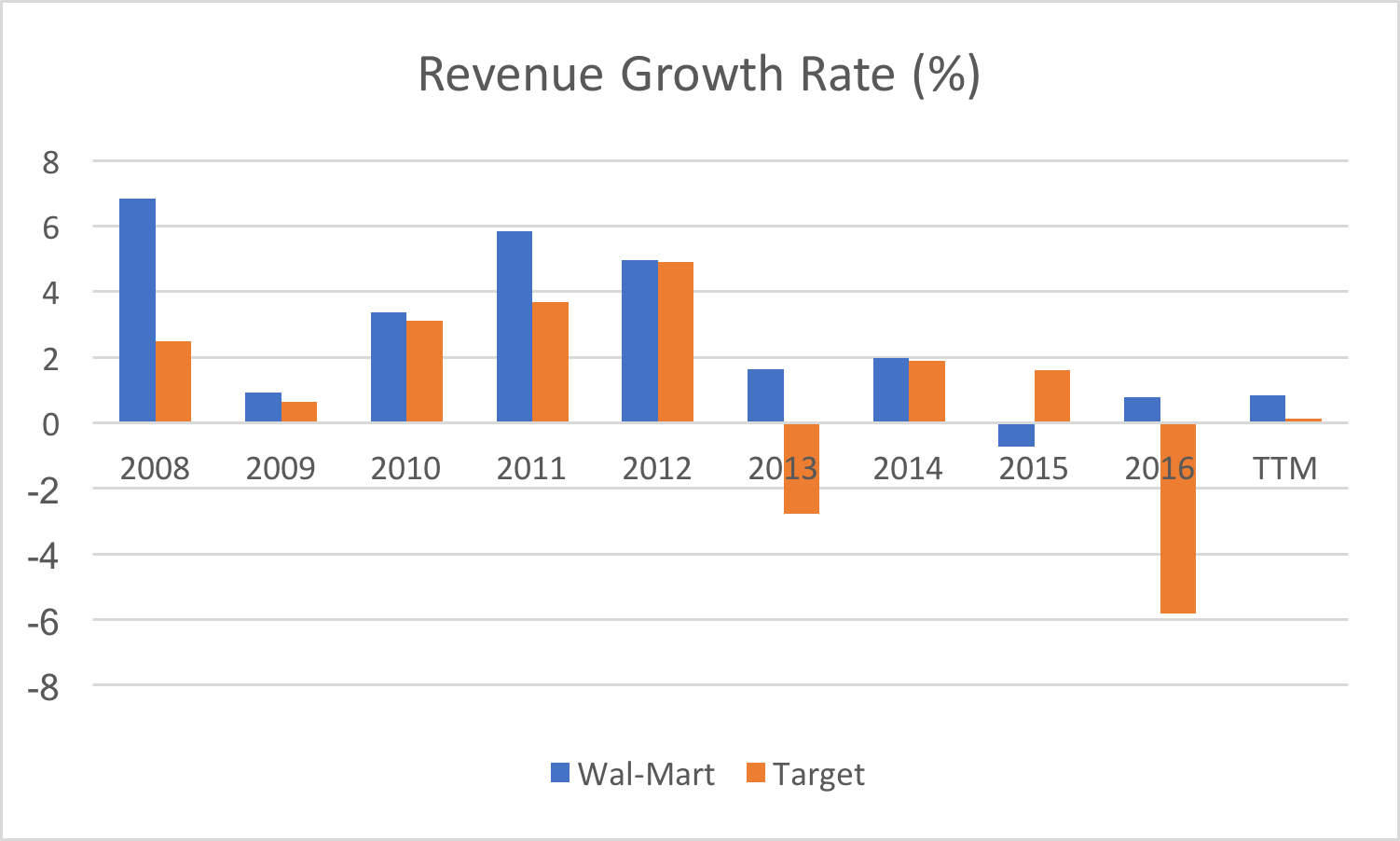
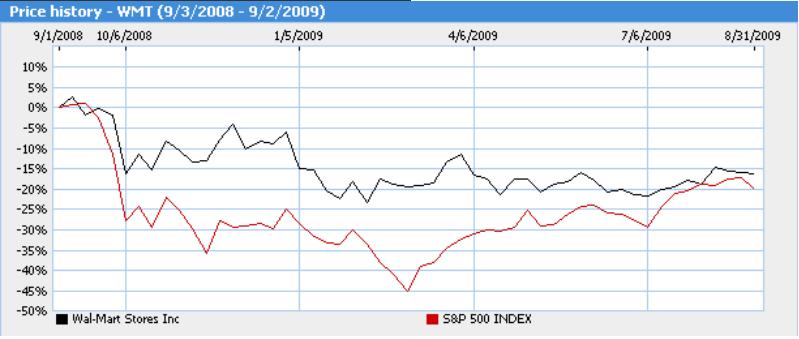
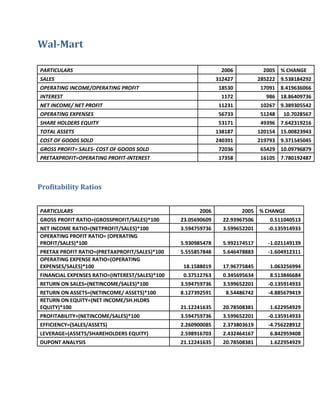
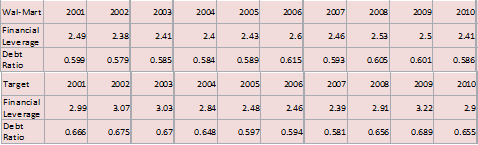
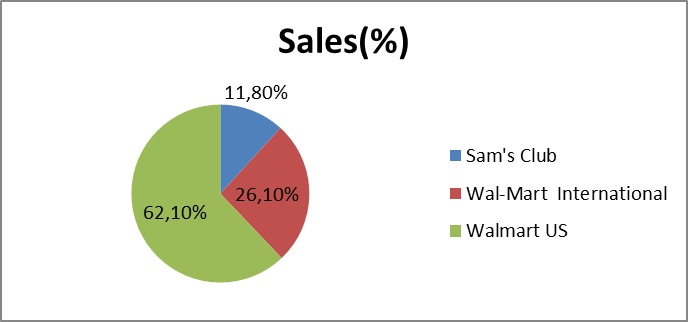
Ratio analysis is a tool used by investors and analysts to evaluate a company's financial health and performance. It involves taking financial data from a company's financial statements and calculating various ratios to get a better understanding of how the company is performing and how it compares to its peers. One company that has been the subject of much ratio analysis is Walmart, the world's largest retailer.
One of the key ratios used in evaluating a company's financial performance is the debt-to-equity ratio. This ratio measures the amount of debt the company has relative to the amount of equity it has. A high debt-to-equity ratio indicates that the company is heavily reliant on borrowing to finance its operations, while a low debt-to-equity ratio suggests that the company is funded primarily through equity, such as shareholder investments.
As of 2021, Walmart had a debt-to-equity ratio of 0.46, which is relatively low compared to the industry average of 0.70. This suggests that the company has a strong balance sheet and is not overly reliant on borrowing to finance its operations. However, it is worth noting that Walmart's debt-to-equity ratio has been steadily increasing in recent years, which could be a cause for concern for investors.
Another important ratio for evaluating a company's financial health is the return on equity (ROE). This ratio measures the amount of profit the company generates for each dollar of shareholder equity. A high ROE indicates that the company is able to generate a lot of profit from its shareholder investments, while a low ROE suggests that the company is not using its equity effectively.
Walmart has a fairly high ROE of 23.5%, which is above the industry average of 17.5%. This suggests that the company is able to generate a good amount of profit from its shareholder investments. However, it is worth noting that Walmart's ROE has been declining in recent years, which could be a cause for concern for investors.
In addition to the debt-to-equity ratio and ROE, there are many other ratios that can be used to evaluate a company's financial performance. For example, the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio measures the relationship between a company's stock price and its earnings per share. A high P/E ratio indicates that the market is willing to pay a premium for the company's earnings, while a low P/E ratio suggests that the market is not willing to pay as much for the company's earnings.
As of 2021, Walmart had a P/E ratio of 21.5, which is relatively high compared to the industry average of 18.5. This suggests that the market is willing to pay a premium for Walmart's earnings. However, it is worth noting that Walmart's P/E ratio has been steadily declining in recent years, which could be a cause for concern for investors.
In conclusion, ratio analysis is a useful tool for evaluating a company's financial performance. While Walmart has a relatively low debt-to-equity ratio and a high ROE, it is worth noting that both of these ratios have been declining in recent years, which could be a cause for concern for investors. Additionally, Walmart's P/E ratio is relatively high, but it too has been declining in recent years. Overall, it is important for investors to carefully consider a company's financial ratios when evaluating its performance and potential for investment.