Chemical weathering is a process that occurs when rocks and minerals are broken down or altered by chemical reactions with the environment. This can happen through various types of chemical reactions, including dissolution, hydrolysis, oxidation, and reduction.
One type of chemical weathering is dissolution, which occurs when a substance dissolves in water. This can happen when water comes into contact with rocks and minerals that contain soluble substances, such as salt or calcium carbonate. As the water moves through the rock or mineral, it dissolves the soluble substances, causing the rock or mineral to break down and eventually disappear. This process is common in areas with high levels of rainfall or where water is present in the ground, such as near coastlines or in wetlands.
Another type of chemical weathering is hydrolysis, which occurs when water reacts with a substance to break it down. This can happen when water comes into contact with minerals that contain cations, or positively charged ions. The water can react with the cations, causing the mineral to break down and release the cations into the water. This process is common in areas with high levels of rainfall or where water is present in the ground, such as near coastlines or in wetlands.
Oxidation is another type of chemical weathering that occurs when a substance reacts with oxygen to form a new compound. This can happen when oxygen comes into contact with certain minerals, such as iron or sulfur, causing them to rust or oxidize. This process is common in areas with high levels of oxygen, such as in the atmosphere or near the surface of the Earth.
Reduction is the final type of chemical weathering, which occurs when a substance gains electrons and becomes more stable. This can happen when a substance reacts with another substance that has a lower oxidation state, such as hydrogen or carbon. This process is common in areas with high levels of hydrogen, such as near bodies of water or in wetlands.
Overall, chemical weathering is an important process that helps to break down and alter rocks and minerals, leading to the formation of new substances and the creation of new landscapes. It is a slow process that occurs over time, but it is a vital part of the Earth's geology and helps to shape the world we live in.
What type of chemical weathering is acid rain?

The five sources of chemical weathering are hydrolysis, oxidation, carbonation, living organisms and acid rain. The resulting aqueous solutions are sulfuric acid H 2 SO 4 and nitric acid HNO 3 , respectively. Do you want to learn more about rocks and geology? Which is a result of chemical weathering? Figure 3 shows that over long geologic time scales dissolution takes places and silicate rockdissolve into calcium, silicon, and bicarbonate ions which are thentransported by afresh water system such as a river to the ocean. Many igneous minerals that are high in magnesium and iron weather quickly to form clays, whereas the more felsicmineralstend experience physical weatheringbecause they are more resistant to chemical weathering. It occurs when oxygen in water reacts with the mineral iron in rocks, which causes them to rust. In the process they act as a wedge, widening and extending the cracks. Over time, this reaction causes rocks to dissolve because of the Water molecules can bind to either the negative or positive ions in the minerals.
3 TYPES OF WEATHERING
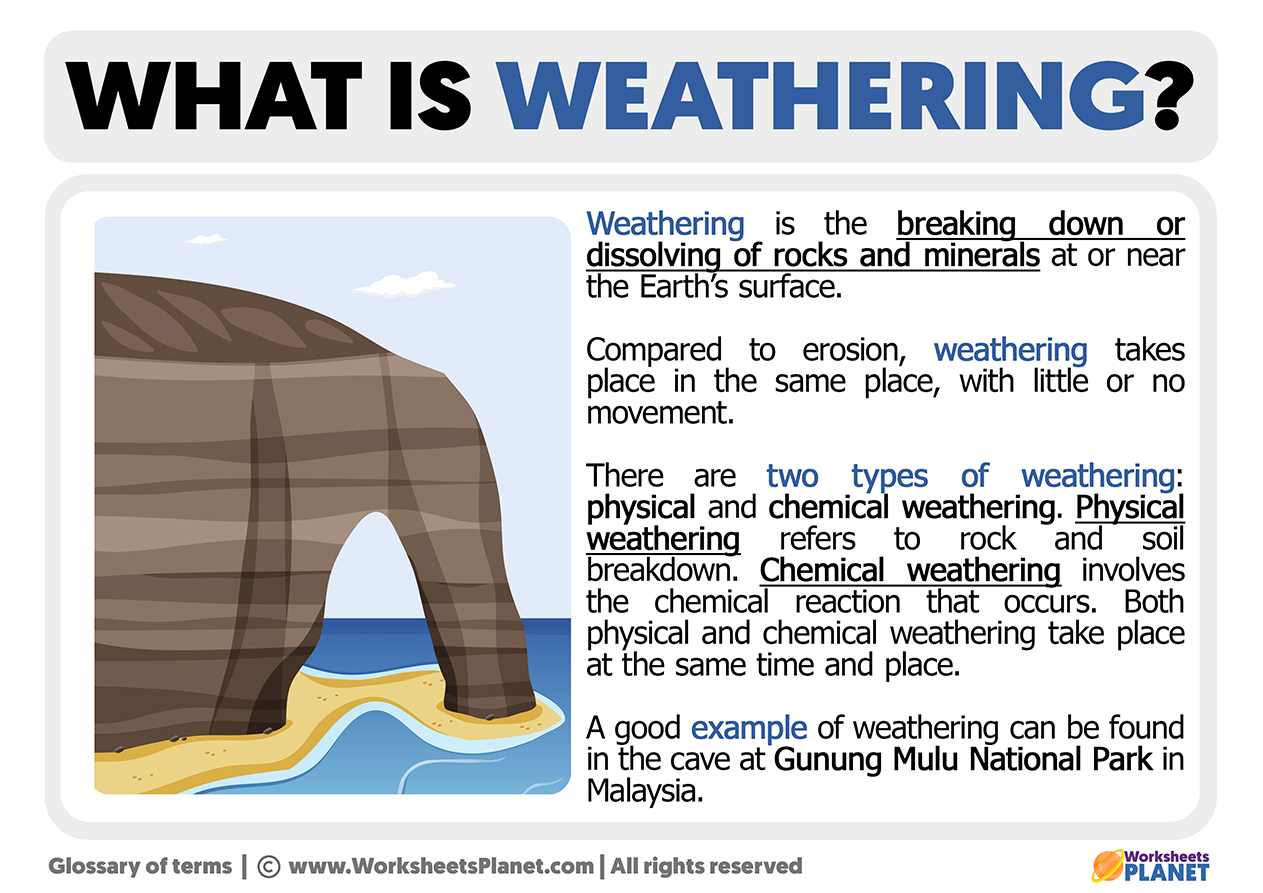
So, to make your dream successful download the now! It occurs in limestone and chalk regions where the weak carbonic acid reacts with limestone or chalk to form calcium hydrogen carbonate which dissolves in water. Which of the following is a chemical weathering agent? This page describes mechanical physical weathering and more. Is the best example of chemical weathering? What is the chemical weathering of rocks? Iron oxide formation is a process that is similar to alteration and forms what we know in everyday life as rust. Feldspar, one of the most abundant rock-forming minerals, chemically reacts with water and water-soluble compounds to form clay. There are five types of chemical weathering: carbonation, hydrolysis, oxidation, acidification, and lichens living organisms. Sinkholes are examples of chemical weathering.
What is the most common type of chemical weathering?

There are different types of chemical weathering processes, such as solution, hydration, hydrolysis, carbonation, oxidation, reduction, and chelation. Hydrolysis occurs, for example, when water comes in contact with granite. Is rust an example of chemical weathering? The rocks that are weathered by carbonation are called carbonate rocks, this means the rocks contain Co3. This occurs in areas where there is extensive cover materials over a limestone layer. Many chemical changes are possible.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Peridotite-5c6a375bc9e77c0001675a9f.jpg)