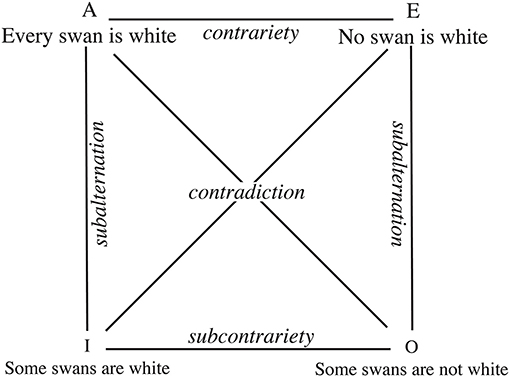
Logical opposition refers to the relationship between two statements or arguments that are in conflict with one another. There are several different types of logical opposition that can occur in discourse, and understanding these different types can be useful in analyzing and evaluating arguments. Below, I will outline and discuss four common types of logical opposition: contradiction, contrary, subcontrary, and contrapositive.
Contradiction is the strongest form of logical opposition, and it occurs when two statements or arguments are completely incompatible with one another. In other words, if one statement is true, the other must be false, and vice versa. For example, the statement "all cats are animals" is logically contradictory to the statement "no cats are animals." These two statements cannot both be true at the same time, as they directly contradict each other.
Contrary statements are also in conflict with one another, but they are not necessarily incompatible. Rather, they are two statements that cannot both be true, but they do not directly contradict each other. For example, the statement "some cats are black" is contrary to the statement "no cats are black." These two statements cannot both be true, but they do not directly contradict each other, as it is possible for some cats to be black while others are not.
Subcontrary statements are similar to contrary statements in that they cannot both be true, but they are not necessarily incompatible. However, subcontrary statements are related to one another in a way that is more complex than simple opposition. For example, the statement "some cats are black" is subcontrary to the statement "some cats are not black." These two statements cannot both be true, but they do not directly contradict each other, as it is possible for some cats to be black while others are not.
Contrapositive statements are a type of logical opposition that involves negating both the subject and the predicate of a statement. For example, the contrapositive of the statement "all cats are animals" is "all non-animals are non-cats." Contrapositive statements are logically equivalent to the original statement, meaning that if the original statement is true, the contrapositive must also be true, and vice versa.
In conclusion, logical opposition refers to the relationship between two statements or arguments that are in conflict with one another. There are several different types of logical opposition, including contradiction, contrary, subcontrary, and contrapositive. Understanding these different types of logical opposition can be useful in analyzing and evaluating arguments.