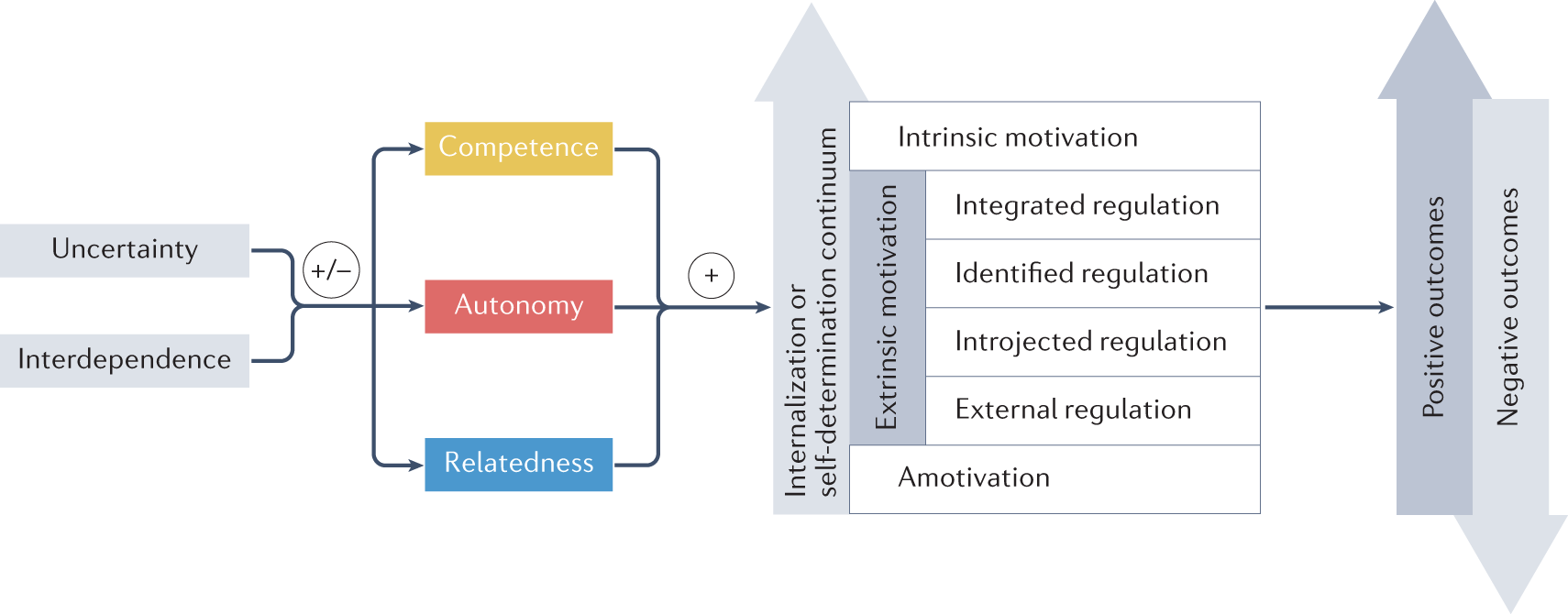
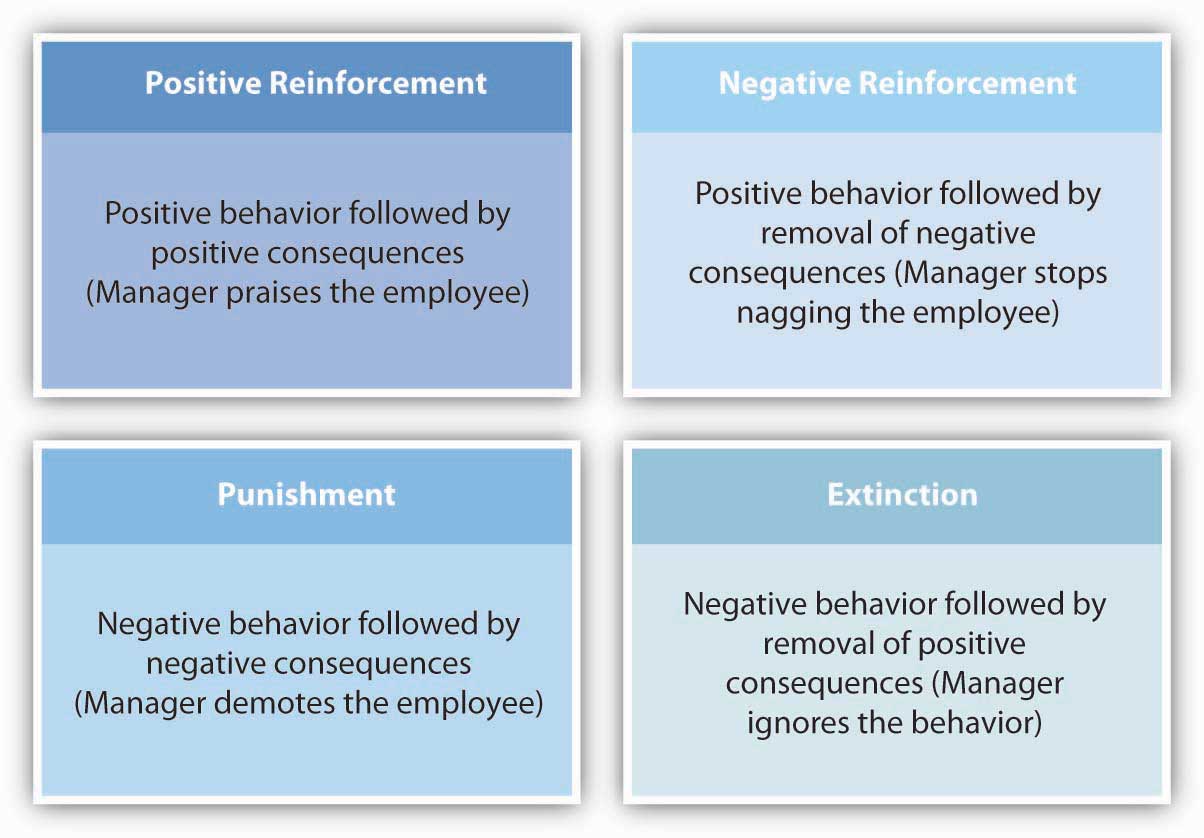
The traditional theory of motivation, also known as the Maslow's hierarchy of needs, is a psychological theory that explains how human beings are motivated to fulfill their needs and achieve their full potential. According to this theory, human motivation is driven by a hierarchy of needs that must be met in a specific order.
According to Maslow, the lower-level needs, such as physiological needs and safety needs, must be met before higher-level needs, such as self-esteem and self-actualization, can be pursued. The lower-level needs, which include the basic physiological needs for survival, such as food, water, and shelter, are considered to be the most fundamental and must be met before higher-level needs can be addressed. Once these lower-level needs are met, individuals can then focus on meeting their safety needs, which include physical and emotional security.
As individuals continue to meet their needs, they move up the hierarchy and begin to focus on their social needs, such as love, belonging, and acceptance. Once these needs are met, individuals can then focus on meeting their self-esteem needs, which include self-respect, self-confidence, and self-worth. The final level of the hierarchy is self-actualization, which refers to the realization of one's full potential and the desire to achieve personal growth and self-fulfillment.
The traditional theory of motivation suggests that individuals are driven to fulfill their needs in a specific order, starting with the most basic physiological needs and moving up the hierarchy as they are met. This theory has been widely accepted and has influenced our understanding of human motivation and behavior. However, it is important to note that the hierarchy of needs is not fixed and can change depending on an individual's personal circumstances and experiences.
In conclusion, the traditional theory of motivation, as proposed by Maslow, provides a framework for understanding how human beings are motivated to fulfill their needs and achieve their full potential. It suggests that motivation is driven by a hierarchy of needs that must be met in a specific order, starting with the most basic physiological needs and moving up the hierarchy as they are met. This theory has had a significant impact on our understanding of human motivation and behavior and continues to be an important theoretical framework in the field of psychology.