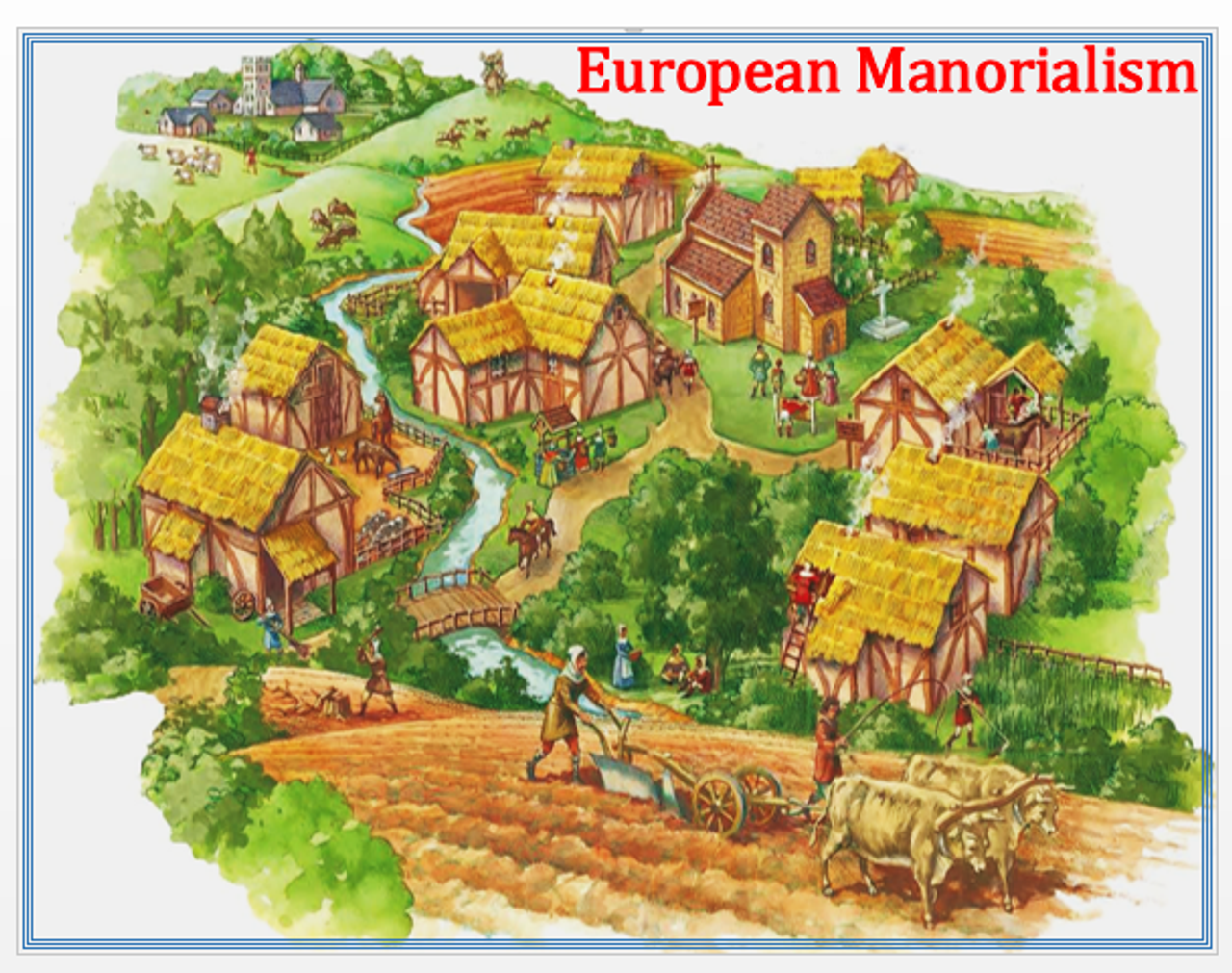
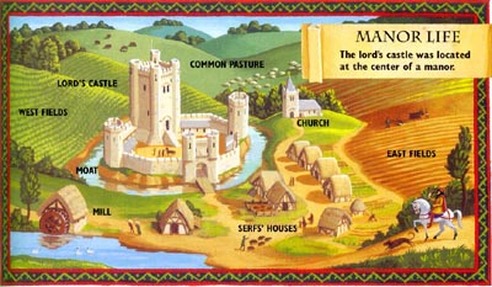
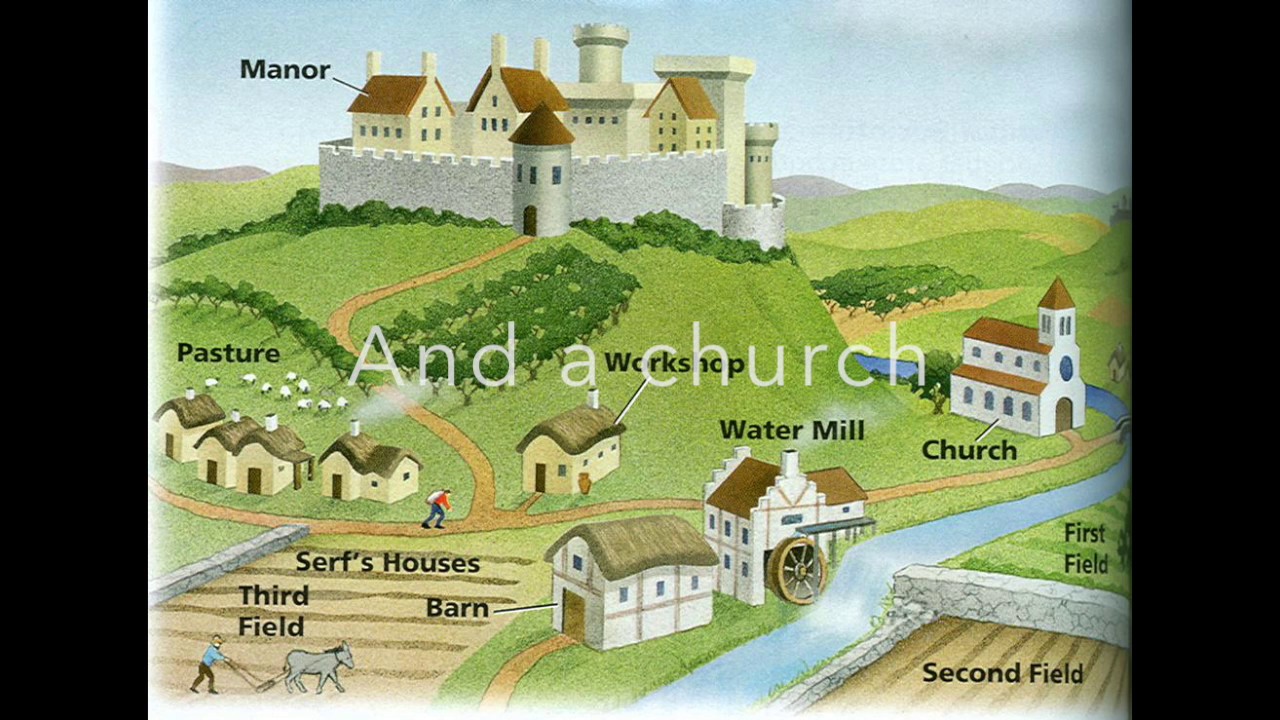
Manorialism was a system of feudalism that dominated the medieval European economy and society from the 9th to the 15th centuries. It was characterized by the ownership of land by lords, or lords and ladies, who granted the use of the land to tenants in exchange for their labor, military service, or other obligations.
Under manorialism, the lord held all of the power and authority in the manor, or estate. The lord owned the land and all of the resources on it, including the crops, animals, and natural resources such as timber and water. The lord also had the right to collect taxes and rents from the tenants, who were also known as serfs or vassals.
The tenants were bound to the land and were not allowed to leave without the permission of the lord. They were required to work a certain number of days each week for the lord, performing tasks such as farming, animal husbandry, and maintenance of the manor's buildings and infrastructure. In return, the tenants were given the use of a plot of land to cultivate for their own food and sustenance.
Manorialism was a hierarchical system, with the lord at the top, followed by the knights and other nobles who served him, and then the peasants and serfs at the bottom. The lord had the right to dispense justice and enforce his own laws on the manor, and the tenants had little recourse if they felt they were being mistreated.
Manorialism played a significant role in shaping the medieval economy and society. It provided a stable and reliable source of labor for the lords, and it allowed for the development of a complex agricultural system that supported the growth of towns and cities. However, it also had its drawbacks, as the tenants were often subject to harsh conditions and had little freedom or mobility.
Overall, manorialism was a dominant system in medieval Europe that shaped the economy, society, and culture of the time. It played a crucial role in the development of feudalism and has had a lasting impact on the history of Europe.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1053285684-96b37b776fea4dfe86631a23a0c23d5c.jpg)