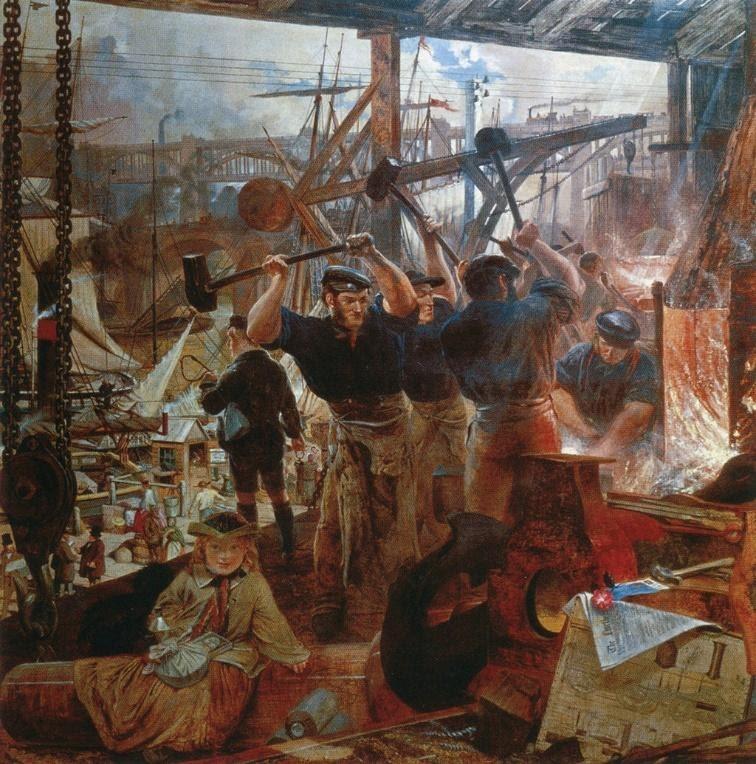
The Industrial Revolution began in Britain in the late 18th century and spread to other parts of the world in the 19th and 20th centuries. It marked a significant shift in the way goods were produced and consumed, as the focus moved from handmade goods to mass production using machinery.
Before the Industrial Revolution, most goods were produced by hand using traditional methods that had not changed for centuries. Production was slow and labor-intensive, and the quality of the goods often varied due to the lack of standardization.
The Industrial Revolution began in Britain for a number of reasons. Firstly, Britain had a large and growing population, providing a ready supply of labor for the new factories that were being built. Secondly, Britain had a well-developed system of transportation, including roads, canals, and rivers, which made it easier to transport raw materials and finished goods. Thirdly, Britain had a strong tradition of innovation and entrepreneurship, which encouraged the development of new technologies and business models.
One of the key drivers of the Industrial Revolution was the development of new sources of energy, including coal and steam power. The use of coal as a fuel allowed for the production of more heat and power, which in turn enabled the development of steam engines and other machinery. The steam engine, in particular, revolutionized transportation and manufacturing, as it could be used to power trains, ships, and factories.
Another important factor in the Industrial Revolution was the development of new technologies and techniques for manufacturing. The use of machines allowed for the mass production of goods, which led to lower prices and increased availability for consumers. The introduction of the factory system, in which workers were brought together in a central location to work on specialized tasks, also contributed to the increase in efficiency and productivity.
The Industrial Revolution had a major impact on society, as it led to the growth of urban areas and the rise of a new industrial working class. It also had significant environmental consequences, as the burning of fossil fuels led to air pollution and the exploitation of natural resources.
Overall, the Industrial Revolution began in Britain in the late 18th century and spread to other parts of the world, transforming the way goods were produced and consumed and having a lasting impact on society and the environment.