laws that govern society and ensure that the needs and interests of the people are taken into account.
There are many different forms of government, including democracy, monarchy, dictatorship, and communism. The form of government that a country has can have a major impact on the rights and freedoms of its citizens, as well as the level of prosperity and stability of the nation.
In a democracy, the people have a say in how they are governed through the process of elections. Elected officials, such as presidents and legislators, are responsible for making decisions on behalf of the people. In a monarchy, power is held by a single person, typically a king or queen, who inherits their position through birthright. In a dictatorship, one person or a small group holds complete control over the government and makes all decisions without input from the people. And in a communist government, the state owns and controls the means of production and distribution, and there is no private property.
Governments also have various branches, each with its own specific responsibilities. The executive branch is responsible for enforcing laws and policies, the judicial branch interprets the laws and resolves disputes, and the legislative branch makes and passes laws. These branches work together to ensure that the government operates effectively and efficiently, and that the rights and freedoms of citizens are protected.
Overall, the role of government is to provide for the common good and ensure the safety and well-being of its citizens. It does this by creating and enforcing laws, providing public services, and working to promote the prosperity and stability of the nation.
Thematic Definition & Meaning

The tropics Cancer and Capricorn are the two imaginary lines directly above which the sun shines on the two The Arctic Circle is a line of latitude at 66. This provides guidance for geography educators organised in parallel with the pages for new teachers , allowing cross-links to be made. The Eastern Hemisphere includes the continents of Europe, Asia, and Australia, while the Western Hemisphere includes North and South America. Master Teachers cater to teaching Maths, Physics, Chemistry and Biology Science for 6th to 12th grades across CBSE and ICSE Boards. Thematic Maps D efinition The word "thematic" may be slightly misleading—these are not the colorful and exaggerated maps you might get in a pamphlet at a zoo or an amusement park. All of the maps we have discussed briefly have something in common.
Thematic Map Definition, Types & Examples

Nevertheless, most people would recognize the general area being discussed when using one of the vernacular terms in a conversation. From these lines, the systems of longitude and latitude are formed, allowing you to locate yourself anywhere on the planet. Which cities are growing? Three main types of boundaries define a region: formal, functional, and vernacular. The Arctic and Antarctic Circles mark the extremities southern and northern, respectively of the polar day twenty-four-hour sunlit day and the polar night twenty-four-hour sunless night. Geography is a much broader field than many people realize. Likewise, between Canada and the United States, a major part of the eastern border is along the Saint Lawrence Seaway and the Great Lakes. However, the population is not distributed evenly across those 3 million square miles.
1.1 Geography Basics

Which would you prefer? Scale gives us information about the size of the area being displayed. In 1607, Flemish cartographer Jodocus Hondius created Designatio orbis christiani, a map showing the distribution of world religions. The subject matter and the location are determined in the mapmaking process and are required for making all thematic maps. Once accurate data is found, there are various ways to use that data that must be considered with the map's theme. The symbol is often selected in a shape, form, or color that increases the readability of the map and its data. GIS, GPS, and remote sensing are tools that geographers use to study the spatial nature of physical and human landscapes. A Natural physical geographic features have a huge influence on where political boundaries of formal regions are set.
Types of Maps

Isoline Map Definition What is an isoline map? If one is familiar with the planet's physical geography, Siberia, the Amazon Basin, the Sahara, the Himalayas, and the Australian Outback can be identified as extreme environments that few people live. What Is a Thematic Map? While the economic and cultural aspects of humanity are primary focuses of human geography, these aspects cannot be understood without describing the landscape on which economic and cultural activities take place. For example, why are the lower population areas lower in population? Contours are an outline, especially a curve or an irregular figure. Geographers and cartographers organize locations on the earth using a series of imaginary lines that encircle the globe. Isoline maps use continuous lines that delineate data of the same value.
Thematic Maps: Examples and Definition

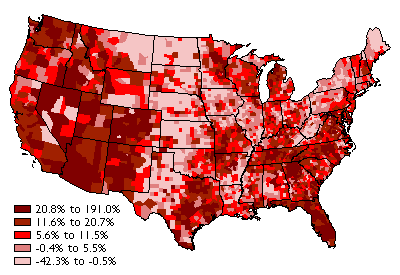
A disadvantage of this type of map is the size of the symbol can be challenging to relate to an exact location instead of connecting it to a general area. For example, a proportional symbols map can use pie charts to display what percent of each US state voted for each candidate in a presidential election; the larger the pie chart, the greater the number of voters. However, some boundaries are created by demilitarized zones or policy, such as the Berlin Conference. The continental United States has four main time zones see Figure 1. The two main branches of geography include physical geography and human geography. The pros to a choropleth map are that they are easy to read, visually effective, and use geographically common regions and countries.