Cells are the basic unit of life and are found in all living organisms. They are the smallest functional unit of an organism, and they perform a variety of functions necessary for the survival and maintenance of the organism. To carry out these functions, cells contain various organelles, which are specialized structures that perform specific tasks within the cell.
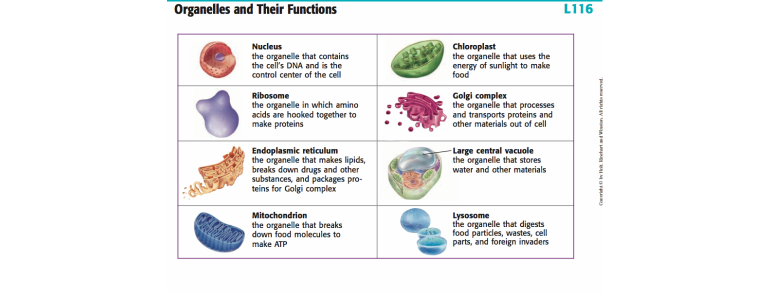
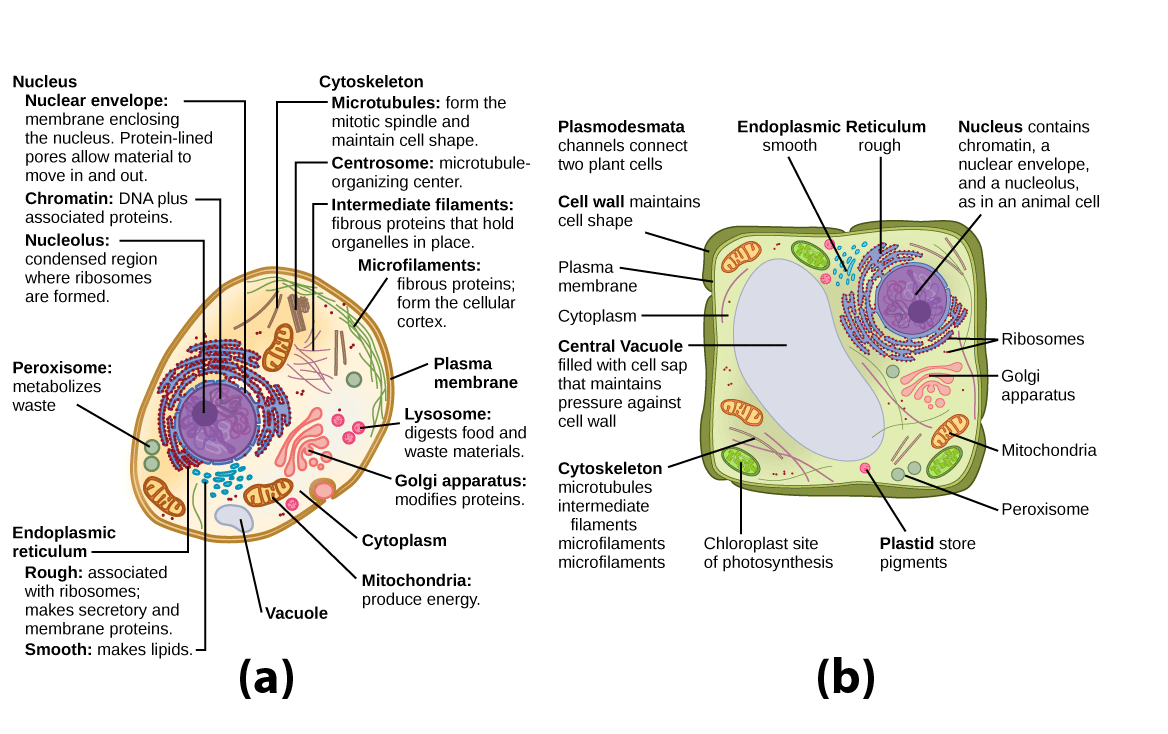
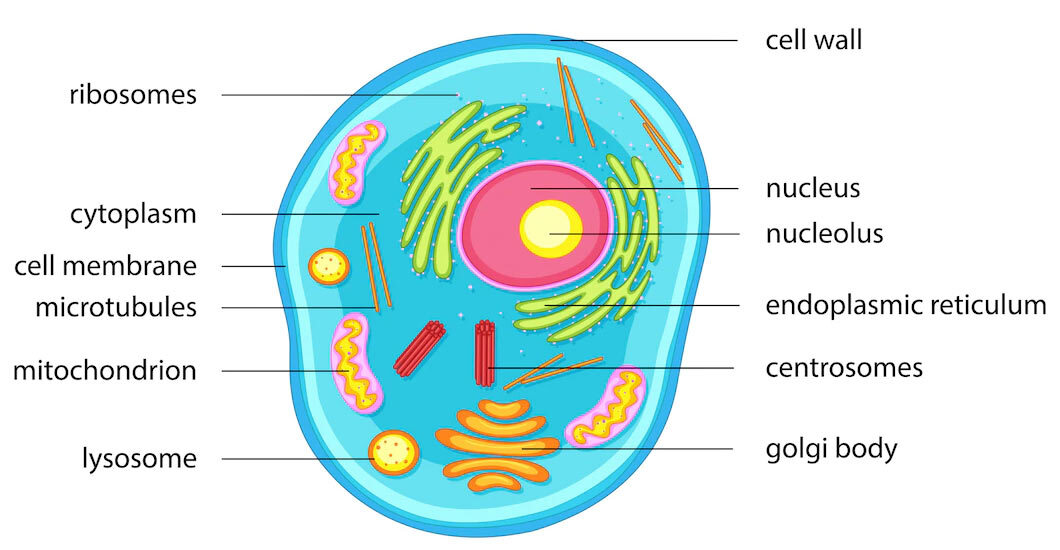
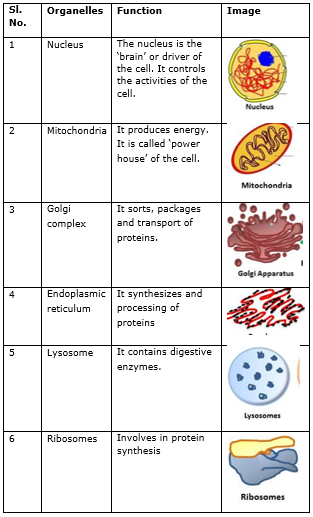
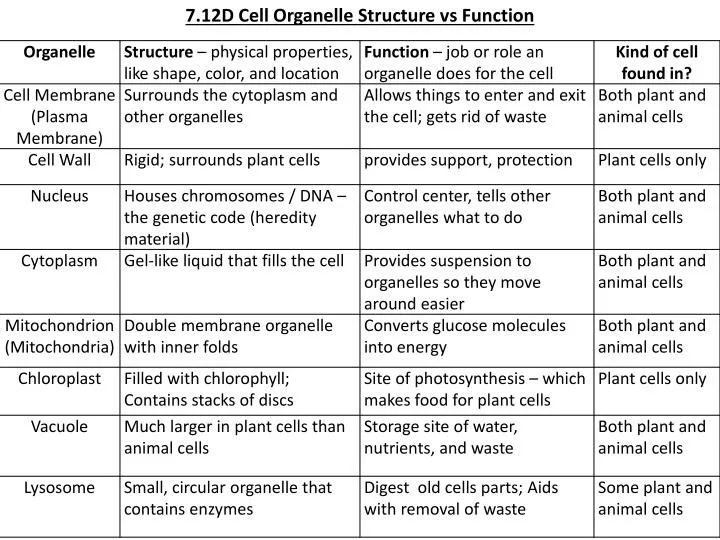
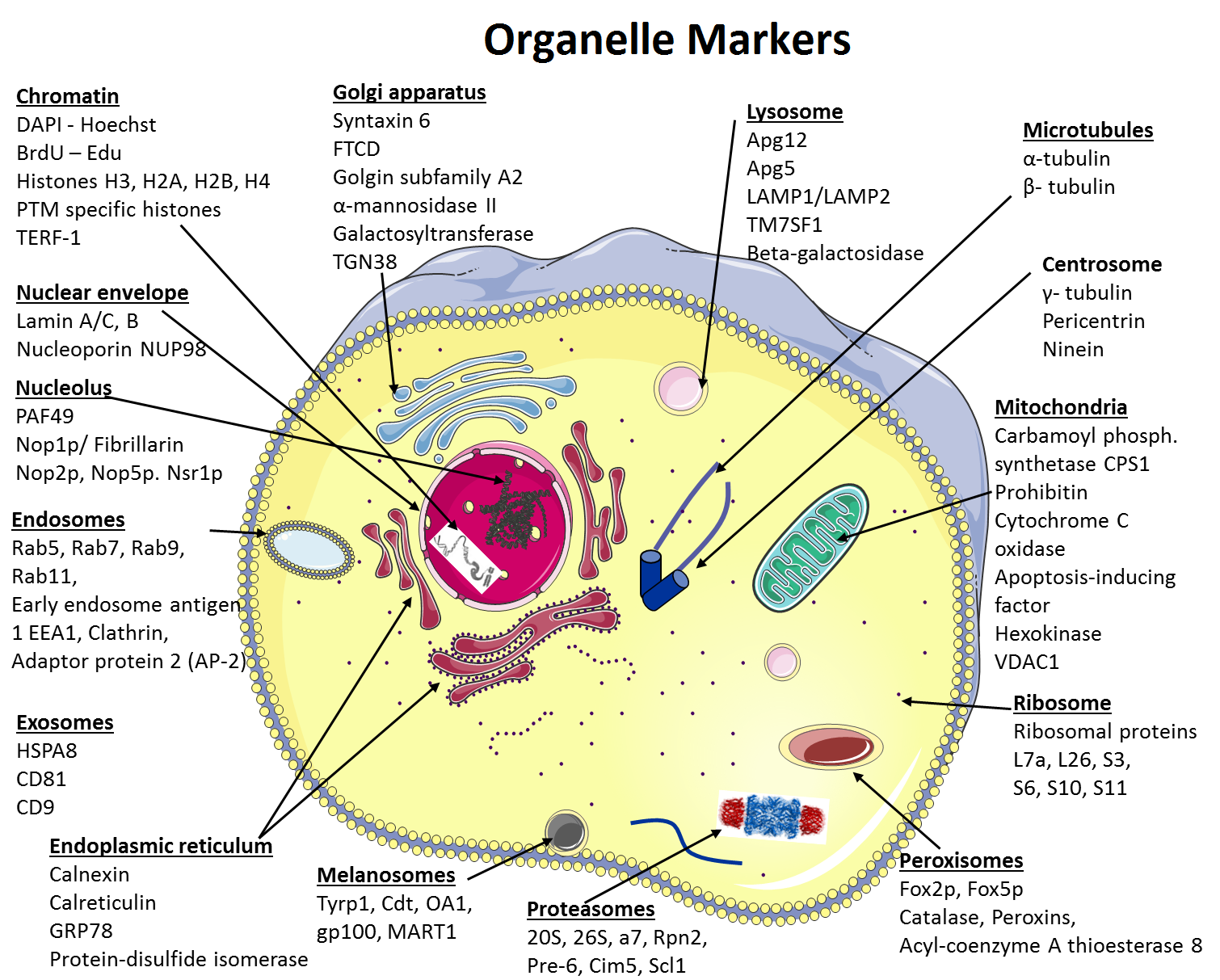
One of the most important organelles in the cell is the nucleus. The nucleus is the control center of the cell and is responsible for storing and processing genetic information. It contains the cell's DNA, which is the genetic material that carries the instructions for the cell's functions and traits. The nucleus is also responsible for producing proteins, which are essential for the structure and function of the cell.
Another important organelle in the cell is the mitochondrion. The mitochondrion is responsible for producing energy for the cell through a process called cellular respiration. It converts the energy stored in food into a form that the cell can use to carry out its functions.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi apparatus are two organelles that are involved in the synthesis and transport of proteins and lipids within the cell. The ER is a network of flattened sacs and tubes that is responsible for the synthesis and modification of proteins and lipids. The Golgi apparatus, on the other hand, is responsible for sorting and distributing these molecules to their final destination within the cell or to other cells.
Lysosomes are small, spherical organelles that contain enzymes that can break down waste materials and cellular debris. They help to keep the cell clean and free of unnecessary materials.
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell and separates the inside of the cell from the outside environment. It is made up of a phospholipid bilayer and serves as a selective barrier, allowing certain substances to enter or leave the cell while preventing others from passing through.
Plants also have special organelles called chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. Chloroplasts contain pigments called chlorophyll, which absorbs sunlight and converts it into chemical energy.
In summary, cells are complex structures that contain various organelles, each with its own specialized function. The nucleus, mitochondrion, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, cell membrane, and chloroplasts are just a few examples of the many organelles found in cells, and together they work to maintain the health and function of the cell.