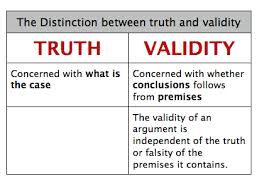
In philosophy, an argument is a series of statements (called premises) that are presented in support of a conclusion. A valid argument is one in which the conclusion follows logically from the premises, meaning that if the premises are true, the conclusion must also be true.
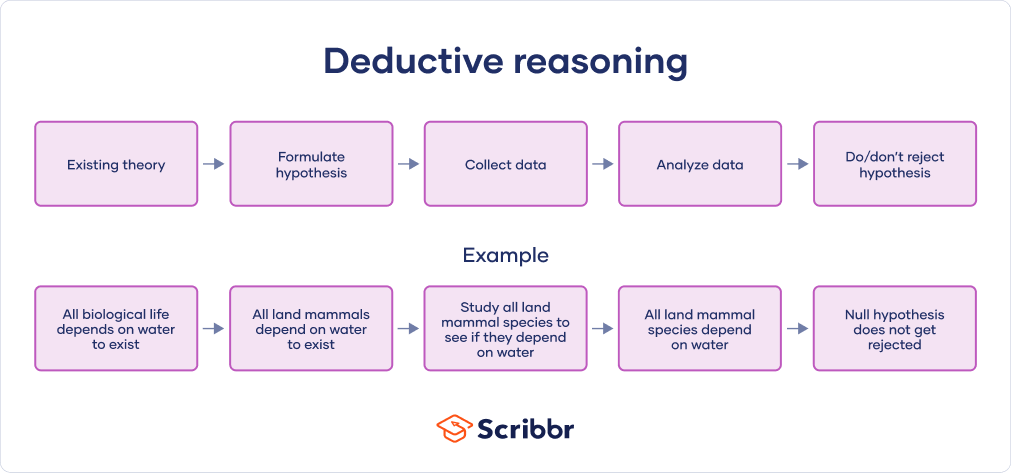
There are different types of valid arguments, including deductive and inductive arguments. A deductive argument is one in which the conclusion is necessarily true given the premises, whereas an inductive argument is one in which the conclusion is likely to be true based on the evidence provided.
To be considered a valid argument, the premises of the argument must be logically consistent with one another and the conclusion must follow logically from the premises. This means that there can be no logical contradictions within the argument and that the conclusion must be a logical consequence of the premises.
For example, consider the following argument:
Premise 1: All dogs are mammals. Premise 2: Fido is a dog. Conclusion: Therefore, Fido is a mammal.
In this argument, the premises are logically consistent with one another and the conclusion follows logically from the premises. Therefore, this is a valid argument.
On the other hand, consider the following argument:
Premise 1: All dogs are mammals. Premise 2: Fido is a mammal. Conclusion: Therefore, Fido is a dog.
In this argument, the conclusion does not follow logically from the premises. The fact that Fido is a mammal does not necessarily mean that he is a dog, as there are other types of mammals besides dogs. Therefore, this argument is not valid.
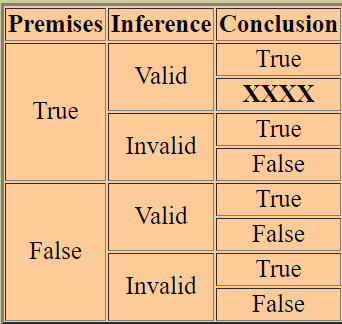
It is important to note that a valid argument does not necessarily mean that the conclusion is true. For example, consider the following argument:
Premise 1: All cows are green. Premise 2: Bessie is a cow. Conclusion: Therefore, Bessie is green.
Even though the conclusion follows logically from the premises, the first premise is false, which means that the conclusion is also false. Therefore, this argument is valid but not sound, meaning that it is logically valid but the premises are not all true.
In summary, a valid argument is one in which the conclusion follows logically from the premises and there are no logical contradictions within the argument. It is important to evaluate the validity of an argument, as it helps determine whether the conclusion is likely to be true based on the evidence provided. However, it is also important to consider the truth of the premises in order to determine whether the argument is sound.