An audit risk model is a framework that is used by auditors to assess the likelihood of material misstatements in a company's financial statements. The purpose of the audit risk model is to identify and evaluate the various risks that may affect the accuracy and reliability of the financial statements, so that the auditor can take appropriate steps to reduce these risks to an acceptable level.
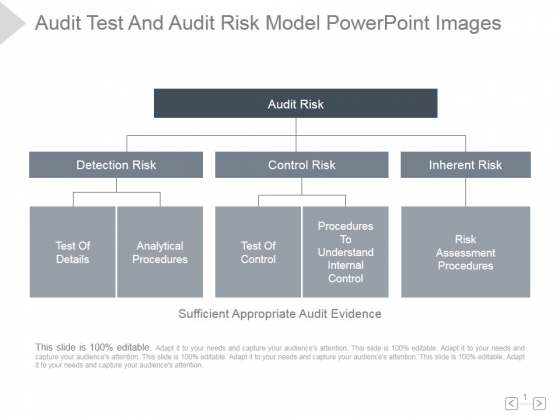
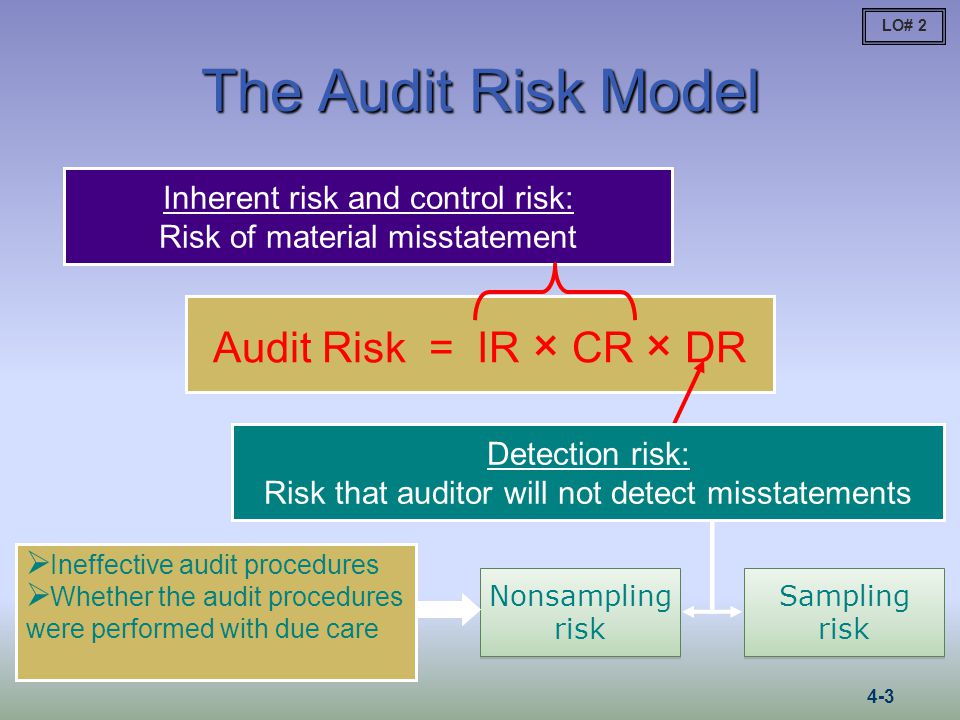
There are several key components to an audit risk model, including the assessment of inherent risk, control risk, and detection risk. Inherent risk is the risk that material misstatements may occur due to the nature of the company and its operations. Control risk is the risk that the company's internal controls may be insufficient to prevent or detect material misstatements. Detection risk is the risk that the auditor will not be able to detect material misstatements, even if they do exist.
The audit risk model is used to guide the auditor's testing procedures and to determine the extent of evidence that needs to be gathered in order to provide reasonable assurance that the financial statements are free of material misstatements. The audit risk model is an important tool for the auditor, as it helps to ensure that the audit is conducted in a systematic and consistent manner, and that the auditor's conclusions are based on a sufficient level of evidence.
There are several factors that can affect the audit risk model, including the complexity of the company's operations, the size and scope of the audit, and the inherent risk and control risk associated with the company. The auditor must consider all of these factors when developing the audit risk model, and must adjust the audit procedures as needed to ensure that the audit is conducted effectively and efficiently.
In conclusion, the audit risk model is a crucial tool for auditors as it helps them to identify and evaluate the various risks that may affect the accuracy and reliability of a company's financial statements. By using the audit risk model, auditors can take appropriate steps to reduce these risks to an acceptable level, and can provide reasonable assurance that the financial statements are free of material misstatements.
What Is An Audit Risk Model? (With Definition And Example)
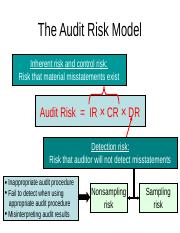
For more information and knowledge on this topic keep on visiting auditorforum. Nonetheless, the equation is a useful way to conceptualize how an audit program should be constructed to collect a sufficient amount of appropriate audit evidence. This particular model suggests that the total risk that exists over the course of the audit is a factor of three risks, inherent risk, control risk, as well as detection risk. What are the elements of the Audit Risk Model? Audit firm generally are insured against audit risk and potential legal liabilities. This risk is inherent in the accounting system and manifests itself through the quality of accounting information. In the case where an organization does not have sufficient internal controls present, it substantially increases the work of the auditors. In the case where existing audit evidence cannot be solely relied on to extrapolate the audit outcome, it is better to gather more evidence so that the risk is minimized.
What is Audit Risk Model its Significance and Documentation

Using this model, the auditing team determines which procedures to use for the transactions and accounts in the financial statements of a company. Your Audit Model helps you to identify weaknesses Above all else, an Audit Model is about how you keep a track of these processes. See also 16 Types of Audit You Should Know - Explained Types of Audit Risk There are three main types of audit risks that are involved during a typical audit process. Therefore, this risk is often higher in the cases where the company does not have sufficient internal controls present. How do you break down the Audit Risk Model? The audits were thus being carried out on the wrong numbers and no one knew until it was too late to do anything about it. How to Minimise Audit Risk? Once an auditor knows the inherent and control risks of your business, they can go on to calculate the detection risk—which is the risk of not detecting a misstatement. The auditors, as well as the accountants in the company are well aware of the materiality threshold.
Audit Risk
Auditors use audit procedures to inspect the financial statements about material misstatements. During an audit process, an audit firm examines financial transactions happened during the reporting year, enquires and substantiate the general ledgers, check internal controls and other factors and then provide their opinion as to whether thefinancial statements are free from misstatements due to error or fraud or not. To be on the safe side, auditors include the maximum allowable amounts or norms of materiality and risk in the audit agreement. This results in a high level of inherent risk because of numerous related entities that could cause misinterpretation of its financial statements. An auditor issues a report about the accuracy and reliability of financial statements based on the country's local operating laws.
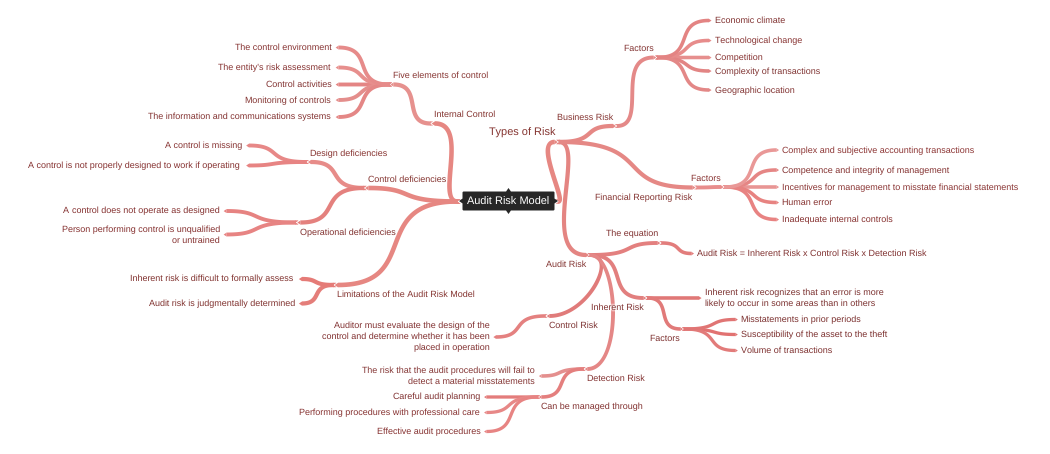
The Components of the Audit Risk Model

Detection risk is the risk that the auditors will unintentionally not discover major problems and create a report which paints a good picture of the company. And instead of sending out dozens of individual e-mail reminders, you have a powerful reminder system that automatically sends out regular reminders and even escalates notifications on your behalf. Therefore, it is fundamentally important for an auditor to reduce these audit risks to an acceptable level. For example, there is inherent risk of misstatement in estimates because they involve judgement. No More Bookkeeping Stress Keeping proper financial records is time-intensive and small mistakes can be costly. The control risk is initially assessed to be 50%, while the inherent risk is assessed at 90%. Management, investors, shareholders, financiers, government, and regulatory agencies rely on financial reports for decision-making.
Why do auditors use the audit risk model when planning an audit explain the audit risk model in short?
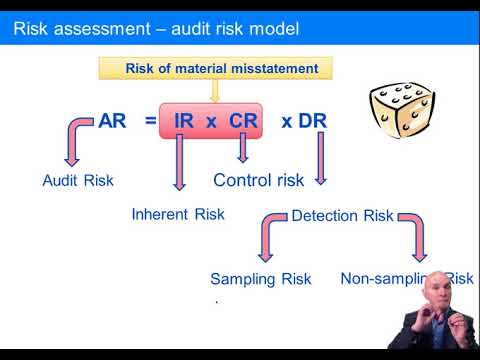
Consequently, the auditor is expected to focus resources on those areas most likely to contain risks of material misstatement, which means that reduced resources are targeted at other areas of an audit. How do you identify audit risk? If the auditor is issuing an unmodified opinion, it is crucial that there are no significant errors or other issues that were missed for one reason or another. Related: Governance, Risk And Compliance Tools With Benefits Detection risk Detection risk DR refers to the risk of the auditors failing to detect a material misstatement in the financial statements. Auditors can reduce audit risk by increasing the number of audit procedures. Related: 10 Types Of Risks In Finance And Tips For Mitigating Impact Risks Included In An Audit Risk Model This model considers the following risks in each audit cycle: Inherent risk A company's inherent risk IR refers to the possibility of a material misstatement in its financial statements caused by errors or omissions other than the failure of internal controls.
The audit risk model: your first step in risk assessment

How do you know if your risk controls are effective? Sometimes, even with the best intentions and the right controls, the audit ends up missing vital information and does not uncover problems. It is important to gauge whether the existing audit evidence is sufficient. How is audit risk calculated? By increasing the number of sampled transactions for detailed testing, auditors can reduce this type of risk. The risk of material misstatement refers to the possibility that the financial statements contain significant errors. Generally speaking, you need to identify the areas where risks are moderate to high and develop more thorough testing to support your claim. Accessed June 14, 2017.