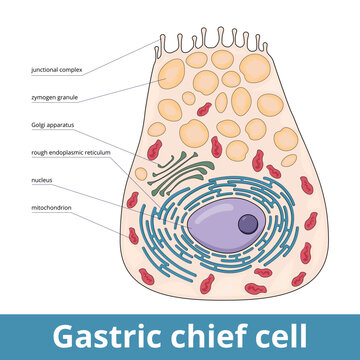
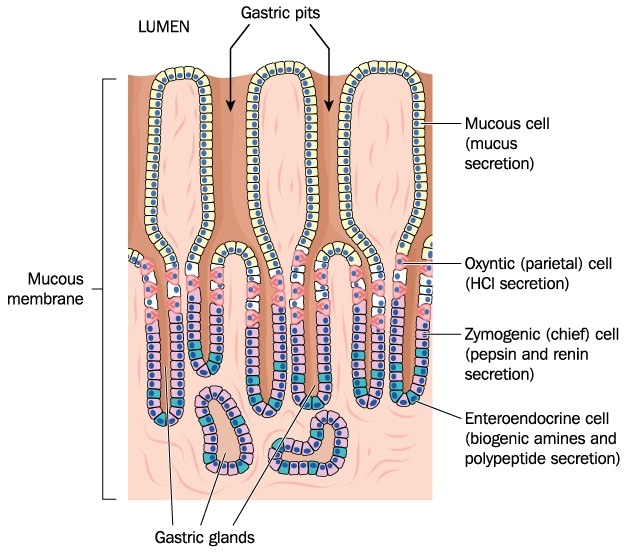
A gastric gland is a specialized structure found in the lining of the stomach that produces and secretes various substances necessary for digestion. These glands are located throughout the stomach, and they are responsible for producing mucus, hydrochloric acid, and several digestive enzymes.
Mucus is a thick, slippery substance produced by the gastric glands that helps to protect the lining of the stomach from the corrosive effects of hydrochloric acid. Hydrochloric acid is a strong acid produced by the parietal cells, which are specialized cells found within the gastric glands. Hydrochloric acid helps to break down food in the stomach and kill any harmful bacteria that may be present.
In addition to mucus and hydrochloric acid, the gastric glands also produce several enzymes that aid in the digestion of food. These enzymes include pepsin, which breaks down proteins, and lipase, which breaks down fats.
The production and secretion of these substances by the gastric glands is regulated by hormones and neural signals from the brain. For example, the hormone gastrin stimulates the production of hydrochloric acid and pepsin, while the hormone somatostatin inhibits their production.
Gastric glands are essential for proper digestion and the overall health of the digestive system. Dysfunction of the gastric glands can lead to a variety of digestive disorders, such as ulcers, gastritis, and even stomach cancer. Therefore, it is important to maintain a healthy diet and lifestyle to keep the gastric glands functioning properly.