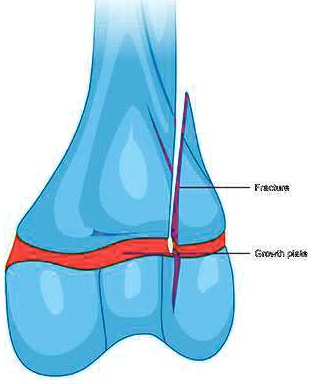
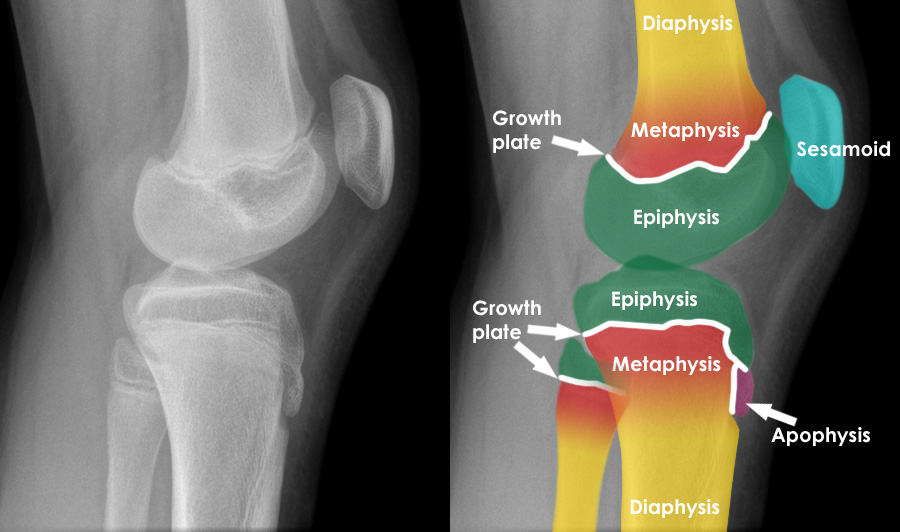
Bone growth occurs in specific areas of the bone called growth plates or epiphyseal plates. These growth plates are found in the long bones of the body, such as the femur, tibia, and fibula in the leg, and the humerus, ulna, and radius in the arm. They are also found in the bones of the hands and feet.
Growth plates are made up of hyaline cartilage, a type of smooth, glossy cartilage that is found in various parts of the body. The cells in this cartilage, called chondrocytes, are responsible for producing new matrix, which helps to lengthen the bone. As the chondrocytes produce new matrix, the bone lengthens and grows.
Growth plates are found at the ends of the long bones, near the joints. They are responsible for the growth of the bone in length, as opposed to the bone's growth in width, which occurs through the process of bone remodeling.
Growth plates play a crucial role in bone growth during childhood and adolescence. As children grow, their bones lengthen due to the activity of the chondrocytes in the growth plates. This process continues until the child reaches their full adult height.
Once a person reaches their full adult height, the growth plates begin to harden and become replaced by solid bone. This process is called ossification and it marks the end of bone growth.
In summary, bone growth occurs in the growth plates of the long bones, and is driven by the activity of chondrocytes, which produce new matrix that helps to lengthen the bone. This process continues until a person reaches their full adult height, at which point the growth plates harden and are replaced by solid bone.
Bone Regeneration
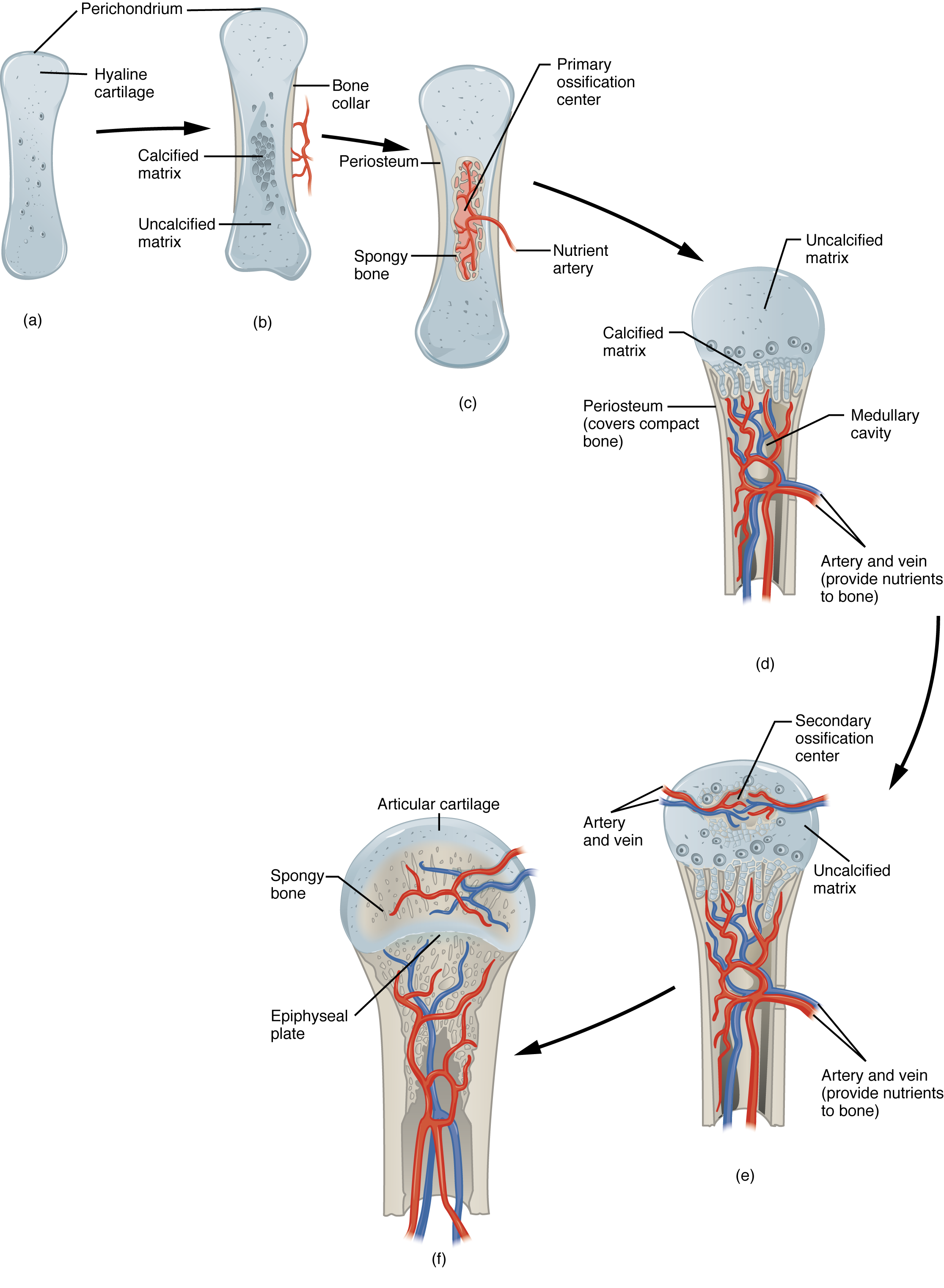
Compact bone is added to create bone tissue that is similar to the original, unbroken bone. While bones are increasing in length, they are also increasing in diameter; growth in diameter can continue even after longitudinal growth ceases. Unlike most connective tissues, cartilage is avascular, meaning that it has no blood vessels supplying nutrients and removing metabolic wastes. Ossification Time period Bones affected 18 to 23 years Bone of the lower limbs and os coxae become completely ossified 23 to 26 years Bone of the sternum, clavicles, and vertebrae become completely ossified By 25 years Nearly all bones are completely ossified What is bone growth in length called? Diseases of the…Skeletal SystemOsteogenesis imperfecta OI is a genetic disease in which bones do not form properly and therefore are fragile and break easily. Injury, exercise, and other activities lead to remodeling. Babies are born with about 300 bones, and full-grown adults have only 206. Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to: Discuss the process of bone formation and development.
Bone Healing

This type of growth, called appositional growth, happens when osteoblasts in the periosteum deposit new bone matrix layers onto already-formed layers of the outer surface of bone. They then differentiate into osteoblasts at the ossification center. What Is Bone Regeneration? If a bone will be cut during a planned surgical procedure, some steps can be taken pre- and postoperatively to help optimize healing. The periosteum is the connective tissue on the outside of bone that acts as the interface between bone, blood vessels, tendons, and ligaments. All of these functions are carried on by diffusion through the matrix from vessels in the surrounding perichondrium, a membrane that covers the cartilage, a. Test the hypothesis: Test the prediction by removing calcium from chicken bones by placing them in a jar of vinegar for seven days.
What Is a Bone Growth Stimulator?

What is the lifespan of a cartilage cell? Bone formation proceeds outward from these centres. As healing progresses, the soft callus is replaced with hard bone known as hard callus , which is visible on x-rays several weeks after the fracture. This is called appositional growth. This cartilage is a flexible, semi-solid matrix that is produced by cartilage cells and consists of chondroitin sulfate, collagen fibres, hyaluronic acid, and water. Endochondral Ossification In endochondral ossification, bone develops by replacing hyaline cartilage.
How do Bones Grow?

In this process, chondroblasts of the perichondrium, which are precursors to chondrocytes, form an extracellular matrix and develop into mature chondrocytes. The remodeling process occurs as bone is resorbed and replaced. Growth of Bone Long bones continue to lengthen, potentially until adolescence, through the addition of bone tissue at the epiphyseal plate. Where does appositional growth take place in the bone? Appositional growth can continue throughout life. How Bones Grow in Diameter While bones are increasing in length, they are also increasing in diameter; growth in diameter can continue even after longitudinal growth ceases.