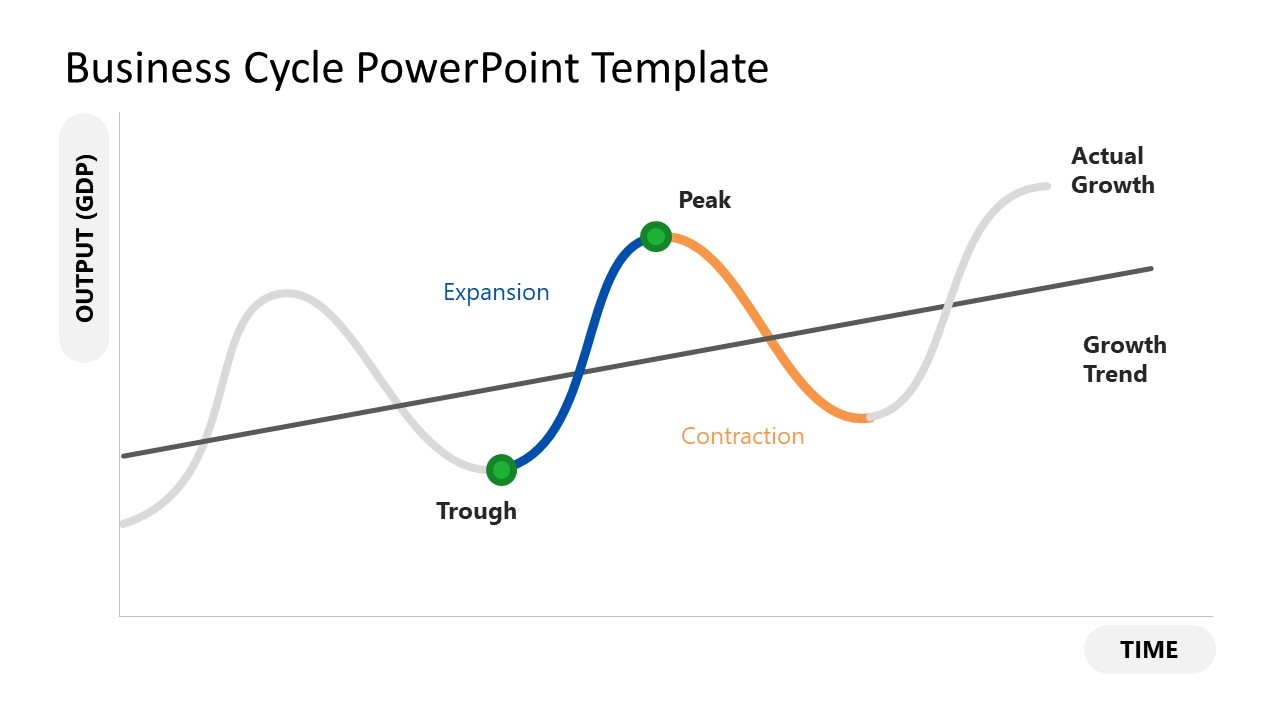
The trade cycle, also known as the business cycle, is a pattern of fluctuations in economic activity that is characterized by periods of expansion and contraction. These fluctuations can have significant impacts on economic indicators such as employment, production, and prices. There have been various theories proposed to explain the underlying causes of the trade cycle and to identify potential ways to mitigate its negative effects.
One of the most influential theories of the trade cycle is the monetary theory, which suggests that changes in the money supply and credit conditions play a key role in driving economic fluctuations. According to this theory, an expansion in the money supply can lead to increased spending, which can drive up demand for goods and services and lead to an economic expansion. Conversely, a contraction in the money supply can lead to a decline in spending and a slowdown in economic activity.
Another theory of the trade cycle is the real business cycle theory, which suggests that fluctuations in the trade cycle are driven by changes in technology and productivity. According to this theory, technological innovations and improvements in productivity can lead to increased output and economic growth, while declines in productivity can lead to economic downturns.
A third theory of the trade cycle is the Keynesian theory, which emphasizes the role of aggregate demand in driving economic fluctuations. According to this theory, changes in the level of aggregate demand can lead to changes in production and employment, and thus influence the trade cycle. The Keynesian theory suggests that government intervention, such as fiscal policy or monetary policy, can be used to stabilize the trade cycle and mitigate its negative effects.
Overall, there are many different theories that attempt to explain the underlying causes of the trade cycle and to identify potential ways to mitigate its negative impacts. While no single theory has been able to fully explain the trade cycle, a combination of these theories can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the forces at play in driving economic fluctuations.
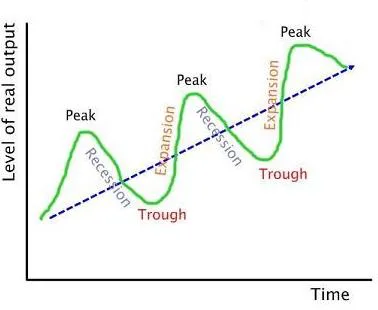

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Investopedia-terms-business-cycle-V2-512bfb0167ed407e9a89e5f266bb5a1d.png)