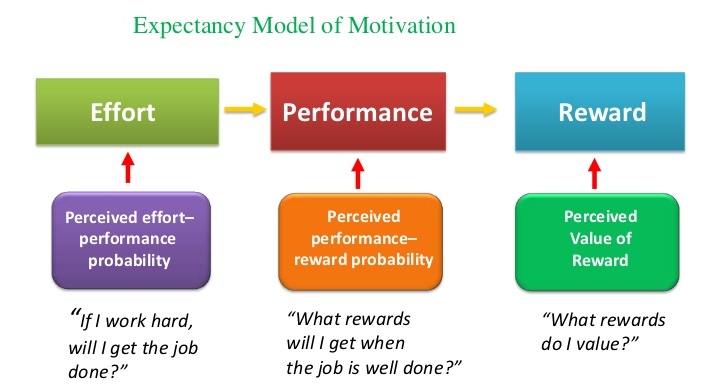
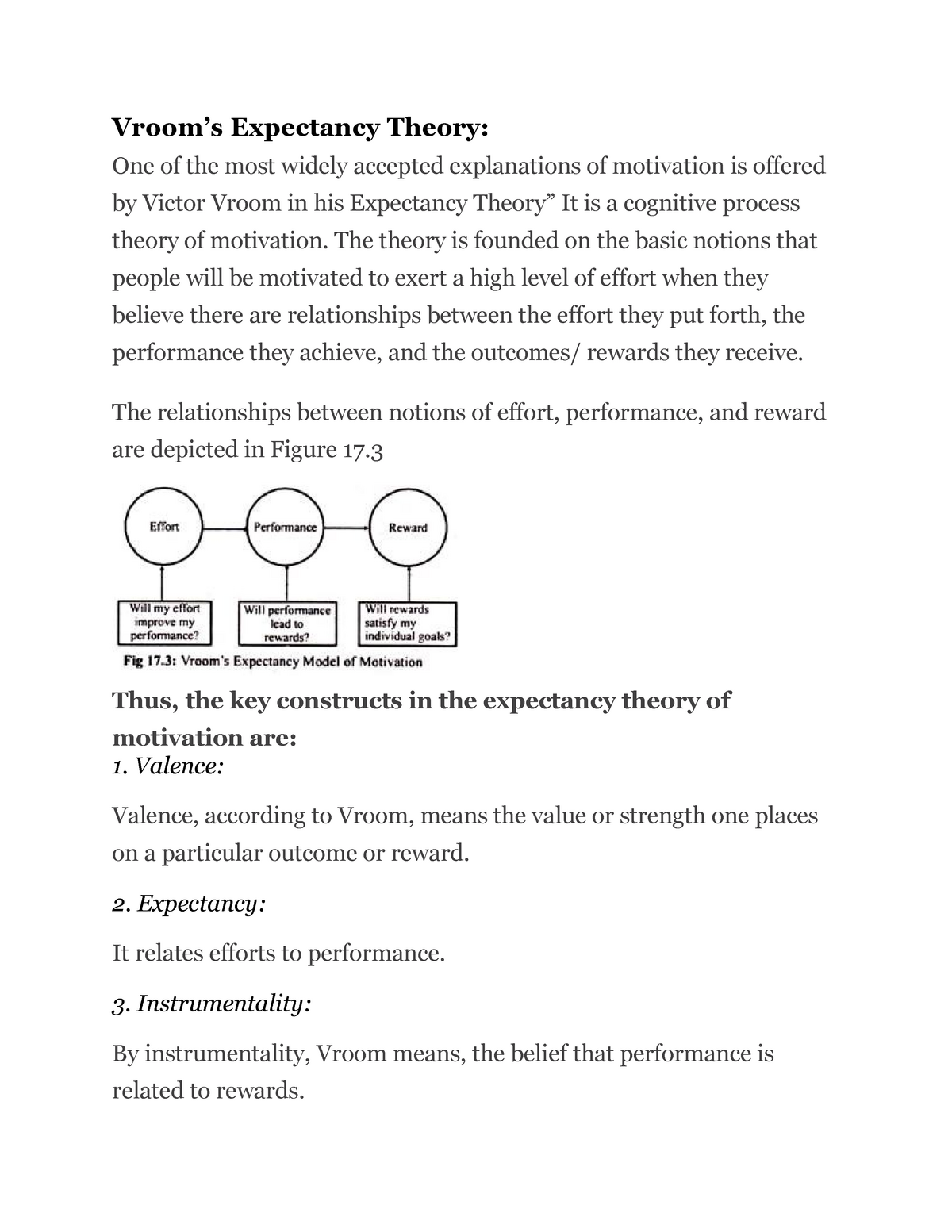
The Vroom motivation theory, also known as the Vroom Expectancy theory, is a model that explains how individuals make decisions about how much effort to exert in a particular task or situation. According to this theory, an individual's motivation to perform a task is determined by three factors: valence, instrumentality, and expectancy.
Valence refers to the value or importance that an individual attaches to a particular outcome. For example, if an individual values a promotion or pay increase highly, they will be more motivated to put in the effort to achieve it. On the other hand, if an individual does not value the outcome, they will be less motivated to put in the effort.
Instrumentality refers to the belief that effort will lead to the desired outcome. For example, if an individual believes that putting in a lot of effort will lead to a promotion, they will be more motivated to put in the effort. On the other hand, if an individual does not believe that their effort will lead to the desired outcome, they will be less motivated.
Expectancy refers to the belief that one has the necessary skills and abilities to successfully complete the task. If an individual believes that they have the necessary skills and abilities, they will be more motivated to put in the effort. On the other hand, if an individual does not believe that they have the necessary skills and abilities, they will be less motivated.
The Vroom motivation theory suggests that an individual's motivation to perform a task is determined by the combination of these three factors. If an individual values the outcome highly, believes that their effort will lead to the desired outcome, and believes that they have the necessary skills and abilities, they will be highly motivated to put in the effort. On the other hand, if any of these factors are low, the individual will be less motivated.
The Vroom motivation theory has been widely accepted and applied in a variety of settings, including the workplace and education. It provides a useful framework for understanding and predicting motivation, and for identifying ways to increase motivation in individuals or groups. For example, organizations can use the Vroom motivation theory to identify ways to increase the valence or instrumentality of a task for employees, or to provide the necessary skills and resources to increase expectancy. Similarly, educators can use the theory to design tasks and assessments that increase the valence, instrumentality, and expectancy of students.
Overall, the Vroom motivation theory is a valuable tool for understanding and predicting motivation, and for identifying ways to increase motivation in individuals and groups. It provides a useful framework for understanding how individuals make decisions about how much effort to exert in a particular task or situation, and how to increase motivation in those situations.