The chaparral biome, also known as the Mediterranean scrubland, is a terrestrial ecosystem characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. It is found in regions with a Mediterranean climate, which is characterized by hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters. These conditions are created by the influence of cool ocean currents, such as the California Current, and the presence of high pressure systems over the land during the summer months.
The chaparral biome is characterized by a diversity of plant life, including evergreen shrubs, trees, and grasses. Many of the plants in this biome are adapted to the dry, hot conditions, with thick, waxy leaves that help to retain moisture and protect them from the hot sun. Some species also have deep root systems that allow them to tap into underground water sources during dry periods.
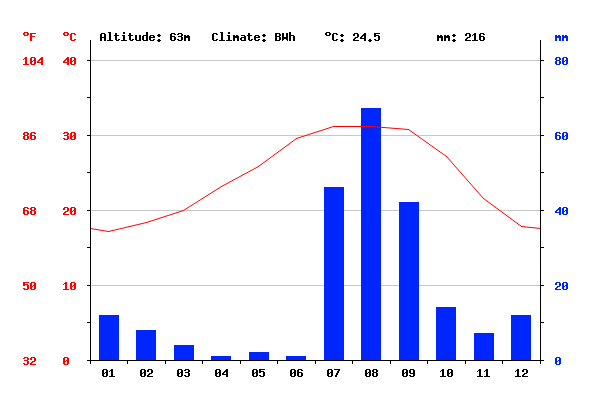
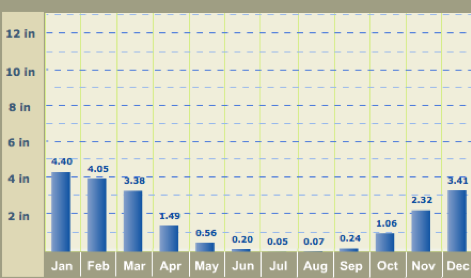
The climate of the chaparral biome is highly variable, with temperatures ranging from below freezing in the winter to over 100 degrees Fahrenheit in the summer. The average annual temperature is around 60-70 degrees Fahrenheit, with an average annual rainfall of 20-30 inches. However, these averages can vary widely from year to year, with some years experiencing drought conditions and others experiencing heavy rainfall.
Despite the dry conditions, the chaparral biome is home to a diverse array of plant and animal life. Many species, including the California chaparral and woodlands ecoregion, have evolved specialized adaptations to survive in this harsh environment. For example, some species of plants have developed the ability to regenerate after fires, which are common in this biome due to the dry conditions. Other species, such as the California condor and the mountain lion, are well adapted to hunting and surviving in the rugged terrain of the chaparral.
Overall, the climate of the chaparral biome is defined by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters, and is characterized by a wide range of temperatures and variable rainfall patterns. Despite the harsh conditions, this ecosystem is home to a diverse array of plant and animal life that have adapted to survive in this unique and challenging environment.