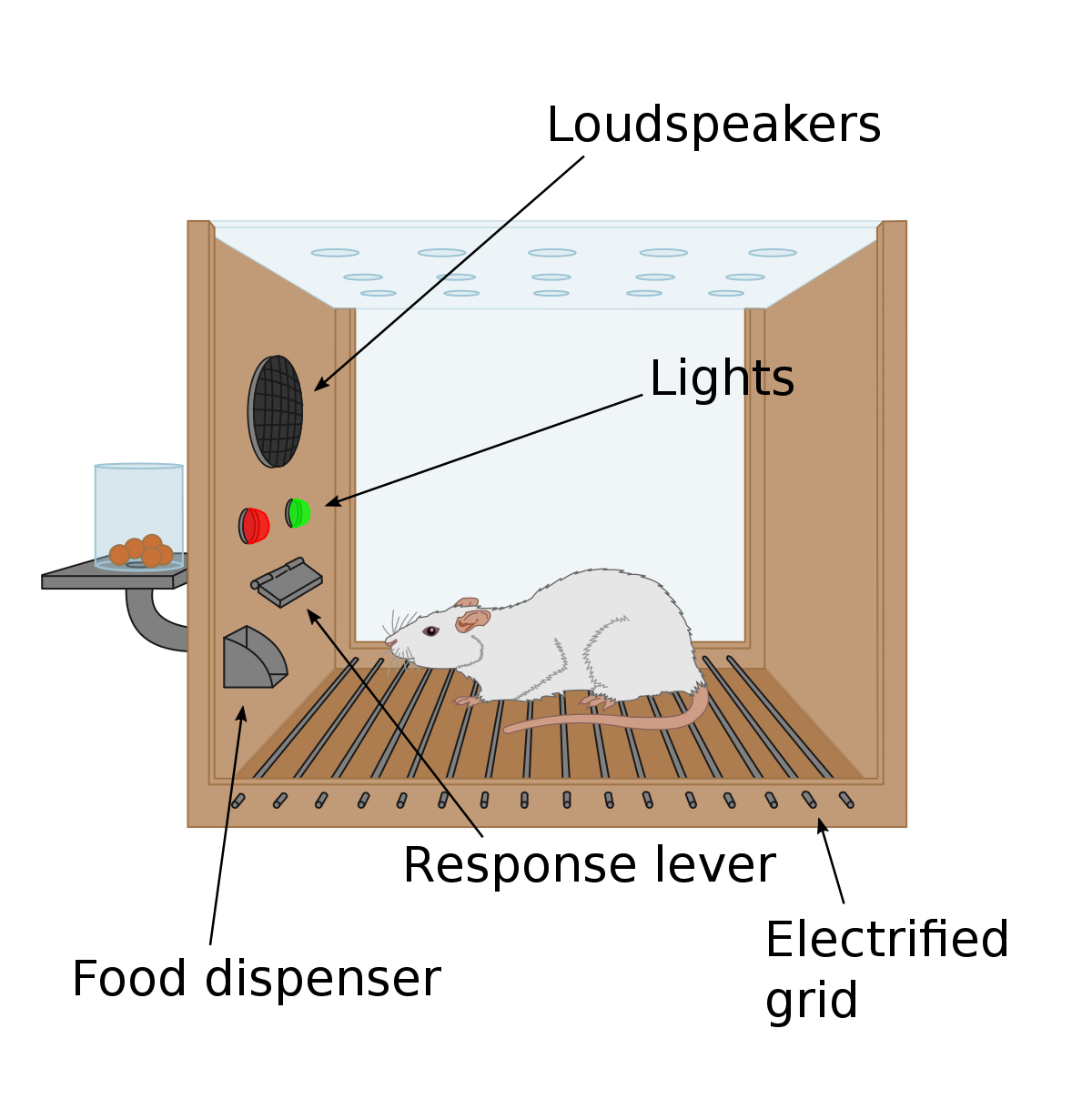
Trial and error learning, also known as experiential learning or problem-based learning, is a type of learning that occurs when an individual encounters a problem or obstacle and actively engages in finding a solution through repeated attempts and corrections. This learning strategy is often used when there is a lack of prior knowledge or experience with the task at hand, and it allows individuals to learn through firsthand exploration and experimentation.
One of the key features of trial and error learning is that it involves repeated attempts and corrections, which allows individuals to gradually refine their approach and improve their performance. This process of trial and error can be slow and frustrating at times, but it ultimately allows individuals to develop a deep understanding of the task and the underlying principles that govern it.
One of the benefits of trial and error learning is that it allows individuals to discover new solutions and approaches to problems that may not have been considered through more traditional learning methods. This can be particularly useful in situations where there are multiple possible solutions or approaches to a problem, as it allows individuals to explore and compare different options.
Another benefit of trial and error learning is that it can be highly motivating for individuals, as it allows them to actively engage with the material and feel a sense of accomplishment as they progress through the learning process. This can be particularly important for learners who may struggle with more traditional forms of instruction, such as lectures or textbook-based learning.
However, trial and error learning is not without its challenges. One of the drawbacks of this approach is that it can be time-consuming, as it involves multiple attempts and corrections before a solution is found. This can be frustrating for some learners, particularly those who may be more accustomed to more structured or efficient forms of learning.
Additionally, trial and error learning can be challenging for learners who may be more risk-averse, as it requires a willingness to take risks and potentially make mistakes in the pursuit of finding a solution. This can be especially difficult for learners who may be perfectionists or who may be more anxious about making mistakes.
In conclusion, trial and error learning is a valuable learning strategy that allows individuals to discover new solutions and approaches to problems through firsthand exploration and experimentation. While it can be time-consuming and challenging at times, it ultimately allows individuals to develop a deep understanding of the task at hand and can be highly motivating for learners.