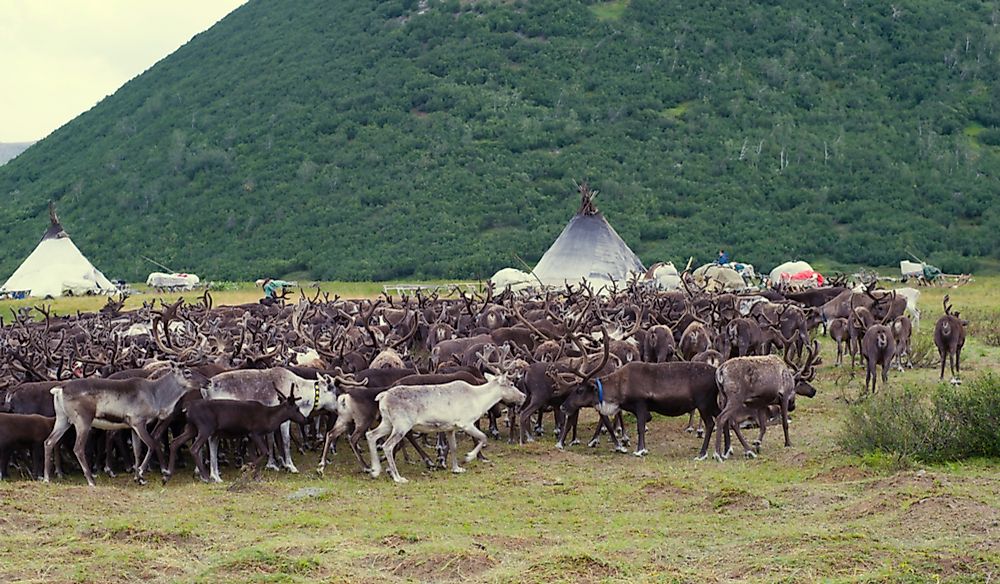
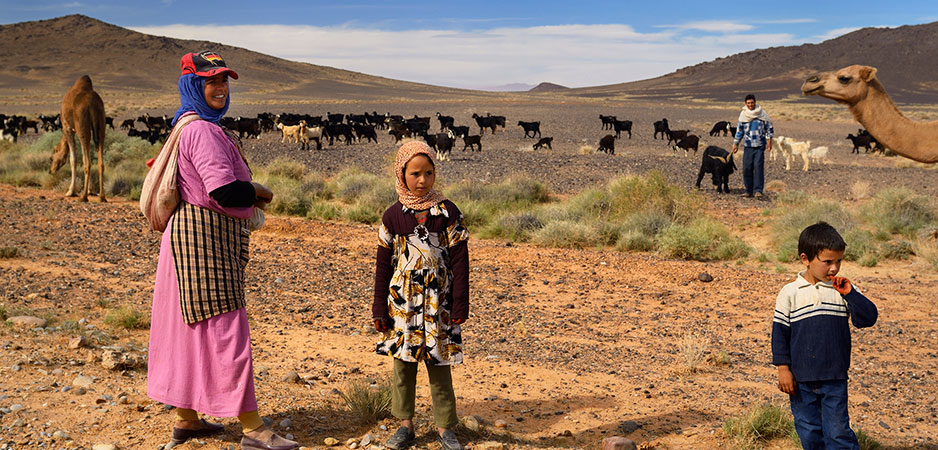
A pastoral society is a type of society that relies on the raising of livestock for their livelihood. Pastoral societies are found in many different parts of the world, and they have a long and varied history. In this essay, we will explore what it means to be a pastoral society, including the key characteristics and features that define this type of society, as well as the challenges and opportunities that they face.
One of the most distinctive features of pastoral societies is their reliance on livestock as a primary source of food, clothing, and other resources. Pastoral societies often live in areas where agriculture is not possible, such as deserts or grasslands, and they rely on their animals to provide them with the necessities of life. This can include milk, meat, and wool, as well as leather and other materials used for clothing and shelter.
Pastoral societies also tend to be mobile, as they must follow their herds in search of pasture and water. This means that they often live in tents or other portable shelters, and they may need to travel long distances to find the resources that they need. In some cases, pastoral societies may also trade with other communities, either for goods or services.
Another key characteristic of pastoral societies is the way in which they are organized. These societies tend to be hierarchical, with a leader or group of leaders who make decisions on behalf of the community. This can be a tribal leader, a council of elders, or some other form of authority. Pastoral societies may also have a system of inheritance, where leadership and other privileges are passed down through the family.
Despite the many challenges that pastoral societies face, they also have many strengths. For example, they tend to have a strong sense of community and a deep connection to the land. Pastoral societies also often have a rich cultural heritage, with their own traditions, rituals, and ways of life. In many cases, these societies have been able to adapt to changing circumstances and continue to thrive in the face of adversity.
In conclusion, pastoral societies are a type of society that relies on the raising of livestock for their livelihood. They are characterized by their reliance on animals, their mobility, and their hierarchical organization. While pastoral societies face many challenges, they also have many strengths, including a strong sense of community and a rich cultural heritage.