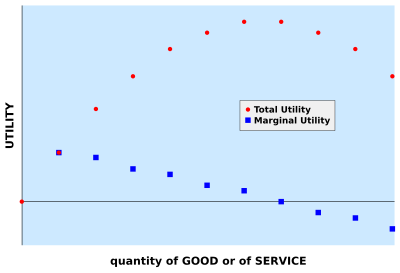
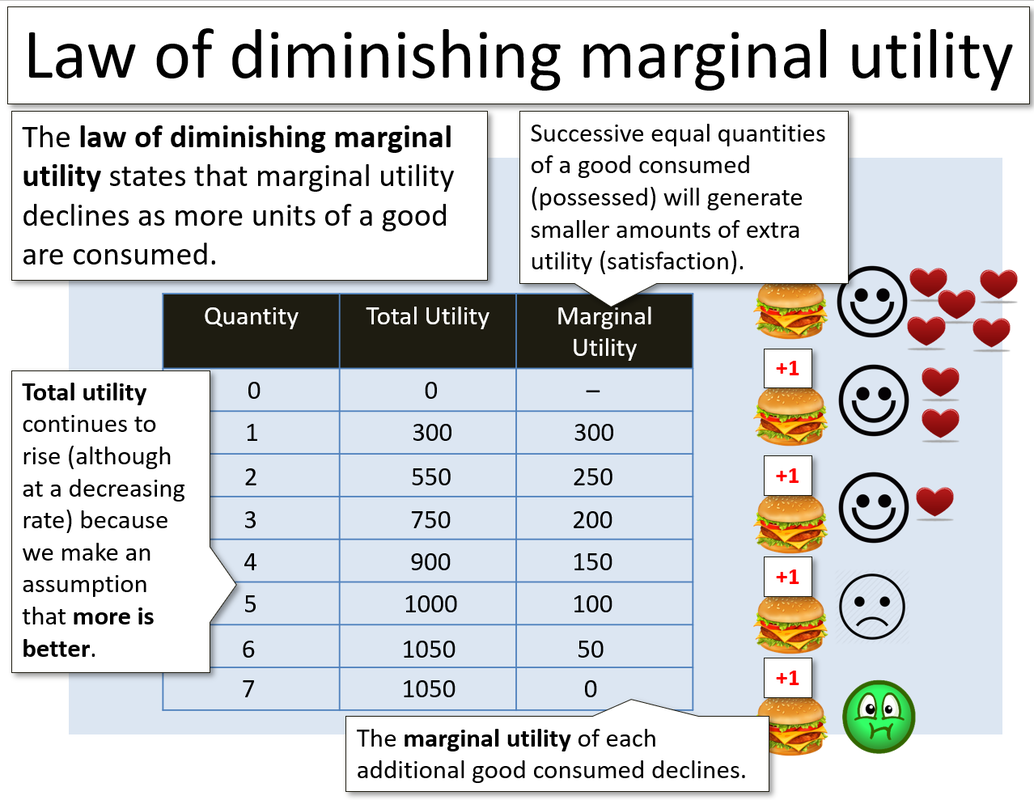
The theory of diminishing marginal utility is a fundamental concept in economics that states that as a person consumes more of a specific good or service, the satisfaction or utility that they derive from each additional unit of that good or service will eventually decline. In other words, the first unit of a good or service will provide more utility than the second, and the second unit will provide more utility than the third, and so on. This concept is often used to explain why people are willing to pay more for the first unit of a good or service than they are for subsequent units.
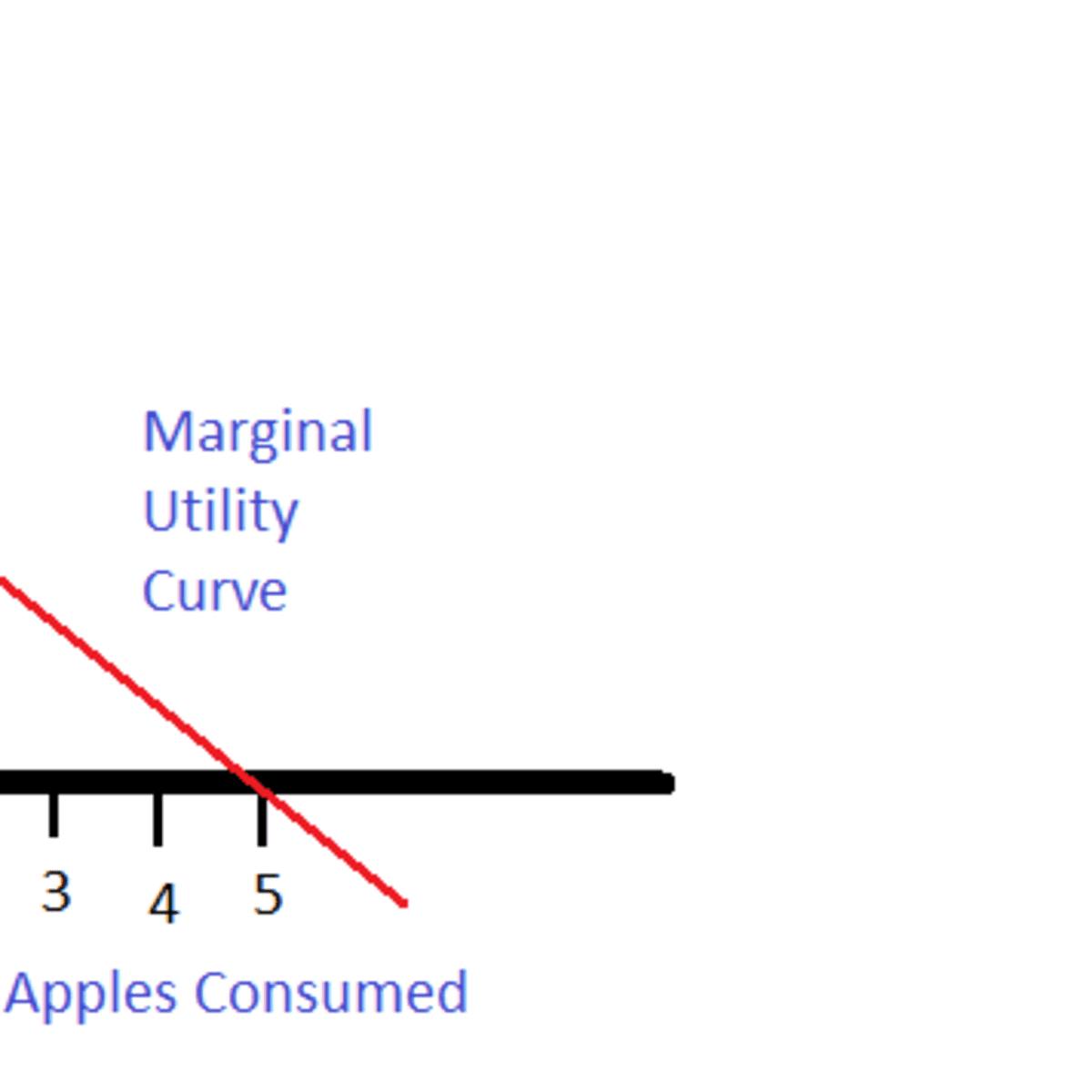
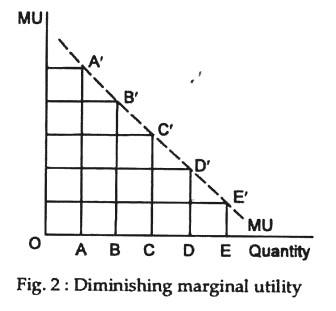
One way to understand this concept is through the use of the concept of marginal utility. Marginal utility refers to the additional satisfaction or utility that a person derives from consuming one more unit of a good or service. When a person consumes the first unit of a good or service, they experience the highest level of marginal utility, as they are experiencing the good or service for the first time and are likely to derive a great deal of enjoyment or utility from it. However, as they continue to consume more units of the good or service, the marginal utility that they derive from each additional unit will decline.
There are a few key factors that can influence the rate at which marginal utility declines. For example, if a person has a strong desire or need for a particular good or service, they may experience a slower decline in marginal utility as they continue to consume more units. On the other hand, if a person is indifferent or has a weaker desire for the good or service, they may experience a faster decline in marginal utility.
The concept of diminishing marginal utility has important implications for economic decision-making and behavior. For example, it can help to explain why people are willing to pay more for the first unit of a good or service than they are for subsequent units. It can also help to explain why people may be willing to pay a premium for certain goods or services that they perceive as being of higher quality or value.
In conclusion, the theory of diminishing marginal utility is a fundamental concept in economics that helps to explain how people make decisions about the consumption of goods and services. It states that as a person consumes more of a specific good or service, the utility or satisfaction that they derive from each additional unit will eventually decline. This concept has important implications for economic decision-making and behavior, and is used to help explain a wide range of economic phenomena.