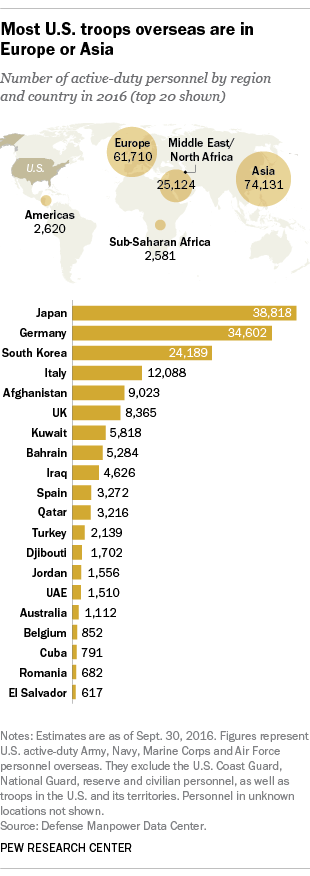
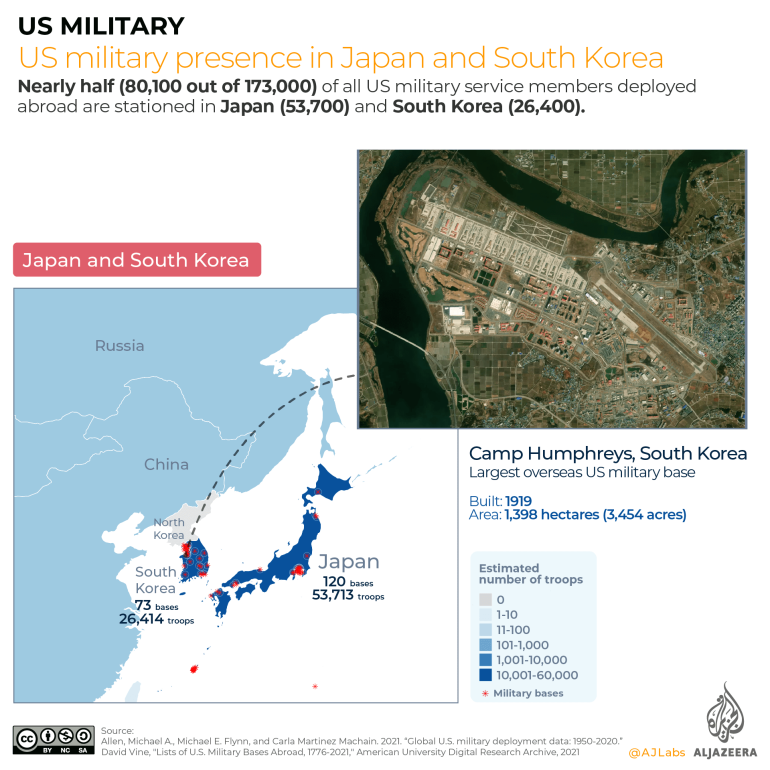
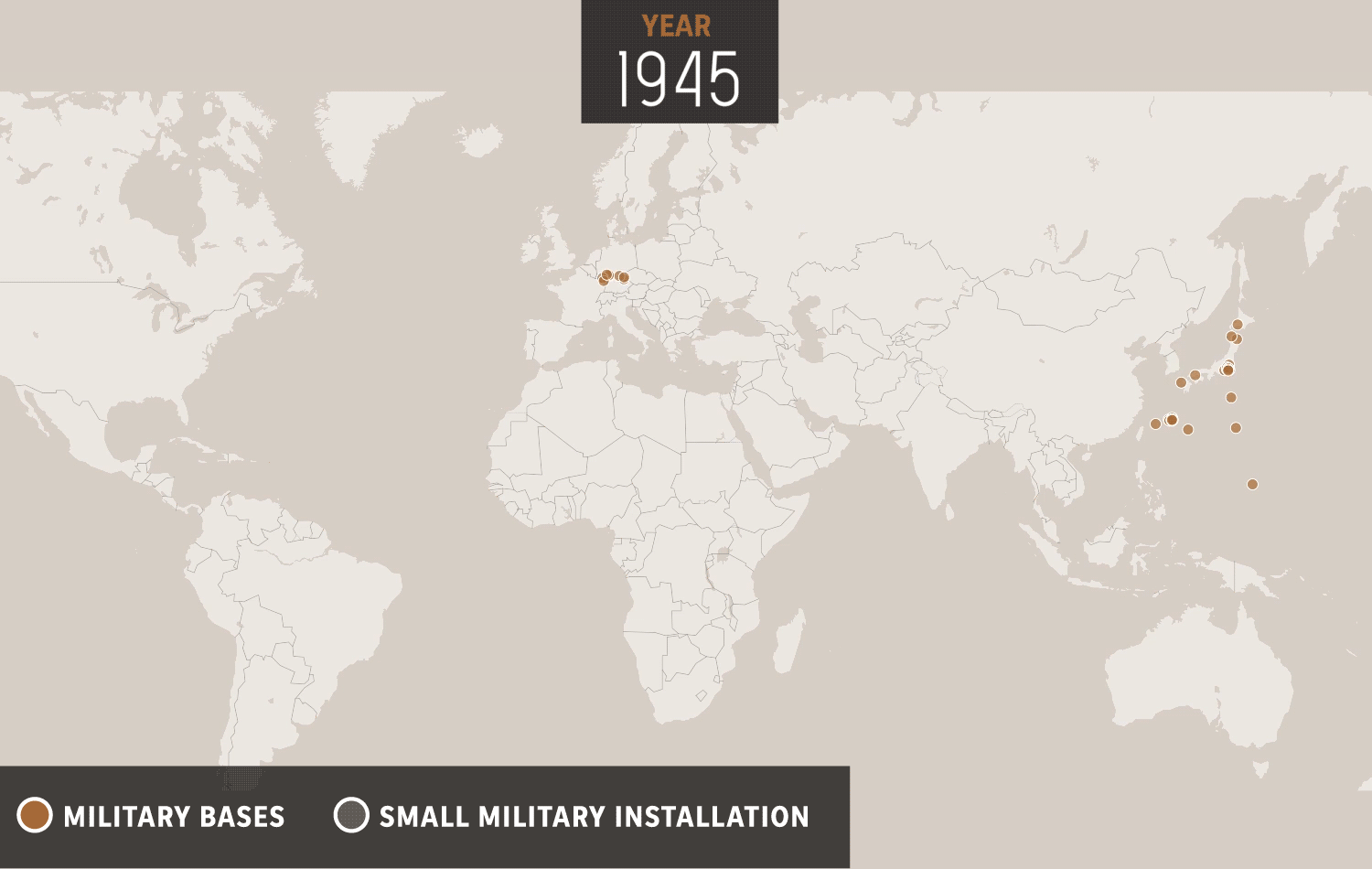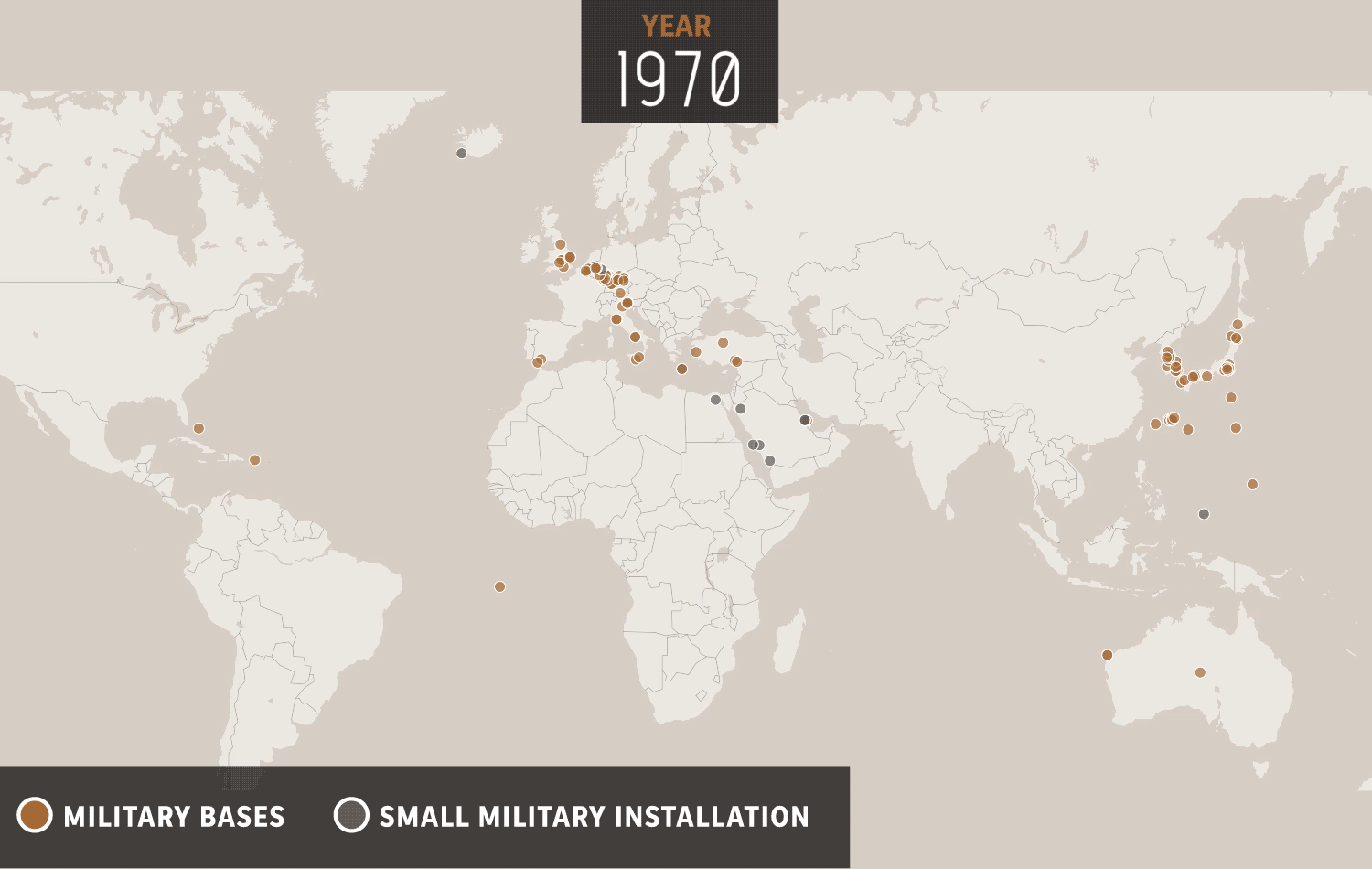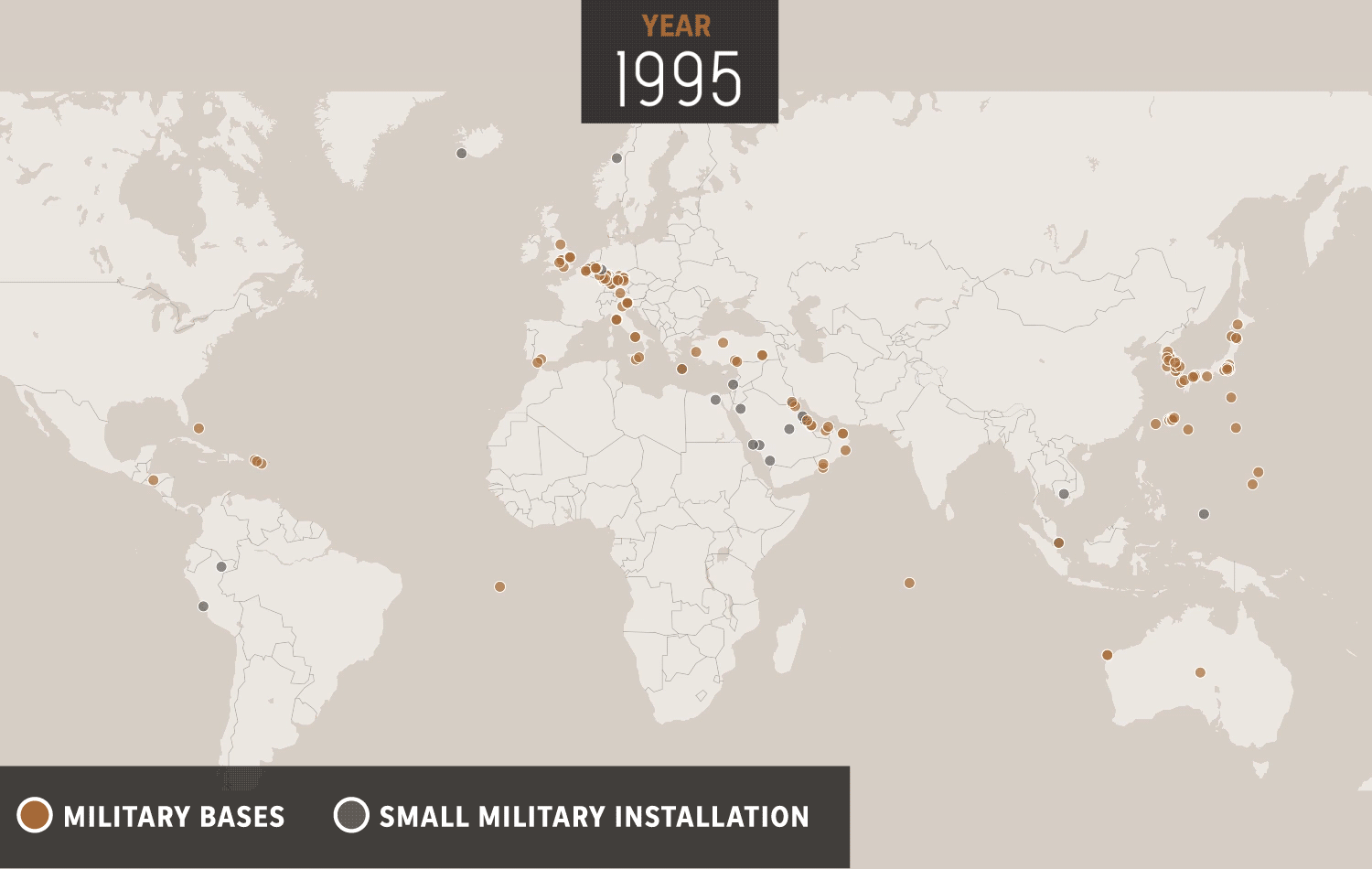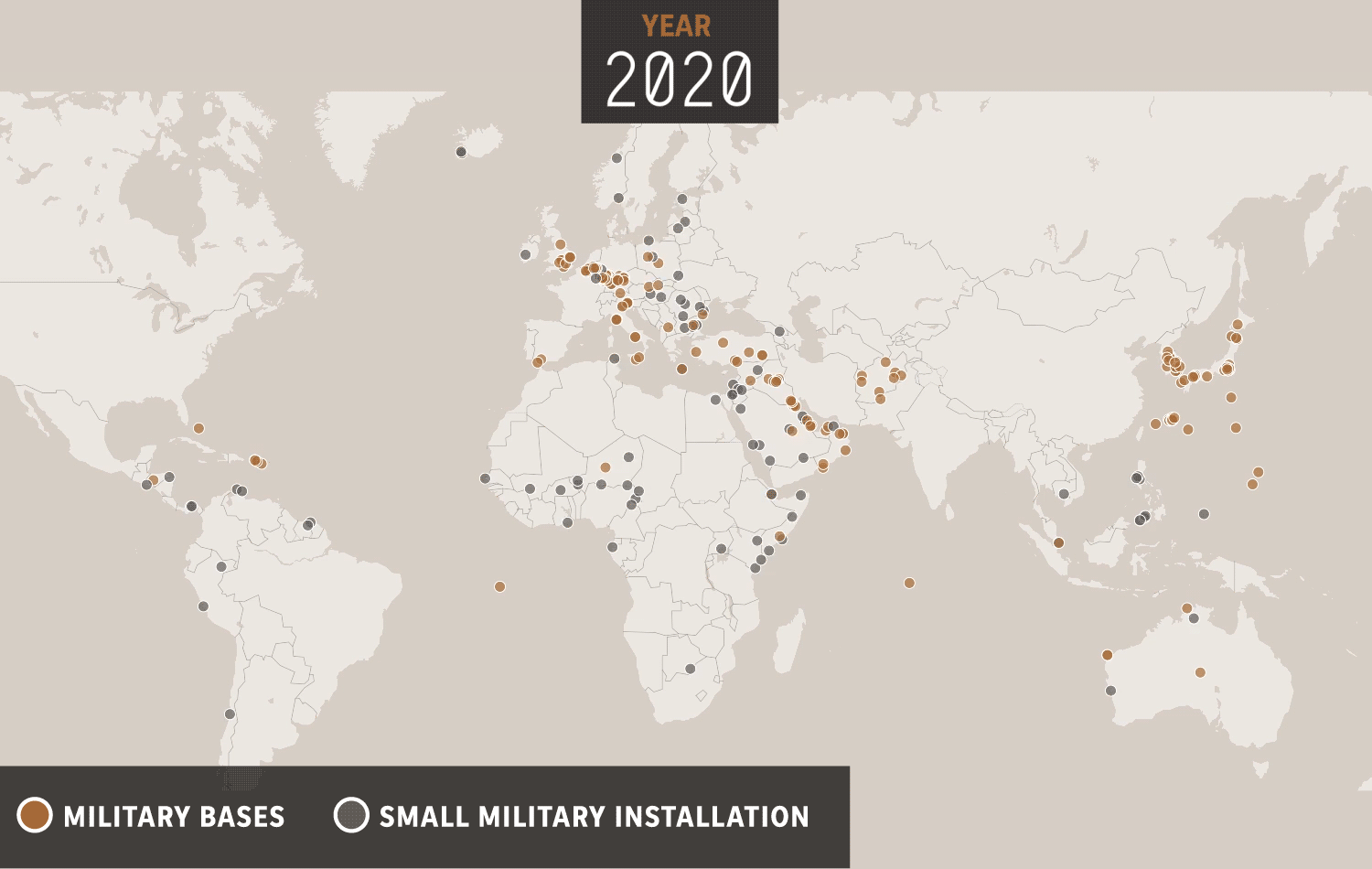
The United States has a long history of military operations overseas, dating back to the country's founding. Throughout its history, the US has deployed its military to various locations around the world for a variety of reasons, including to protect national interests, to defend allies and partners, and to promote peace and stability. These military operations have often been controversial and have had significant consequences for both the US and the countries where they have taken place. In this essay, we will examine the history of US overseas military operations, the reasons behind them, and the impact they have had.
One of the earliest examples of US military intervention overseas was the Spanish-American War in 1898. This conflict, which arose from tensions between the US and Spain over the latter's colonial holdings in the Caribbean and Pacific, resulted in the US acquiring several territories, including Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines. The US then established military bases in these territories, which it used as launching points for further military interventions in the region.
Throughout the 20th century, the US military engaged in numerous overseas operations, often in the context of the Cold War. For example, the US intervened in Korea in 1950 to defend South Korea from an invasion by communist North Korea, and later fought in Vietnam to prevent the spread of communism in Southeast Asia. These conflicts were costly in terms of both lives and resources, and they had lasting effects on US foreign policy and public opinion.
In the post-Cold War era, the US has continued to engage in military operations overseas, often in the context of the "war on terror." This has included deployments to Afghanistan, Iraq, and other countries in the Middle East and North Africa. These operations have been controversial, with some arguing that they were necessary to protect national security, while others have criticized them as costly and ineffective.
One of the main reasons behind US military operations overseas is the protection of national interests. This can include economic interests, such as access to natural resources or strategic trade routes, as well as more abstract interests, such as the promotion of democratic values and the defense of allies. In some cases, the US has also intervened militarily to prevent or respond to humanitarian crises, such as genocide or mass atrocities.
Another reason for US military operations overseas is the defense of allies and partners. The US has a network of international alliances, including NATO and other regional organizations, which it uses to coordinate its security efforts and to provide a defense umbrella for its partners. When an ally or partner is threatened, the US may choose to intervene militarily to provide support and protection.
Finally, the US has often intervened militarily in an attempt to promote peace and stability in regions of the world that are beset by conflict or crisis. This can include efforts to prevent the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction, to counter terrorism and extremism, or to stabilize failed states.
The impact of US military operations overseas has been significant, both for the US and for the countries where they have taken place. On the one hand, military intervention can help to protect national interests, defend allies, and promote peace and stability. On the other hand, it can also have unintended consequences, such as creating new enemies, destabilizing governments, and damaging the economy. In addition, military operations can be costly in terms of lives and resources, and they can have a negative impact on public opinion and political support.
Overall, US military operations overseas have played a significant role in shaping the country's foreign policy and its relationships with other nations. While they can have positive effects, they also carry risks and costs, and as such, they should be carefully considered and executed.