Elasticity refers to the degree to which the quantity demanded or supplied of a good or service changes in response to a change in price. There are several types of elasticity of demand and supply that are important for businesses and policymakers to understand in order to make informed decisions about pricing, production, and other economic variables.
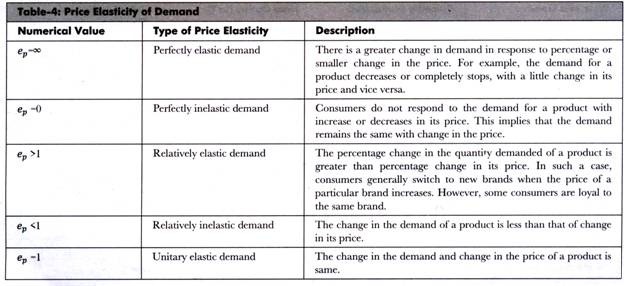
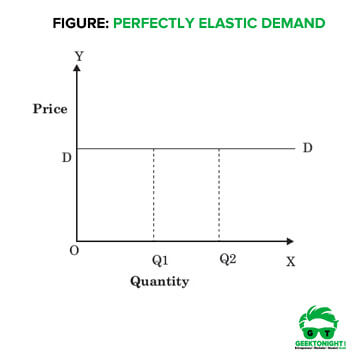
The first type of elasticity is elastic demand. Elastic demand occurs when the quantity demanded of a good or service changes significantly in response to a change in price. For example, if the price of a product increases by 10%, the quantity demanded may decrease by more than 10%. This occurs because consumers have other options available to them, and they are willing to switch to a substitute if the price of the original good becomes too high. Elastic demand is typically observed for goods or services that are considered non-essential or luxury items, as well as those that have many close substitutes.
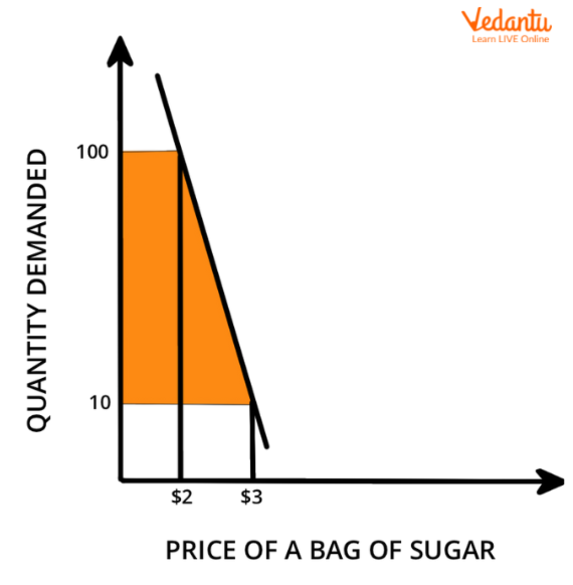
The second type of elasticity is inelastic demand. Inelastic demand occurs when the quantity demanded of a good or service changes only slightly in response to a change in price. For example, if the price of a product increases by 10%, the quantity demanded may only decrease by a small amount. This occurs because the good or service is considered essential, and consumers are willing to pay a higher price in order to continue to purchase it. Inelastic demand is typically observed for goods or services that are considered necessities, such as food, clothing, and housing.
The third type of elasticity is unit elastic demand. Unit elastic demand occurs when the quantity demanded of a good or service changes by the same percentage as the price. For example, if the price of a product increases by 10%, the quantity demanded may decrease by exactly 10%. This occurs when the good or service has few close substitutes and is not considered essential, so consumers are willing to pay a higher price but will also decrease their consumption of the good or service.
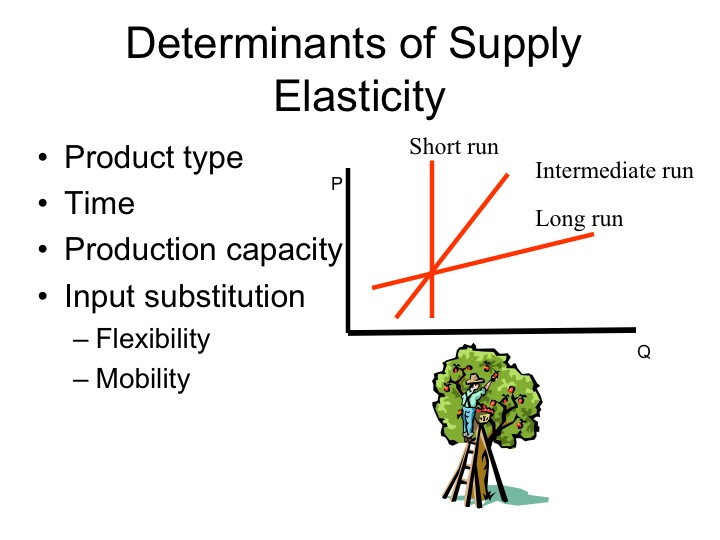
The fourth type of elasticity is elastic supply. Elastic supply occurs when the quantity supplied of a good or service changes significantly in response to a change in price. For example, if the price of a product increases, producers may be willing to increase their production of the good or service in order to take advantage of the higher price. Elastic supply is typically observed for goods or services that have low production costs and can be produced quickly and easily.
The fifth type of elasticity is inelastic supply. Inelastic supply occurs when the quantity supplied of a good or service changes only slightly in response to a change in price. For example, if the price of a product increases, producers may not be able to significantly increase their production due to constraints such as limited resources or time. Inelastic supply is typically observed for goods or services that have high production costs or take a long time to produce.
The sixth type of elasticity is unit elastic supply. Unit elastic supply occurs when the quantity supplied of a good or service changes by the same percentage as the price. For example, if the price of a product increases by 10%, the quantity supplied may increase by exactly 10%. This occurs when the good or service has moderate production costs and can be produced at a reasonable pace.
In conclusion, elasticity of demand and supply refers to the degree to which the quantity demanded or supplied of a good or service changes in response to a change in price. There are several types of elasticity, including elastic, inelastic, and unit elastic, and the type of elasticity observed can depend on a variety of factors such as the availability of substitutes, the essential nature of the good or service, and the costs of production. Understanding the elasticity of demand and supply is important for businesses and policymakers in order to make informed decisions about pricing,