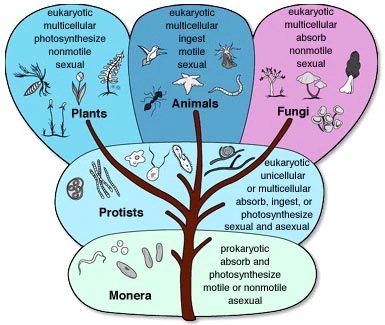
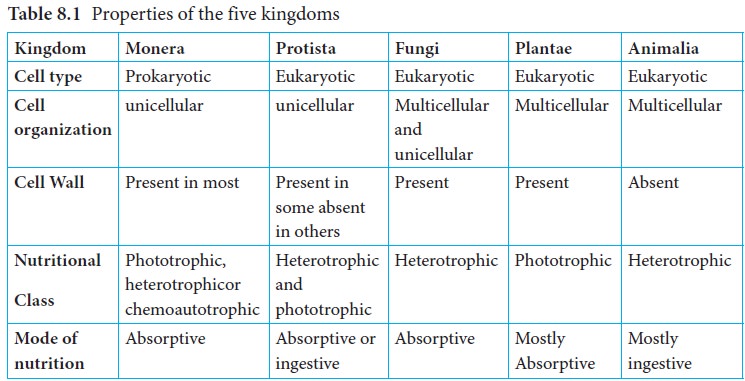
The five kingdom system is a classification system used to categorize and organize living organisms into five broad categories based on their shared characteristics and evolutionary relationships. It was first proposed by microbiologist Robert Whittaker in the 1950s and has been widely accepted and used in the field of biology for the classification of organisms.
The five kingdoms are Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. These kingdoms are further divided into smaller groups known as phyla, classes, orders, families, genera, and species.
The kingdom Monera includes prokaryotic organisms, such as bacteria, that are characterized by their simple cell structure and the absence of a true nucleus. These organisms are important in many ecological processes, including nitrogen fixation and the decomposition of organic matter.
The kingdom Protista includes eukaryotic organisms, such as algae and protozoa, that are characterized by their more complex cell structure and the presence of a true nucleus. These organisms play important roles in many aquatic ecosystems as primary producers, and some species are also important vectors of diseases.
The kingdom Fungi includes organisms such as yeasts, molds, and mushrooms that are characterized by their heterotrophic mode of nutrition and their cell walls made of chitin. Fungi play important roles in many ecological processes, including the decomposition of organic matter and the mutualistic relationships they form with other organisms.
The kingdom Plantae includes photosynthetic organisms such as algae, mosses, ferns, and flowering plants. These organisms are characterized by their ability to produce their own food through photosynthesis and their cell walls made of cellulose. Plants play important roles in many ecosystems as primary producers and also provide habitat and food for other organisms.
The kingdom Animalia includes multicellular organisms such as insects, vertebrates, and invertebrates that are characterized by their heterotrophic mode of nutrition and the presence of specialized organ systems. Animals play important roles in many ecosystems as consumers and also interact with each other and with their environment in complex ways.
The five kingdom system is a useful tool for organizing and understanding the diversity of life on Earth. It allows scientists to classify and study organisms based on their shared characteristics and evolutionary relationships, and helps to provide a framework for understanding the complex interrelationships between different groups of organisms. Despite its widespread use, the five kingdom system has also been criticized for its oversimplification of the diversity of life and the difficulty in placing some organisms into a single kingdom.