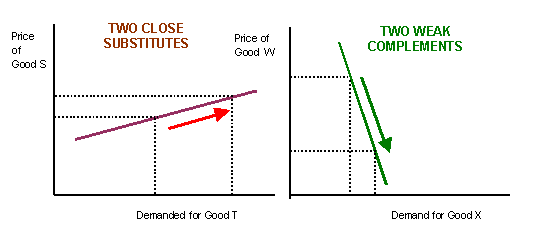
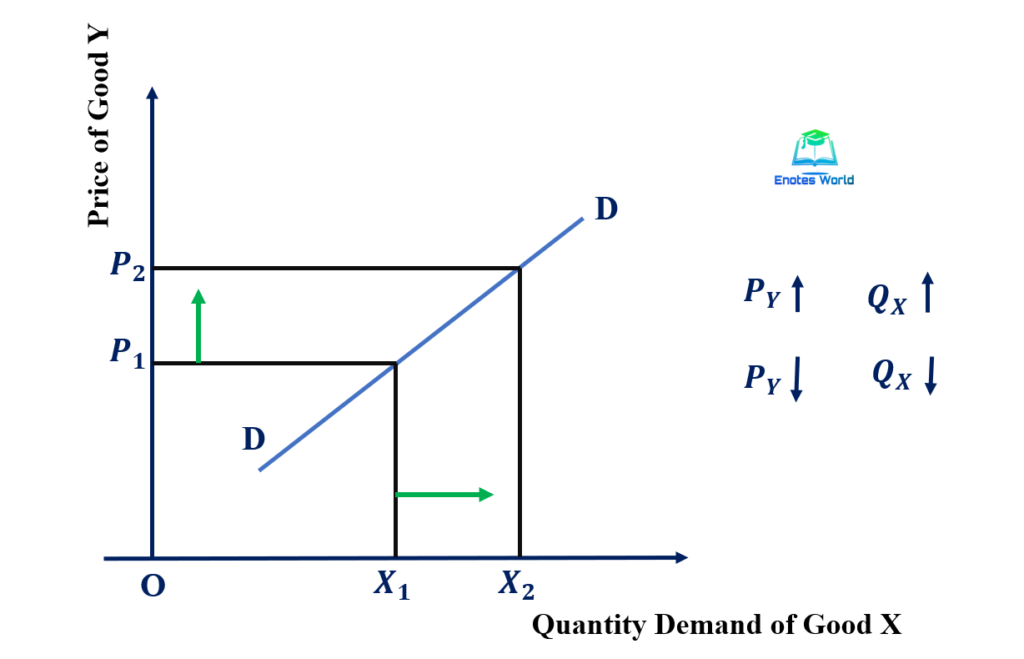
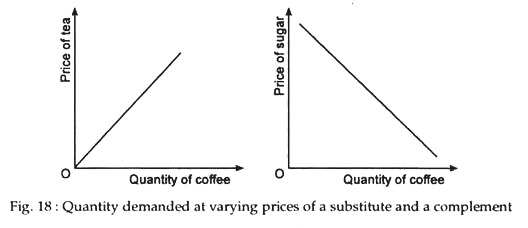
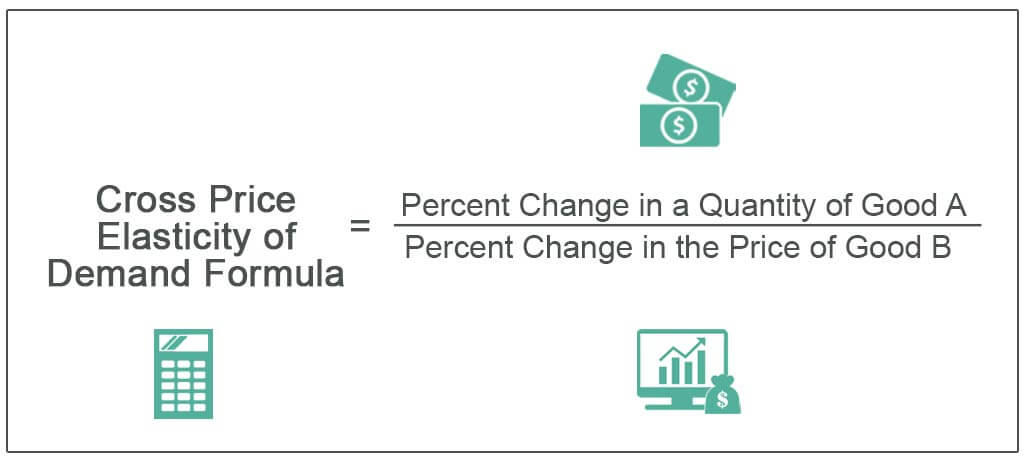
The cross elasticity of demand is a measure of the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good or service to a change in the price of a related good or service. It is calculated as the percentage change in the quantity demanded of the first good or service divided by the percentage change in the price of the related good or service.
For example, if the price of a good increases by 10% and the quantity demanded decreases by 5%, the cross elasticity of demand would be -0.5. This indicates that the two goods are substitutes, as the increase in the price of one good leads to a decrease in the demand for the other good. On the other hand, if the price of a good increases by 10% and the quantity demanded increases by 5%, the cross elasticity of demand would be 0.5. This indicates that the two goods are complements, as the increase in the price of one good leads to an increase in the demand for the other good.
The cross elasticity of demand is an important concept in economics because it helps to understand how changes in the price of one good or service can affect the demand for other goods and services. This understanding can be useful for businesses and policymakers in making pricing and marketing decisions.
For example, if a business sells a good that is a substitute for another good, it may be able to increase its sales by lowering its price. On the other hand, if a business sells a good that is a complement to another good, it may be able to increase its sales by raising its price, as the demand for the other good will increase as well.
In addition, policymakers may use the cross elasticity of demand to evaluate the potential impacts of policy changes on the demand for different goods and services. For example, if a policy change is expected to increase the price of a good, policymakers may consider the cross elasticity of demand to understand how this change could affect the demand for other goods and services.
Overall, the cross elasticity of demand is a useful tool for understanding the relationship between the prices and quantities of different goods and services, and can be used to make informed decisions in a variety of settings.