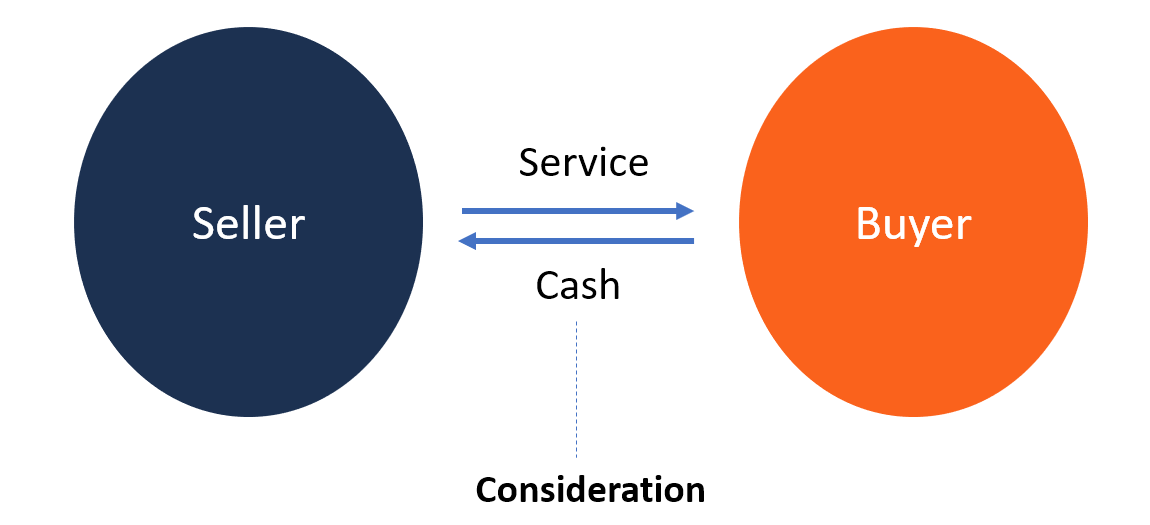
Executed consideration, also known as performance or completed consideration, is a legal concept that refers to the fulfillment of a promise or agreement. In contract law, it refers to the performance of an act or the rendering of a service that is promised in exchange for something else, such as money or another act or service.
For a contract to be enforceable, there must be mutual assent between the parties, meaning that both parties must agree to the terms of the contract and have the intention to be bound by it. In addition, there must be consideration, which is the exchange of something of value between the parties. Consideration can be either executed or executory, depending on whether it has been performed or is still outstanding.
Executed consideration occurs when the promise or agreement has been fulfilled by one party, and the other party has received the promised benefit or performance. For example, if Party A agrees to paint Party B's house in exchange for $500, and Party A completes the painting, the consideration has been executed. Party A has performed the agreed-upon act, and Party B has received the benefit of a freshly painted house.
The concept of executed consideration is important because it shows that both parties have fulfilled their obligations under the contract and that the exchange has been completed. It is also a key element in determining whether a contract is enforceable, as it demonstrates that there has been a valid exchange of value between the parties.
In contrast, executory consideration refers to a promise or agreement that has not yet been fulfilled. For example, if Party A agrees to paint Party B's house in exchange for $500, but the painting has not yet been completed, the consideration is executory. Once the painting is finished and Party B has received the benefit of a freshly painted house, the consideration becomes executed.
In conclusion, executed consideration refers to the fulfillment of a promise or agreement, in which one party has performed an act or rendered a service in exchange for something else. It is an important concept in contract law and is necessary for a contract to be enforceable.