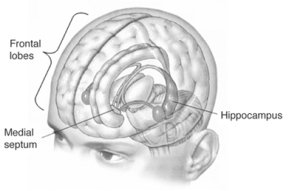
Amnesia is a type of memory loss that can occur due to various reasons, such as brain injury, psychological trauma, or disease. It can affect different types of memory, including short-term memory, long-term memory, or both. Amnesia can have a significant impact on a person's daily life and their ability to function normally.
There are two main types of amnesia: retrograde amnesia and anterograde amnesia. Retrograde amnesia is the inability to recall events that occurred before the onset of amnesia. This type of amnesia is often associated with brain injury or trauma. Anterograde amnesia, on the other hand, is the inability to form new memories. This type of amnesia is often associated with brain damage, such as from a stroke or a concussion, or with certain medications or substance abuse.
Amnesia can also be classified based on the duration of memory loss. For example, transient global amnesia is a temporary form of amnesia that usually lasts for a few hours or days and is often associated with stress or physical exertion. Dissociative amnesia, on the other hand, is a type of amnesia that occurs as a result of psychological trauma and can last for a longer period of time.
The treatment of amnesia depends on the underlying cause. For example, if amnesia is caused by a brain injury, treatment may involve medications to reduce swelling or surgery to repair the damage. If amnesia is caused by psychological trauma, treatment may involve therapy to address the underlying emotional issues. In some cases, amnesia may resolve on its own, while in other cases, it may be permanent.
In conclusion, amnesia is a type of memory loss that can have a significant impact on a person's daily life and their ability to function normally. It can be caused by various factors, such as brain injury, psychological trauma, or disease, and can be classified based on the type and duration of memory loss. The treatment of amnesia depends on the underlying cause and may involve medications, surgery, or therapy.