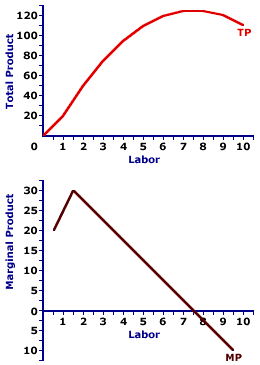
A total product curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the quantity of a good or service produced by a firm and the total amount of inputs, such as labor and capital, used in the production process. The curve is typically upward sloping, indicating that as more inputs are used, the firm is able to produce more output.
There are two main types of total product curves: the short-run total product curve and the long-run total product curve. The short-run total product curve represents the relationship between output and a single input, such as labor, while holding all other inputs constant. The long-run total product curve represents the relationship between output and all inputs, including both variable and fixed inputs.
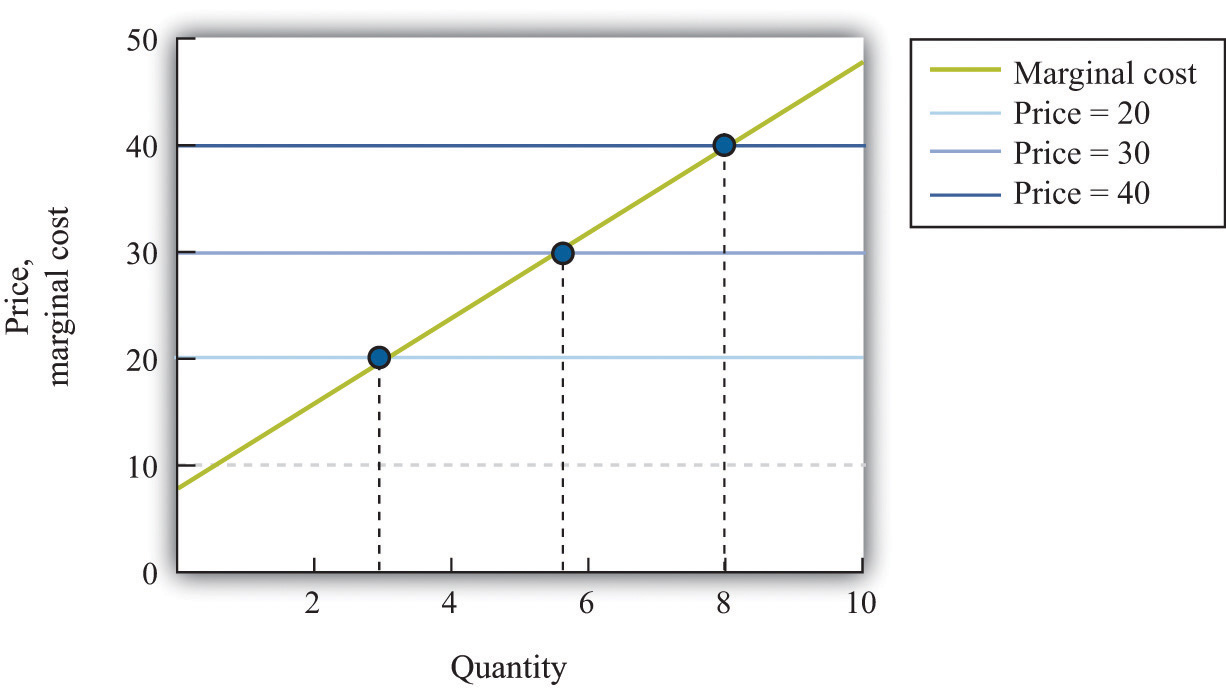
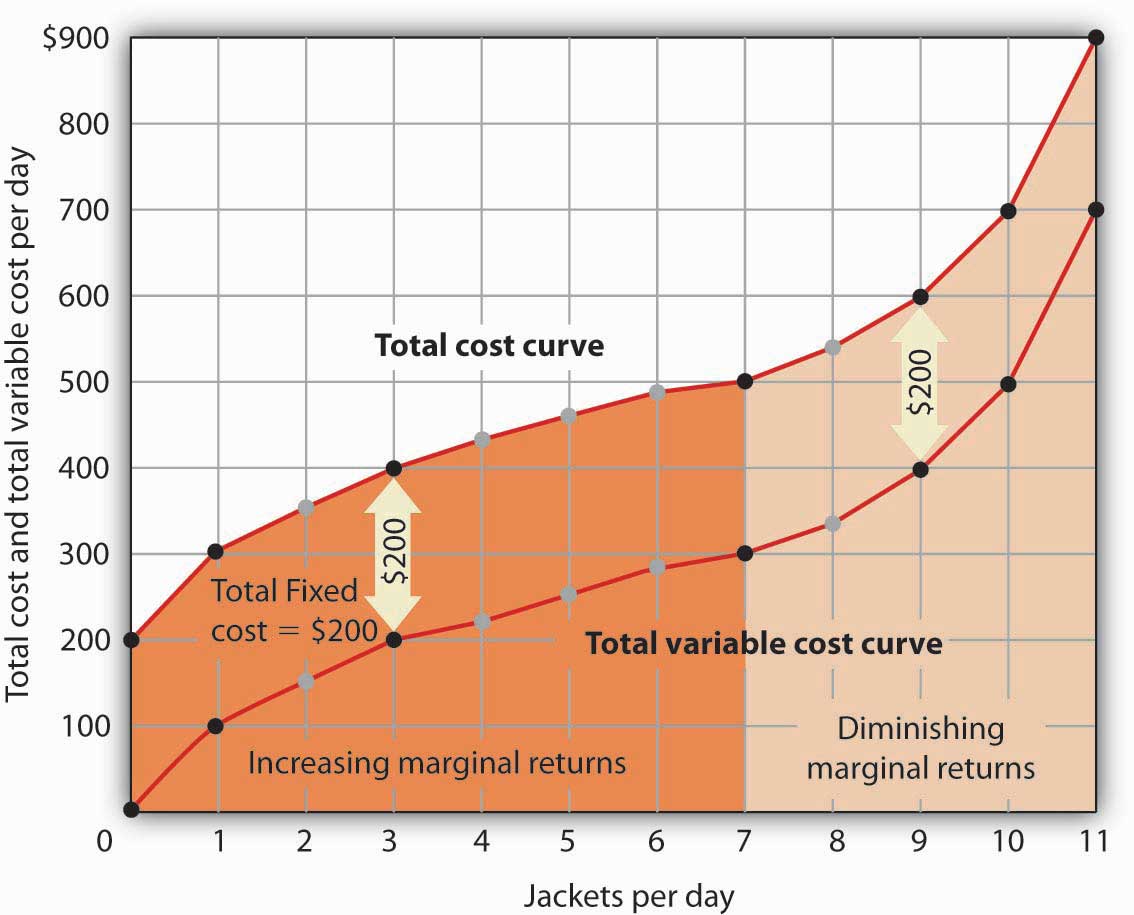
The shape of the total product curve depends on a variety of factors, including the technology used in production, the efficiency of the inputs, and the level of competition in the market. In general, the total product curve is concave, meaning that it becomes flatter as more inputs are used. This is due to the law of diminishing returns, which states that as more of a variable input is used in production, the marginal product of that input eventually decreases.
The total product curve is an important tool for firms because it allows them to understand the most efficient level of production given their inputs and technology. By examining the total product curve, firms can identify the point at which they are maximizing their production and profits. This information can be used to make decisions about how to allocate resources and optimize production processes.
In addition to its use in firm decision-making, the total product curve is also an important concept in economic analysis. It can be used to understand the relationship between output and inputs in the economy as a whole, and to analyze the impact of changes in technology or other factors on the production process.
Overall, the total product curve is a useful tool for understanding the relationship between inputs and outputs in the production process, and for analyzing the efficiency of production and the allocation of resources.