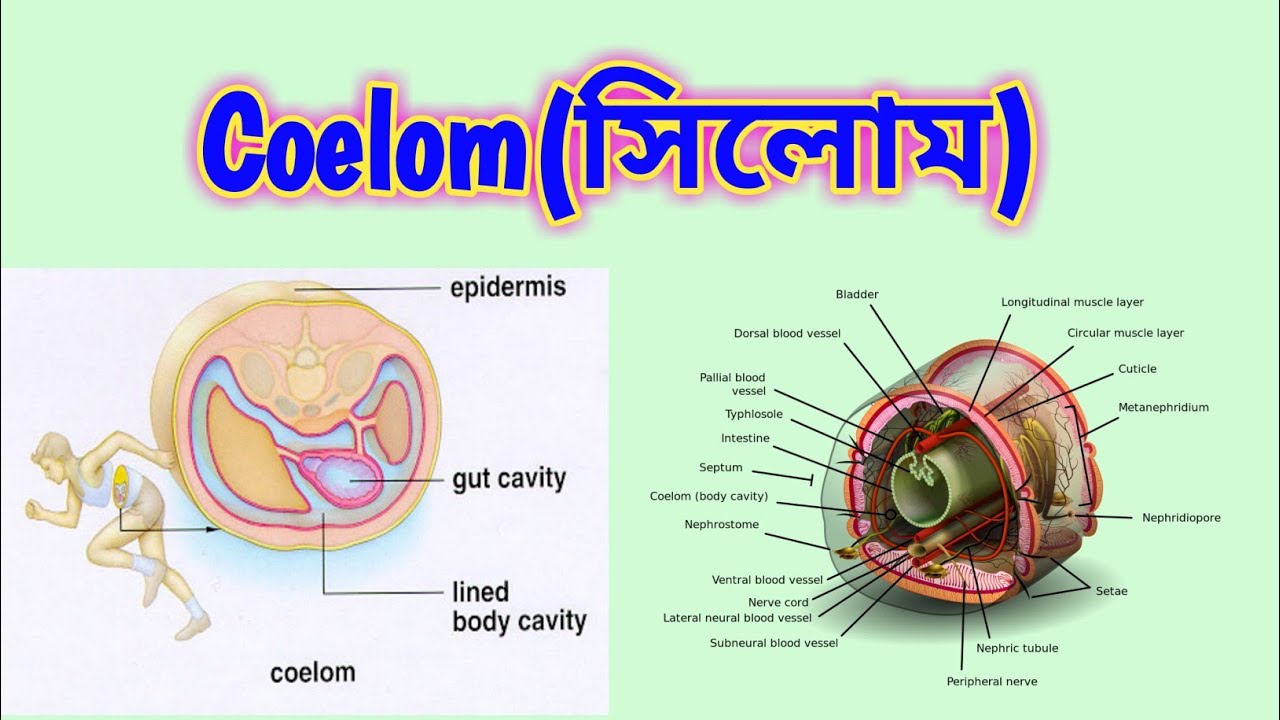
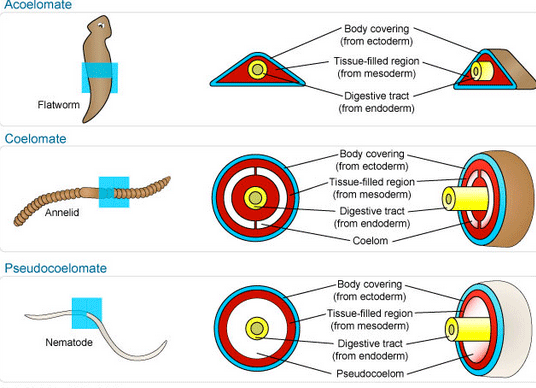
Coeloms are fluid-filled body cavities that develop within the mesoderm, or middle layer, of an animal's embryo. These cavities serve as a supportive scaffold for the internal organs, allowing them to move and function within the body. Coeloms also play a role in circulation, excretion, and reproduction.
There are three main types of coeloms in animals: true coeloms, pseudocoeloms, and haemocoeloms.
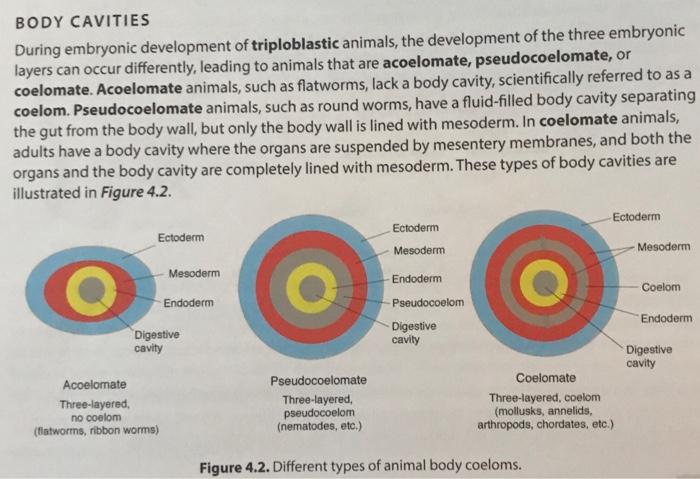
True coeloms, also known as enterocoeloms, are the most advanced type of coelom. They are found in animals that belong to the phylum Chordata, which includes vertebrates such as mammals, birds, and reptiles. True coeloms are completely enclosed and separated from the outer body wall by a thin layer of mesoderm. They are divided into two main compartments: the peritoneal cavity, which surrounds the digestive organs, and the pleural cavity, which surrounds the lungs. True coeloms allow for greater freedom of movement and support for the internal organs, and they also provide a space for the circulation of nutrients, gases, and waste products.
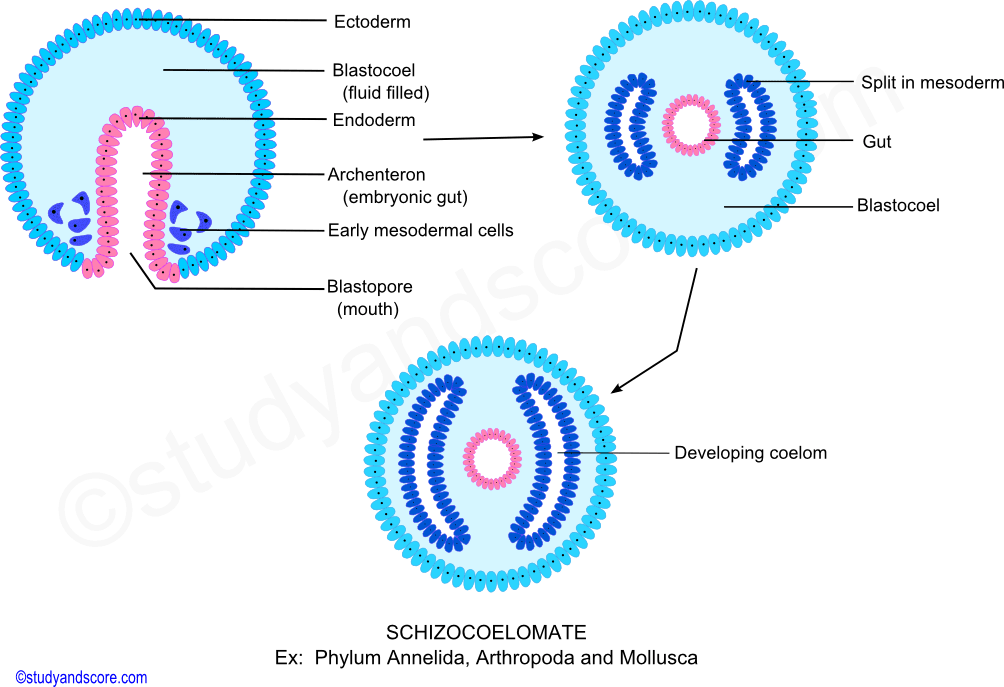
Pseudocoeloms, also known as schizocoeloms, are a type of coelom that is partially enclosed by mesoderm. They are found in animals that belong to the phylum Nematoda, which includes worms such as roundworms and pinworms. Pseudocoeloms are formed when the mesoderm splits, creating a cavity between the outer body wall and the internal organs. These coeloms are not as well-defined as true coeloms, and they do not provide as much support or freedom of movement for the internal organs.
Haemocoeloms, also known as open coeloms, are the simplest type of coelom. They are found in animals that belong to the phylum Arthropoda, which includes insects, spiders, and crustaceans. Haemocoeloms are not enclosed by mesoderm, and they are not separated from the outer body wall. Instead, they are simply a cavity within the body that is filled with blood. Haemocoeloms provide a space for circulation, but they do not provide as much support or protection for the internal organs as true coeloms or pseudocoeloms.
In summary, coeloms are important body cavities that play a variety of roles in animal anatomy and physiology. True coeloms are the most advanced type, found in chordates such as mammals, birds, and reptiles. Pseudocoeloms are partially enclosed by mesoderm and found in nematodes such as roundworms and pinworms. Haemocoeloms, the simplest type of coelom, are found in arthropods such as insects, spiders, and crustaceans.