World War II was a global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945 and involved the majority of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis. It was the most widespread war in history and directly involved more than 100 million people from more than 30 countries. The causes of World War II are complex and numerous, but the main factors that led to the outbreak of the war were militarism, alliances, imperialism, and nationalism.
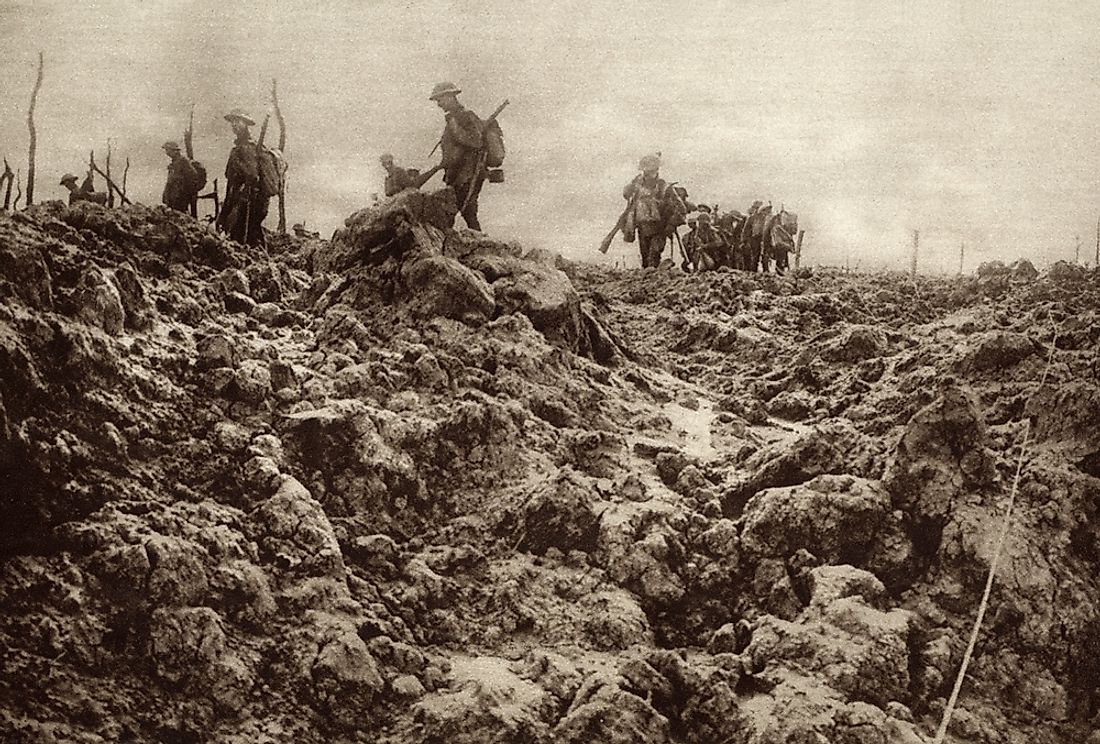
Militarism played a significant role in the buildup to World War II. Many countries, particularly Germany, Italy, and Japan, had strong militaries that were used to further their own interests and assert their power on the world stage. These countries also had leaders who believed in the use of military force to achieve their goals, and they pursued policies of rearmament and expansion in order to build up their military capabilities.
Alliances were another important factor that contributed to the outbreak of World War II. Countries formed alliances with one another for a variety of reasons, including to protect their interests and to deter potential enemies. These alliances could be bilateral, such as the agreement between Germany and Italy, or they could be multilateral, such as the alliance between the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and the United States. These alliances were meant to provide mutual support and protection, but they also made it easier for smaller conflicts to escalate into larger ones.
Imperialism was another factor that contributed to the outbreak of World War II. Many countries, particularly European powers, had established colonies around the world, and they used their military and economic power to exert control over these territories. This led to tensions between different countries as they competed for resources and influence.
Nationalism was also a significant factor in the buildup to World War II. Nationalism is a belief in the superiority of one's own nation and a desire to protect and promote its interests. It can be a powerful force, and it was used by many leaders during the war to rally support for their cause and to justify their actions.
In conclusion, the causes of World War II were complex and multifaceted, but the main factors were militarism, alliances, imperialism, and nationalism. These forces interacted with one another and contributed to the buildup of tensions between countries, which eventually led to the outbreak of the war.