Thermodynamics in everyday life. everyday life 2023-01-03
Thermodynamics in everyday life
Rating:
6,6/10
332
reviews
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of heat and its relationship to work and energy. It is a fundamental concept that has a wide range of applications in our everyday lives, from the operation of heat engines to the design of refrigerators and air conditioners.
One of the most basic principles of thermodynamics is the conservation of energy, which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another. This principle is at work in many common household appliances, such as a refrigerator. A refrigerator works by using a refrigerant, which is a substance that readily absorbs and releases heat. The refrigerant is circulated through a system of coils and a compressor, which pumps it through a cycle of evaporation and condensation. When the refrigerant evaporates, it absorbs heat from its surroundings, cooling the interior of the refrigerator. When it condenses, it releases this heat to the outside air, allowing the refrigerant to start the cycle again.
Another important principle of thermodynamics is the second law of thermodynamics, which states that the total entropy of a closed system will always increase over time. Entropy is a measure of the disorder or randomness of a system, and the second law of thermodynamics is often referred to as the "arrow of time" because it determines the direction in which time flows. This principle has a number of practical applications, including the design of heat engines, which convert heat into work. The efficiency of a heat engine is determined by the difference in temperature between the heat source and the heat sink, and the second law of thermodynamics dictates that there is a limit to the efficiency that can be achieved.
Thermodynamics also plays a role in the operation of internal combustion engines, such as those found in automobiles. In an internal combustion engine, fuel is burned to create heat, which is used to expand a gas and create mechanical work. The efficiency of an internal combustion engine is determined by the amount of heat that is converted into useful work, with the remainder being wasted as heat.
Thermodynamics is also important in the field of thermochemistry, which deals with the study of the energy changes that occur during chemical reactions. This knowledge is used to predict the feasibility of chemical reactions, as well as to calculate the amount of energy that is required to drive a particular reaction.
In conclusion, thermodynamics is a fundamental concept that has a wide range of applications in everyday life. From the operation of heat engines and refrigerators to the design of automobiles and the study of chemical reactions, thermodynamics plays a crucial role in many aspects of our daily lives.
12 Examples of Thermodynamic Systems

Heating and cooling systems in our homes and other buildings, engines that power our motor vehicles, even the design of buildings and vehicles, all incorporate information from thermodynamics to make them perform well. This phenomenon happens because the ice absorbs the heat from the surrounding air, thereby cooling the air and changing the ice to water. What are the 4 Law of Thermodynamics? There are four known laws of thermodynamics, with the first law being one of the most fundamental principles of physics. Cooling the air reduces the entropy of the air in that system. Thermodynamics teaches us that ideas and concepts can flow in either direction, between the basic and the applied. Those infrared waves are detectable to infrared sensors and cameras such as the The Laws of Thermodynamics One cannot properly talk about heat and energy transfer without mentioning the Laws of Thermodynamics.
Next
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is used in everyday life all around us. Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Company. A computer system IS is a system that allows information to be stored and processed; It is the set of interrelated parts: hardware, software and IT personnel. For example, take the burning of natural gas, which is commonly used to heat homes. What is a computer system and specify with an example? The emission of electromagnetic waves creates thermal radiation, carrying thermal energy away from the emitting object It is because of thermal radiation that technology like infrared waves, a type of electromagnetic wave on the electromagnetic scale between visible light and radio waves.
Next
everyday life

The root «thermo» means heat and dynamics refers to movement, so thermodynamics studies the movement of heat in a body. The primary impact thermodynamics has on our daily lives is the many ways it shows us how to use energy efficiently, and minimize the wastes that inevitably accompany that use. Where are thermodynamics used? What is a system in thermodynamics give simple examples? This may be different from the definition you came up with. What makes driving the most dangerous is factors you cannot control, such as wildlife in the road, pedestrians, other vehicles, and more. What is the concept of thermodynamics? What is the application of thermodynamics in automobile engineering? What do we learn from thermodynamics? Thermodynamics is heart of mechanical engineering.
Next
How does thermodynamics affect your daily life?

And traditional thermodynamics focuses on finding those limits and hence on how best to get real systems to approach those limits. Thermodynamic cycles govern the operation of all forms of air and gas compressors, blowers, and fans. The heating of the molecules in fluids causes those molecules closest to the heat source to expand and displace the rest of the fluid. The isolated system allows neither the entry nor the exit of energy or matter. The concept of the second law of thermodynamics applied to heat engine is equally applicable on the internal combustion engines used in our cars, motorcycles, ships, airplanes, etc. The biological evolution may be explained through a thermodynamic theory.
Next
What is the importance of thermodynamics in everyday life?

All types of air and gas compressors, blowers, fans, run on various thermodynamic cycles. Almost all process and engineering industries, agriculture, transport, commercial and domestic activities use thermal engineering. The four laws of thermodynamics. There are several ways to produce heat. On the other hand, there are three types of thermodynamic systems: closed, open and isolated. The closed system is one where there is transfer only of energy. The third, and generally the most important in thermodynamics, is the internal energy U or internal energy per unit mass , which depends on the temperature, state of aggregation, and chemical composition of the substance.
Next
Why is thermodynamics important in our daily life?

Firm understanding of thermodynamics by graduating engineers is critical for addressing key current and future global issues, e. How can we see the second law of thermodynamics in our daily lives? That is where thermal dashcams come in! Examples of open thermodynamic systems include: -Water boiling in a pot without a lid heat and steam, which is matter, escape into the air -Turbines -Compressors -Heat exchangers -The human body Isolated Systems An isolated system is one where the work is not performed on or by the system. In short, human thermodynamics is the study of heat and its relation to the motion and changes in the equilibriums of human bodies. As such, our western lifestyle in 2019 is entirely dependent on thermodynamics and the mastery of this topic among others, of course is the objective of every engineering college that offers a mechanical engineering program. Explain how the second law of thermodynamics applies to these two scenarios. One small example of thermodynamics in daily life is cooling down hot tea with ice cubes. How are heat engines governed by thermal energy? This creates what is known as a convection current and is a continuous cycle of convection until the heat source is removed and all molecules return to an equilibrium temperature A practical example of the convection process is, again, the pot of boiling water.
Next
First Law of Thermodynamics Examples in Real Life

A Modern Course in University Physics: Optics, Thermal Physics, Modern Physics. All the refrigerators, deep freezers, industrial refrigeration systems, all types of air-conditioning systems, heat pumps, etc work on the basis of the second law of thermodynamics. One way of understanding the environment is to understand the way matter and energy flow through the natural world. How is the starting point of thermodynamics marked? The embedded hydrogen bonding, functional groups, ionic arrays or pockets further generate extraordinary friccohesics and tentropy via intramolecular multiple force theory IMMFT. In addition, matter does not flow in or out of it.
Next
First Law of Thermodynamics: Interesting Everyday Examples

The third law of thermodynamics has two important consequences: it defines the sign of the entropy of any substance at temperatures above absolute zero as positive, and it provides a fixed reference point that allows us to measure the absolute entropy of any substance at any temperature. One of the most commonly known methods is fire. Such science of molecules is expressed in solvents of varied polarity similar to the elution of the molecules due to solvent polarity. Thermodynamics is, in some ways, the science that most influences our daily lives, because we use its concepts and information in the ways we design and operate so many of the devices we take for granted in our daily lives. When the heater is turned on, the electrical energy travels through the heating coil and is converted into heat energy. We live, after all, in a physical world, and so we develop general rules that indicate how physical things behave; commonly, it's known as common-sense. A thermodynamic system also called a working substance is defined as the part of the universe under study.
Next
Thermodynamics in Our Daily Lives

Thermodynamics has very wide applications as basis of thermal engineering. Nor is it possible to get "something for nothing," as the first law of thermodynamics demonstrates: the work output of a system can never be greater than the net energy input. Thermal energy is transferred between two systems based on the difference in temperature between them. What types of thermodynamic systems are known and what do examples consist of? Any system that would operate at its ideal limit would operate infinitely slowly and one could not tell whether it was going forward or backward. Finally, the universe is the combination of these two elements.
Next
The Role of Thermodynamics in Everyday Life

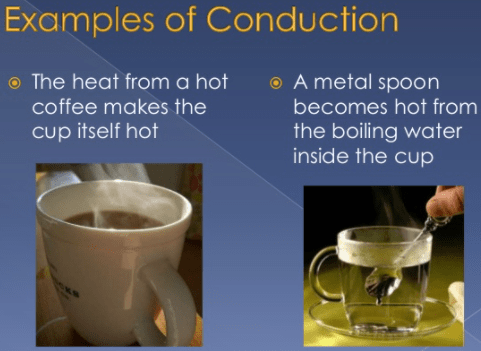
What are the applications of third law of thermodynamics? It also provides functions of temperature, pH, and ionic strength for the standard transformed Gibbs energies of formation, standard transformed enthalpies of formation, standard transformed entropies of formation, and average numbers of hydrogen atoms for 94 reactants. Further Reading: Featured photo by. Open Systems are those that tend to have a permanent relationship with their environment, such as a constant exchange of energy and information, such as, for example, a family that is related to the neighborhood, that receives visits at home and that accepts members from outside. The Laws of Thermodynamics are the foundation of heat transfer and energy work. No life can create energy but must obtain it through its environment. Examples of good conductors would be metals, such as gold, silver, iron, brass, bronze, copper, and aluminum, to name a few. The best way to get started with using infrared technology to enhance your life and safety is through infrared dashcams.
Next









