Tolerable misstatement is a concept that refers to the acceptable level of error or deviation from the expected or ideal result in financial reporting. It is a term used in auditing and refers to the acceptable level of error in financial statements that does not affect the overall reliability and fairness of the financial statements.
Tolerable misstatement is determined by the auditor based on a number of factors, including the materiality of the error, the complexity of the transactions being reported, and the inherent risk of the transactions. Materiality refers to the importance of the error in relation to the overall financial statements. An error that is considered material would have a significant impact on the financial statements and would therefore require more thorough investigation and correction.
The complexity of the transactions being reported also plays a role in determining tolerable misstatement. Complex transactions are more likely to result in errors, so the acceptable level of error may be higher in these cases. Inherent risk refers to the likelihood of an error occurring due to the nature of the transactions being reported. If a transaction has a high inherent risk, the acceptable level of error may be lower.
Tolerable misstatement is an important concept in financial reporting because it helps to ensure the reliability and fairness of financial statements. By setting an acceptable level of error, auditors can focus their efforts on correcting errors that are material and have the greatest impact on the financial statements. This helps to ensure that financial statements accurately reflect the financial position of the company and provide useful information to stakeholders.
In conclusion, tolerable misstatement is a concept that refers to the acceptable level of error in financial reporting. It is determined by the auditor based on factors such as materiality, complexity, and inherent risk, and helps to ensure the reliability and fairness of financial statements.
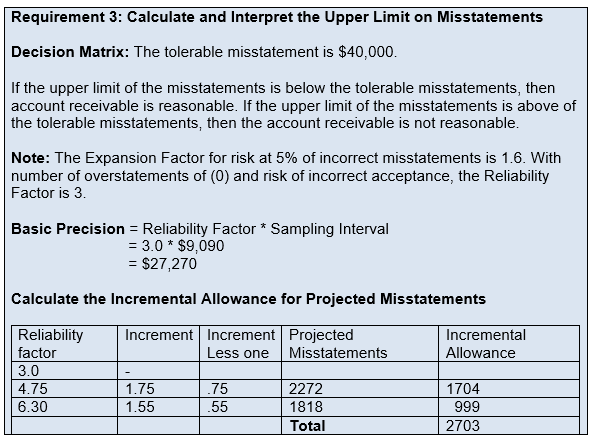
Materiality and Tolerable Misstatement

Auditors calculate the materiality for ABC Co. Thank you for your interest in our publications. Reperformance for Audit Clients Reperformance is an audit procedure in which the auditor independently repeats an activity that the audit client has done, normally as part of the client's internal control system. Annual Report Report to the stockholders of a company which includes the company's annual, audited BALANCE SHEET and related statements of earnings, stockholders' or owners' equity and cash flows, as well as other financial and business information. The auditor may assess control risk at the maximum, or assess control risk below the maximum based on the sufficiency of evidential matter obtained to support the effectiveness of controls. A tolerable misstatement is the amount by which a financial statement line item can differ from its true amount without impacting the fair presentation of the entire The tolerable misstatement that an auditor allows is a judgment call, based on the proportion of planning materiality for an audit. Accounting Recording and reporting of financial transactions, including the origination of the transaction, its recognition, processing, and summarization in the FINANCIAL STATEMENTS.
What is Planning Materiality and Tolerable Misstatement?
To determine the existence of the accounts receivable balances at the balance sheet date, Smith would most likely: A. Previous experience with the entity. Borrowing money at an interest rate significantly below the market rate. Should have equal credit and debit totals. All of the answers 4. For example, if a group is composed of three large components and 35 relatively small components, the group engagement partner would not likely allocate more than two times group overall materiality in aggregate to the three large components, based on the suggested benchmark multiple associated with three components. If all other factors specified in an attributes sampling plan remain constant, decreasing the tolerable rate and increasing the estimated population deviation rate would have what effect on sample size? Credit Balance BALANCE remaining after one of a series of bookkeeping entries.
Calculating Performance Materiality & Tolerable Misstatements

The ineffectiveness of the board of directors. Equal the actual control risk. Reperformance and recalculation procedures are typically not used for non-audit engagements. Recalculation for Audit Clients Recalculation involves doing a calculation the client has done to check its mathematical accuracy. This total is the CONTRA ACCOUNT to the related asset account. Is the entity's process for identifying business risks relevant to financial reporting objectives and deciding about actions to address those risks, and the results thereof. To properly plan the nature and extent of audit procedures for the group audit, the group engagement partner, who is the lead auditor for the consolidated entity, must determine group overall materiality and establish or approve appropriate materiality levels for the individual components.
Audit Chapter 9 Flashcards

Planning materiality can help auditors focus on critical areas or significant misstatements in the financial statements. Cost of Goods Sold Figure representing the cost of buying raw materials and producing finished goods. Assume that the auditor detected the following four exceptions in the sample of 100 and that each item was selected only once: 70. The auditor expresses no opinion on the financial statements, and therefore, no audit procedures are performed. Similarly, if the auditor's evaluation of a sample leads him to unnecessarily assess control risk too high for an assertion, he would ordinarily increase the scope of substantive tests to compensate for the perceived ineffectiveness of the controls. Either approach to audit sampling can provide sufficient evidential matter when applied properly. Controls over the reliability of financial reporting are ordinarily most directly relevant to a financial statement audit, but other controls may also be relevant.
IAASB
The auditor can, for example, foot and cross-foot the age analysis. For non-audit engagements, such as compilation and review engagements, no or limited audit procedures are performed. Discount Bond BOND selling below its REDEMPTION VALUE. Should compare the deviation rate of the sample to the tolerable rate. The auditor should examine those items for which, in his judgment, acceptance of some sampling risk is not justified. Evaluate whether the financial statements are materially misstated. Reducing the scope of tests of controls and substantive tests.