Meteorology is the scientific study of Earth's atmosphere and the processes that occur within it. It encompasses a wide range of topics, including the physical properties of the atmosphere, the behavior of air masses, and the dynamics of weather and climate.
One of the primary goals of meteorology is to understand and predict weather patterns. This involves collecting data from various sources, including weather stations, satellites, and balloons, and using computer models to analyze and forecast future conditions. Meteorologists use this information to create weather reports and forecasts that help people plan for and respond to changing weather conditions.
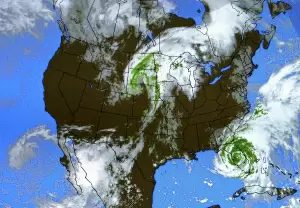
In addition to predicting weather, meteorologists also study the causes and impacts of severe weather events, such as hurricanes, tornadoes, and thunderstorms. They may use radar and other tools to track and predict the movements of these storms, and work with emergency management agencies to help mitigate their potential impacts on people and property.
Meteorologists also play a vital role in understanding and predicting long-term climate trends. They use data from a variety of sources, including tree rings, ice cores, and sediment samples, to track changes in Earth's climate over time. This information helps us understand how human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, may be contributing to global warming and other changes in the Earth's climate.
In summary, meteorology is a diverse and important field that helps us understand and predict the weather and climate, and enables us to plan for and respond to changing conditions. Its insights and forecasts help us make informed decisions about everything from agricultural planning and transportation to disaster preparedness and energy use.
Meteorology Definition & Meaning

Meteorology is one of the most important atmospheric scientists yet one that most of us do not think about. Atmospheric sciences is an umbrella term for the study of the atmosphere, its processes, and its interactions with the Earth's hydrosphere water , lithosphere earth , and biosphere all living things. Buffalo, New York: Firefly Books Inc. What is the importance of Earth science? They use data from weather stations to make predictions and provide information on the weather. Respectively, the Other subclassifications are used to describe the unique, local, or broad effects within those subclasses. Speculation on the cause of the flooding of the Nile ended when During the era of In 25 AD, From 400 to 1100, scientific learning in Europe was preserved by the clergy. First, cities need to be able to predict the weather because they need to be ready for things like tornadoes and snowstorms to avoid disasters.
What is Meteorology? 15 Branches of Meteorology

For example, air temperature and wind speed affect how well an airplane works. Neither of these can be seen but can be felt. Meteorology refers to a great difference in processes, including the appearances of the movements of the atmosphere, where the interaction with the emission of radioactive energy and thermodynamic processes, is what describes the states of equilibrium at the microscopic level that lead to the formation of clouds and their climatological manifestations such as rain, snow and hail. No, weather people are not meteorologists. The science of meteorology was restricted eventually to the study of the atmosphere.
What Is Aviation Meteorology? Why Is Meteorology Important In Aviation? Do Pilots Need To Know Meteorology?

In this early work, Lavoisier calls it "igneous fluid". These forecasts give you all the details you need about winds, turbulence, and jet streams to make safer decisions before takeoff and during your flight. The elements of meteorology are the atmosphere, the sun, and the moon. Climatology, the study of atmospheric changes that define climates over time, is another. For example, biometeorology measures how atmospheric conditions and short-term weather patterns impact living things.
What is meteorology and why is it important?

Retrieved 2 January 2009. Meteorology is used in everyday life to predict weather conditions, including rain, snow, and thunderstorms. Because of this, pilots need to understand meteorologyso they can make good decisions. The History of Meteorology: to 1800. The use of ensembles and model consensus help narrow the error and pick the most likely outcome. There is a lot of overlap between meteorology and earth science, as both deal with the behavior of the atmosphere and the surface of the Earth. He thought dense air produced propulsion in the form of wind.