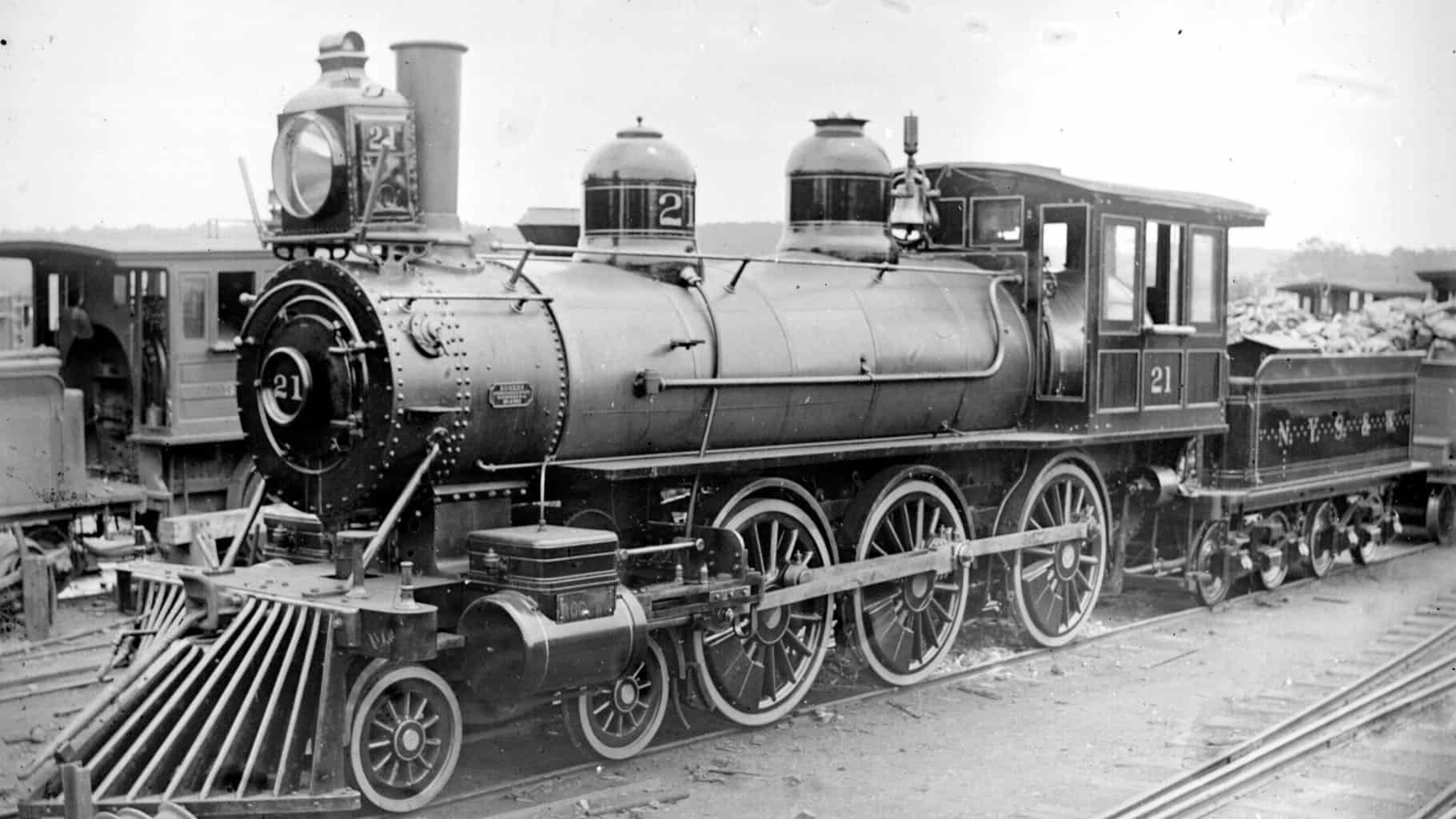
The goal of the Interstate Commerce Act, which was passed by the United States Congress in 1887, was to regulate the transportation of goods and people across state lines by railroads, steamboats, and other modes of transportation. The Act was prompted by widespread concerns about the abuse of power and monopolistic practices by the railroads, which had become an integral part of the American economy but were also seen as a threat to competition and the public interest.
The Interstate Commerce Act was the first federal legislation to address these issues, and it established the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC), an independent agency responsible for enforcing the provisions of the Act. The ICC was empowered to investigate complaints, set rates, and issue orders to ensure that the railroads and other carriers were operating in a fair and reasonable manner.
One of the main goals of the Act was to promote competition and prevent the railroads from engaging in discriminatory practices. Under the Act, railroads were prohibited from charging different rates for the same service based on the distance traveled or the location of the shipper or receiver. The Act also required the railroads to publish their rates and to disclose any rebates or discounts they offered to certain customers.
Another goal of the Act was to ensure that the railroads and other carriers were accountable for the safety and welfare of their passengers and the goods they transported. The Act required carriers to maintain safe equipment and facilities, and it gave the ICC the authority to impose penalties for violations of these safety standards.
Overall, the goal of the Interstate Commerce Act was to promote fair competition and protect the public interest by regulating the transportation of goods and people across state lines. While the Act was not perfect and did not solve all of the problems associated with the railroads and other carriers, it represented an important step in the development of federal regulation of interstate commerce in the United States.
The Purpose of the Interstate Commerce Act of 1887

Many Southern states pushed back on Congress's ability to regulate interstate trade because they didn't want the federal government interfering with the slave trade. The Compact Theory was created in response to AGI. What did the Interstate Commerce Commission do and why was its creation significant quizlet? As a result, more companies are looking to enter interstate compacts, which are agreements between two or more states that regulate business relationships between businesses. So it was later replaced with the Clayton Antitrust Act. For example, they could help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, protect biodiversity, and make it easier for goods to move between countries.
chapter 4

Why was the Interstate Commerce Commission created to regulate railroads quizlet? Source: Yale University Libraries, Wikimedia Commons Railroads also played an important role in the Civil War 1861-1865 : the more industrialized Northern U. Corporate greed, monopolistic power, and corruption were rampant, and public outrage grew over how the railroads were operated. Why did the Interstate Commerce Commission have difficulty enforcing reforms? Interstate compacts are important because they help to keep the trade between the United States and other countries flowing smoothly. To learn more about US history, check out this Sources 1 Hilton, George W. What is the purpose of interstate compacts? These railroads were privately owned and unregulated.
Interstate Commerce Act of 1887

What were the benefits of the Interstate Commerce Commission? This took away their ability to make secret deals with certain companies and could no longer offer favorable deals to some companies and not others. The Interstate Commerce Act was to monitor railroad operations. As the Department of Justice DOJ investigates whether or not state and local law enforcement officers have abused their power in Ferguson, Missouri, it becomes apparent that there are many interstate compact agreements in place between different jurisdictions which were not properly vetted by Congress. Railroads were required to submit annual reports to the Interstate Commerce Commission if they operated railroads that crossed state lines. What constitutes interstate commerce? Teddy Roosevelt helped to bring more power to the ICC and is depicted in the middle holding a dove and olive branch via The law itself was wildly inconsistent, promoting competition in some sections and hobbling it in others. Interstate Commerce Act Purpose The Interstate Commerce Act made some important changes to the railroad industry. With many of those questions of approach decided, Congress passed the Interstate Commerce Act the following year; it was signed into law by President Grover Cleveland on February 4, 1887.