In economics, the production process can be divided into three stages: primary, secondary, and tertiary. Each stage plays a unique role in the creation of goods and services, and each has its own set of characteristics and challenges.
The primary stage of production involves the extraction and production of raw materials. This can include activities such as farming, mining, and forestry. The primary sector is often associated with the extraction of natural resources and is a crucial part of many economies. The primary sector is often subject to fluctuations in commodity prices and can be affected by weather and other natural disasters.
The secondary stage of production involves the processing and manufacturing of raw materials into finished goods. This can include activities such as assembly line production, construction, and refining. The secondary sector is crucial for the creation of many of the goods that we use on a daily basis and is a significant contributor to economic growth. The secondary sector is often characterized by the use of technology and the division of labor.
The tertiary stage of production involves the provision of services. This can include activities such as education, healthcare, and retail. The tertiary sector is often associated with the service industry and is a significant contributor to many modern economies. The tertiary sector is characterized by the use of knowledge and expertise to provide services to customers.
Overall, the three stages of production play a vital role in the creation of goods and services and the functioning of modern economies. The primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors are all interconnected and rely on each other to function effectively. Understanding the characteristics and challenges of each stage can provide valuable insights into the functioning of an economy and the role that different sectors play in its success.
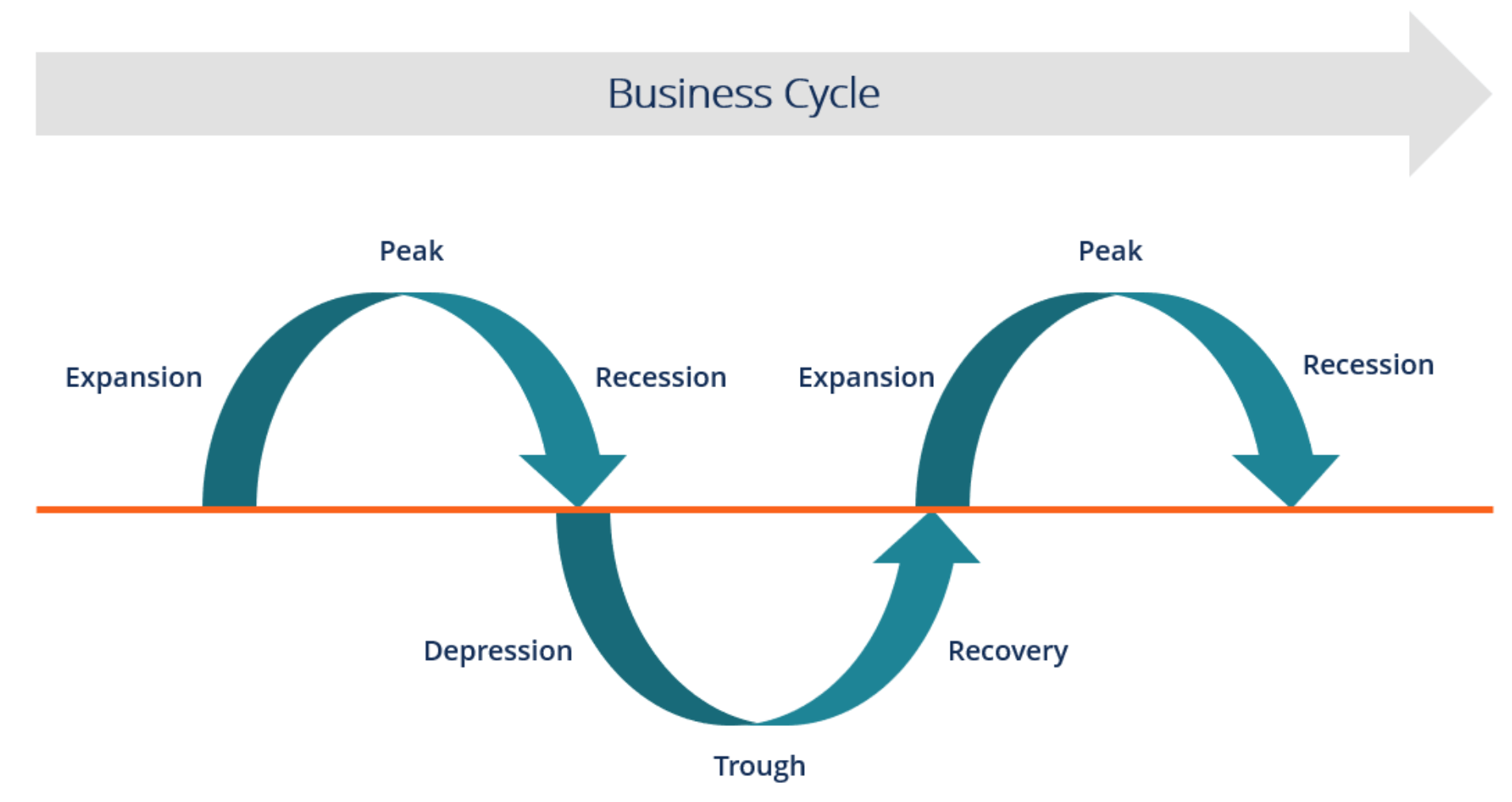
Economic Cycle
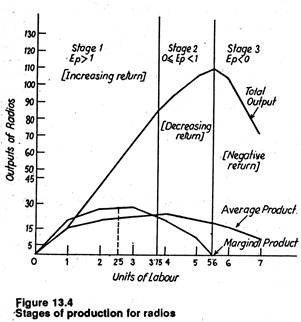
These curves show the various combinations of two variable inputs resulting in the same level of output. Therefore, the unemployment rate would decrease. Stage 2 is rational which means relevant range for a rational firm to operate. When more units of variable factors are applied to a fixed factor, the fixed factor is used more intensively and production increases rapidly. The important conclusion from this study can be derived as when we try to maximize the welfare effects of production we have to maximize real income formation. This process applies on all types of manufacturing whether it relates to production of goods, clothes, equipments or other. Too many workers get in each other's way and do not produce as much as in Stage 1 or even Stage 2.
A Note on the Three Stages of Production on JSTOR

Adding more variable entries is counterproductive; an additional source of labor will decrease global production. The relationship between physical outputs of a production process and physical inputs that is factors of production represents the theory of production function. This stage is not rational, at this stage the firm would need to reduce labor in order to increase Economic Effects Of Deflation The deflation leads a negative shock in aggregate demand, therefore the AD curve shifts to the left, both of the price level and real national output falls. Finally, capitol is the money needed to fund industry. It continues until the cycle reaches a trough. The same shirt can be as well made with less cloth C 2 , if more labor L 2 is used because the tailor will have to cut the cloth more carefully and reduce wastage. Importance of the Economic Cycle Every person is a participant in the market-based economy.
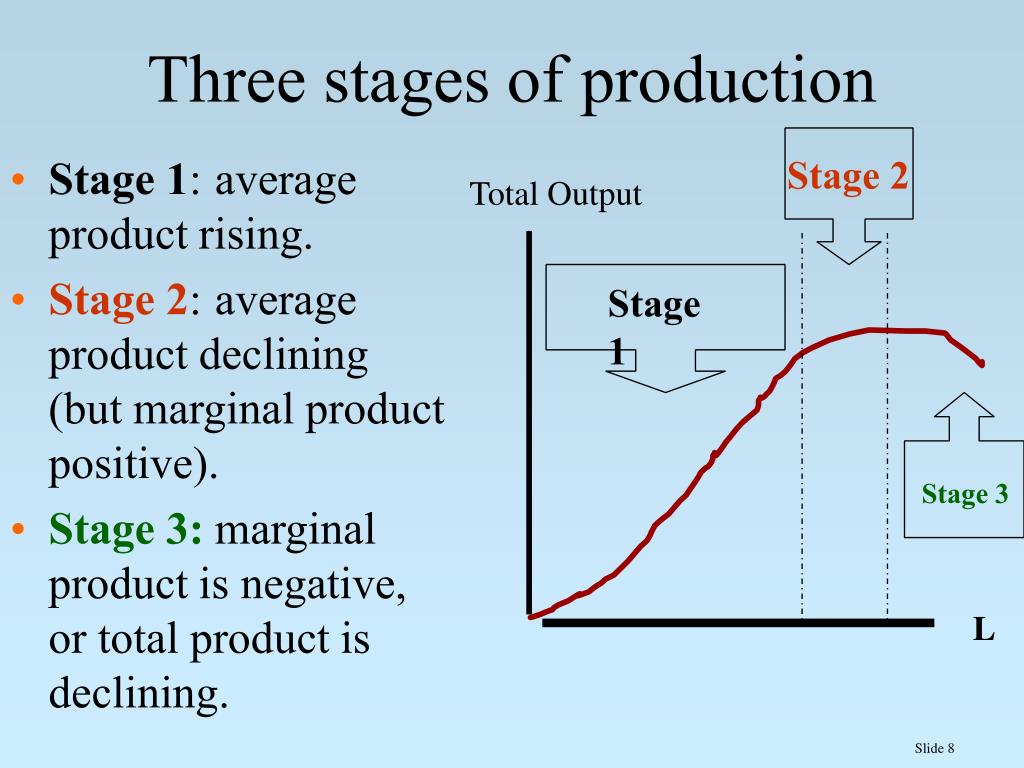
The Three Stages Of Production

But what is the value of an idea without a way to bring it to life? From the above graph, the gross profit margin has shown a decreasing trend over the last ten years with minor increase in the years 2008 and 2010. This project includes literature review, wherein various worldwide organizations with distinct production stages are studied. Take, for example, a messenger company that delivers packages around a city. As per economists, there are three stages of production. In the long run, it is essential for having a better understanding of the marginal return received on the marginal product. In case of industries with constant returns to scale, firms of all sizes would survive equally well.
3.16: The Theory of Production
However, automation is increasingly replacing the need for workers. Now producing a car has become more expensive. For example, exactly two wheels and one frame are required to produce a bicycle and in no way can wheels be substituted for frames or vice-versa. The use of money in measuring the product may show increasing rather than decreasing returns if the price of the product rises, even though the output may have declined. Iron ore was necessary for machines, buildings, and bridges.
What Is Production In Economics? Concept, Factor, Importance

The wage or salary is the form of payment for the use of this factor. This is also known as Leontief isoquant or input-output isoquant See Fig. Thus, the substitutability of labor for cloth diminishes from L 1 to L 2 to L 3. When the consumer continues to use more units of factors A, B, and C to produce a fixed quantity of X columns 1, 3, 5 of the table, their marginal productivities continue to decline columns 2, 4, 6. The marginal productivity of each factor is independent of the other.
Three Stages of Production in Economics

Profits and puppet theatre: Economics beyond permanent stages. As a result average productivity decreases but the real income per capita increases. This law holds that as you add more workers to the production process, output will increase, but the size of that increase will get smaller with each worker you add. For example, hiring an additional employee to produce cans will actually result in fewer cans produced overall. At some point, if you keep adding workers, your output may even start shrinking.
What are the three stages of production in economics?
As an example, if one employee produces five cans by himself, two employees may produce 15 cans between the two of them. If the technique of production undergoes a change, the product curves will be shifted accordingly but the law will ultimately operate. Gas and oil are perfect substitutes only, oil only, or varying amounts of each. Thank you for your cooperation Factors of production are the resources the economy has available to produce goods and services. This function or curve is based on the law of diminishing returns, which happens when the output of production decreases, after a certain threshold of labor or other inputs is reached. For example, given the lower gasoline prices, the company can now serve a greater area and increase its supply. If the marginal product of labor is greater in cotton textile industry than in the jute industry, labor will move from the latter to the former till marginal productivity of labor becomes equal in both the industries.






