The legal classification system for medication is a system that categorizes medications based on their potential for abuse, misuse, and dependency. This system is used to regulate the distribution and use of medications and to ensure that they are used safely and effectively.
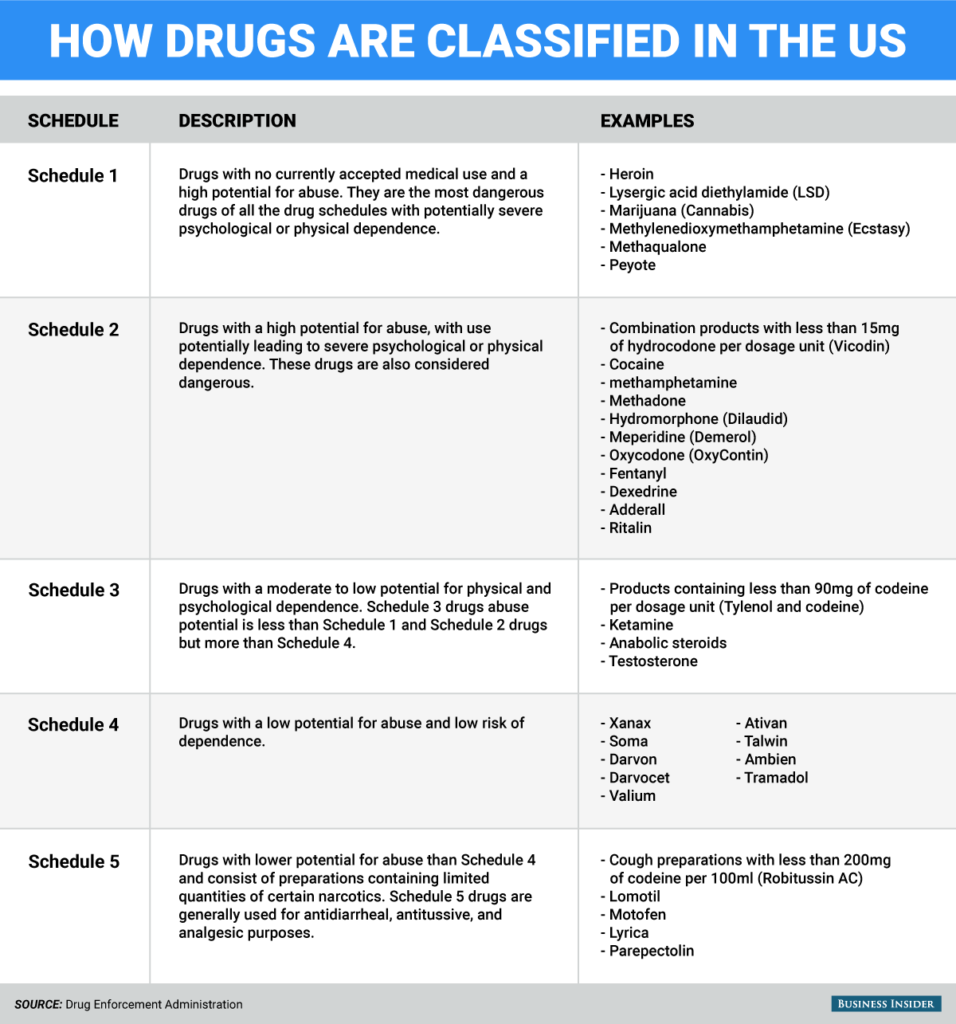
There are several different classification systems used around the world, but the most widely used is the United States' Controlled Substances Act (CSA). This act divides medications into five schedules, with Schedule I being the most restrictive and Schedule V being the least restrictive.
Schedule I drugs are considered to have a high potential for abuse and no accepted medical use. Examples of Schedule I drugs include heroin, LSD, and marijuana. These drugs are heavily regulated and are only available for research purposes.
Schedule II drugs have a high potential for abuse and dependence, but they also have accepted medical uses. Examples of Schedule II drugs include oxycodone, methadone, and fentanyl. These drugs are strictly regulated and are only available with a prescription from a licensed healthcare provider.
Schedule III drugs have a lower potential for abuse and dependence than Schedule II drugs, but they still have accepted medical uses. Examples of Schedule III drugs include some prescription opioids, stimulants, and anabolic steroids. These drugs are available with a prescription, but they may have additional restrictions, such as limits on the amount that can be prescribed at one time.
Schedule IV drugs have a low potential for abuse and dependence and accepted medical uses. Examples of Schedule IV drugs include prescription sedatives and anti-anxiety medications. These drugs are available with a prescription and may have additional restrictions on their distribution and use.
Schedule V drugs have the lowest potential for abuse and dependence and accepted medical uses. Examples of Schedule V drugs include some prescription cough and cold medications that contain small amounts of controlled substances. These drugs are available with a prescription and may have additional restrictions on their distribution and use.
In addition to the CSA, there are also other legal classification systems for medications. For example, the World Health Organization (WHO) has its own system for categorizing medications based on their potential for abuse and dependence. The WHO system is used by many countries around the world to regulate the distribution and use of medications.
In conclusion, the legal classification system for medication is a system used to regulate the distribution and use of medications based on their potential for abuse, misuse, and dependency. The CSA is the most widely used classification system in the United States, but other systems exist around the world. This system helps to ensure that medications are used safely and effectively, and it helps to prevent the abuse and misuse of these substances.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-938938858-7b656e6317ab4e2797556bdddce9595d.jpg)