Economic planning is the process of allocating resources and setting goals for an economy. It involves making decisions about what should be produced, how it should be produced, and for whom it should be produced. Economic planning can be carried out by governments, businesses, or individuals, and it can be done using various methods, such as central planning, market-based planning, or a combination of the two.
One of the main objectives of economic planning is to achieve economic growth, which is the increase in the production of goods and services within an economy over a period of time. Economic planning can also be used to address issues such as unemployment, poverty, and inequality, by implementing policies and programs that aim to create jobs, reduce poverty, and distribute wealth more evenly.
There are several different approaches to economic planning, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Central planning, also known as command planning, is a system in which a central authority makes all decisions about the allocation of resources and the production of goods and services. This approach is often associated with socialist or communist economies, where the government owns and controls the means of production.
Market-based planning, on the other hand, relies on the market to determine the allocation of resources and the production of goods and services. This approach is commonly associated with capitalist economies, where individuals and businesses make decisions based on supply and demand, and prices are determined by the market.
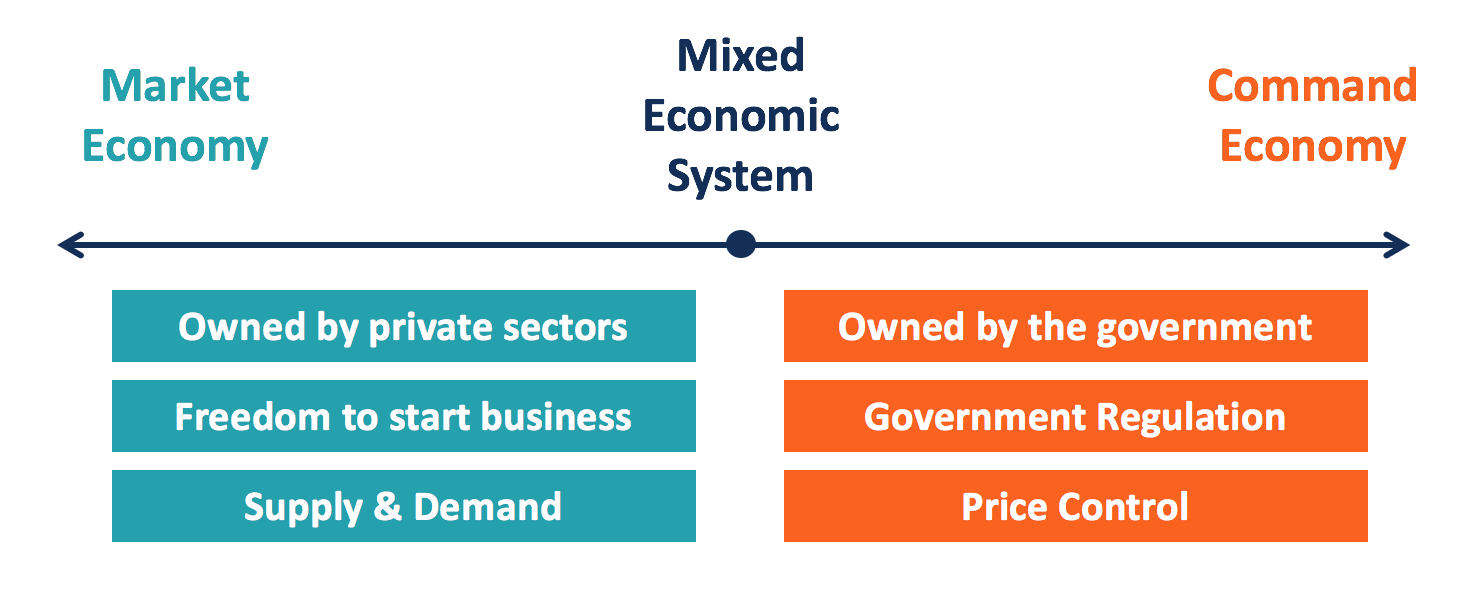
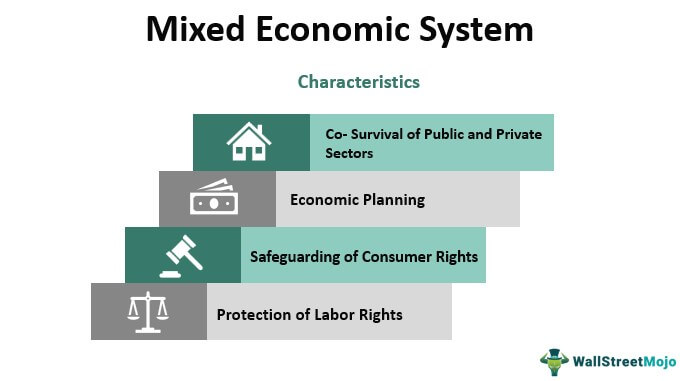
A mixed economy, which combines elements of both central and market-based planning, is a system in which both the government and the market play a role in resource allocation and economic decision-making. Many countries, including the United States, have mixed economies.
Economic planning can be a useful tool for achieving economic growth and addressing social and economic issues. However, it is not without its challenges and limitations. Economic planning can be difficult to implement effectively, as it requires a high level of coordination and cooperation between different sectors and stakeholders. It can also be subject to biases and unintended consequences, and it can be disrupted by external events such as natural disasters or economic crises.
Overall, economic planning is a complex and multifaceted process that plays a critical role in shaping the direction and performance of an economy. It is an important consideration for governments, businesses, and individuals seeking to make informed and strategic economic decisions.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TermDefinitions_Marketeconomy_finalv1-1d03048c89124873ac0350e7e96b1c4e.png)