Type 1 diabetes, also known as insulin-dependent diabetes or juvenile diabetes, is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar. Insulin is necessary for the body to use sugar as an energy source, so without it, blood sugar levels can become too high, leading to serious health complications.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder, meaning that the body's immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. It is not clear what causes this immune system malfunction, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Type 1 diabetes typically develops in children and young adults, but it can occur at any age. Symptoms of type 1 diabetes include increased thirst and urination, weight loss, fatigue, and blurred vision. If left untreated, type 1 diabetes can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, blindness, nerve damage, and amputations.
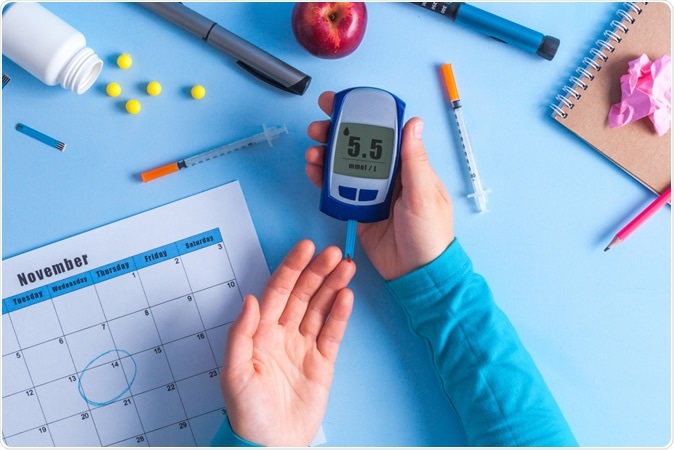
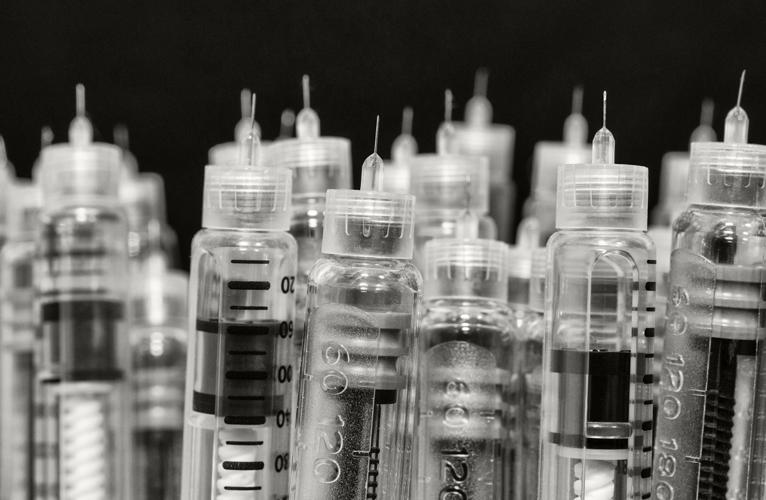
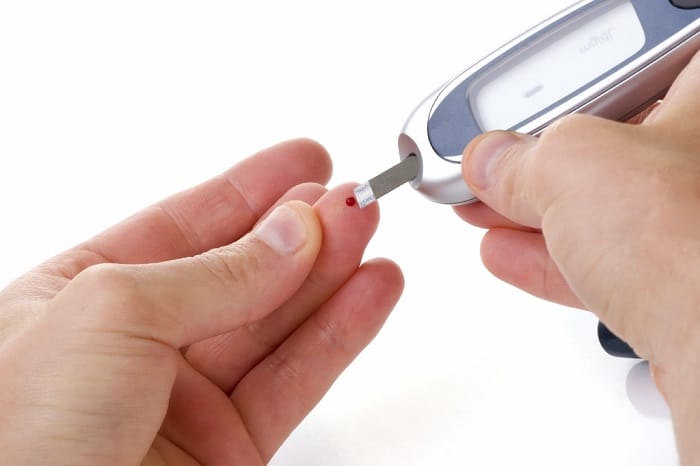
Treatment for type 1 diabetes involves daily insulin injections or the use of an insulin pump. People with type 1 diabetes must also closely monitor their blood sugar levels and make adjustments to their insulin doses based on their activity levels, diet, and other factors.
Living with type 1 diabetes requires a lot of effort and dedication, but with proper management, people with type 1 diabetes can live full and healthy lives. Advances in insulin delivery methods, blood sugar monitoring technology, and diabetes education have made it easier for people with type 1 diabetes to manage their condition.
Type 1 diabetes is a serious and chronic condition, but with proper treatment and management, it is possible to live a long and healthy life. It is important for people with type 1 diabetes to work closely with their healthcare team and to be vigilant about their blood sugar control. With the right support and treatment, people with type 1 diabetes can lead full and active lives.