The unification of Germany, also known as the German Confederation, was a significant event in European history that occurred in the late 19th century. It involved the merger of various German-speaking states into a single, unified country that would eventually become known as the German Empire.
Before unification, Germany was a patchwork of different states, each with its own ruler and laws. This led to a lack of unity and cooperation among the various states, which made it difficult for Germany to effectively address issues such as military defense and economic development.
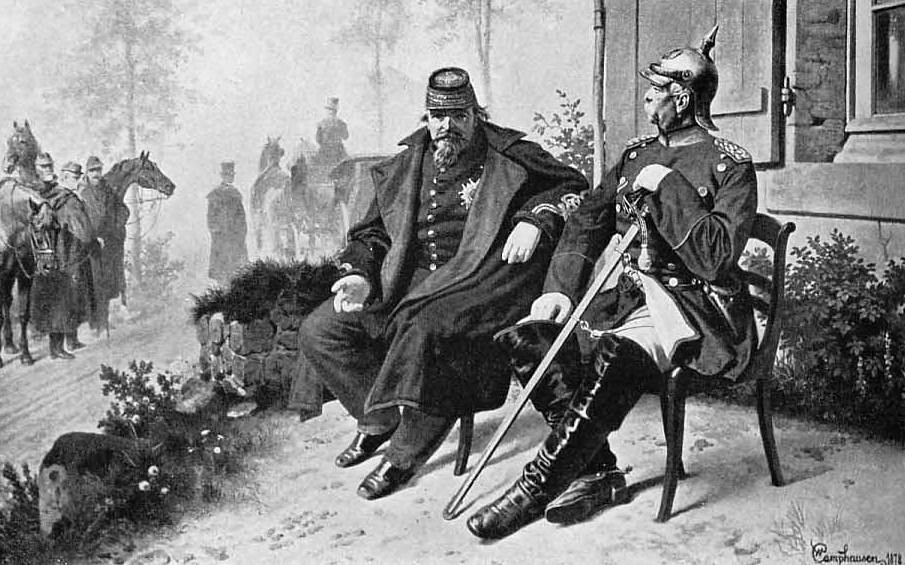
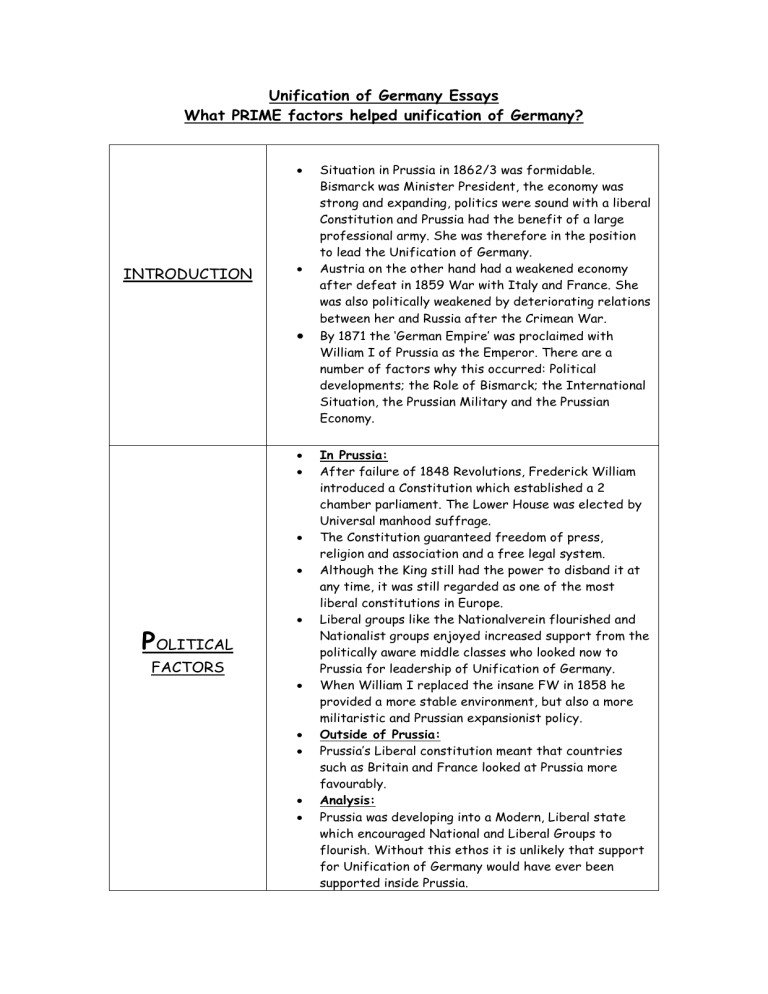
The main driving force behind the unification of Germany was Prussia, a powerful and influential state that had emerged as a dominant player in the region. Prussia was led by Otto von Bismarck, a shrewd and ambitious politician who saw the opportunity to unite the German states under Prussian leadership. Bismarck used a combination of diplomacy and military force to bring the various states together, eventually achieving the goal of unification in 1871.
There were several key factors that contributed to the success of Germany's unification. One was the weakness of the smaller German states, which were unable to effectively defend themselves against Prussia's military might. Another was the support of the German people, who were eager for a stronger, more unified Germany that could assert itself on the world stage.
The unification of Germany had far-reaching consequences for Europe and the world. It marked the end of the Holy Roman Empire, which had been a major European power for centuries. It also led to the emergence of a strong, industrializing Germany that would become a major player in international affairs.
Despite these successes, the unification of Germany was not without its challenges. The country was faced with a number of economic and social issues, including rising tensions between the industrial north and the agricultural south, and the emergence of radical political movements that sought to challenge the new government.
In conclusion, the unification of Germany was a significant event in European history that marked the end of the Holy Roman Empire and the emergence of a strong, industrializing Germany. It was driven by the leadership of Prussia and the support of the German people, and had far-reaching consequences for the world. However, it was not without its challenges, and the new Germany would have to navigate a number of economic and social issues in the years ahead.
The unification of Germany, which occurred in 1871, was a significant event in European history that marked the end of centuries of division and conflict. Prior to unification, Germany was a patchwork of small states, each with its own rulers and political systems. These states were frequently at odds with one another, and their relations were often marked by warfare and hostility.
The process of unification began in the early 19th century, when the Napoleonic Wars ended and the Congress of Vienna redrew the map of Europe. At this time, the German states were still divided and autonomous, but they were also influenced by the larger political and economic forces at play in Europe.
One of the main drivers of German unification was the rise of nationalism, which had taken root in many parts of Europe during the Napoleonic Wars. Nationalism is a political ideology that emphasizes the importance of national unity and the sovereignty of the nation-state. It was fueled by a sense of shared cultural and historical identity, as well as a desire for political and economic independence.
In Germany, nationalism was fueled by a number of factors, including the country's rich cultural and artistic traditions, as well as the desire to create a strong and united nation that could stand up to the other major powers of Europe. The German states had long been overshadowed by Austria and France, and many Germans saw unification as a way to assert their own national identity and independence.
The main leader of the unification movement was Prussia, which was the most powerful and influential of the German states. Prussia was led by Otto von Bismarck, who was a masterful politician and diplomat. Bismarck understood the importance of nationalism in unifying the German states, and he worked tirelessly to build support for unification among the German people.
Bismarck's strategy was to use a combination of diplomacy and military force to bring the German states together. He formed alliances with some of the smaller states and used Prussia's military might to coerce others into joining the unification movement. In 1866, Prussia went to war with Austria, which was one of the main rivals for control of Germany. Prussia emerged victorious from this conflict, which strengthened its position as the leader of the unification movement.
In 1871, the unification of Germany was finally achieved, with the creation of the German Empire. The new nation was led by Wilhelm I, the King of Prussia, who became the first Emperor of Germany. The unification of Germany was met with widespread celebration among the German people, who saw it as a triumph of national unity and a sign of their nation's growing strength and influence.
The unification of Germany had a number of significant consequences, both for the country itself and for the wider world. Within Germany, it brought about significant political, economic, and social changes, as the new nation sought to assert its power and influence on the international stage. The German Empire became a major industrial and military power, and it played a significant role in shaping the course of European and global history in the years that followed.
Overall, the unification of Germany was a complex and contentious process that was driven by a variety of political, economic, and cultural factors. It was a pivotal moment in European history that marked the end of centuries of division and conflict, and it laid the foundations for a new era of unity and prosperity.