Why did elephants evolve. Elephant Evolution 2022-12-20
Why did elephants evolve
Rating:
6,1/10
1348
reviews
Elephants are one of the most iconic and beloved animals on the planet, known for their massive size, intelligent social behavior, and long lifespan. But how did these majestic creatures come to be? In this essay, we will explore the evolution of elephants, examining the factors that led to their development and the adaptations that allowed them to thrive in a variety of environments.
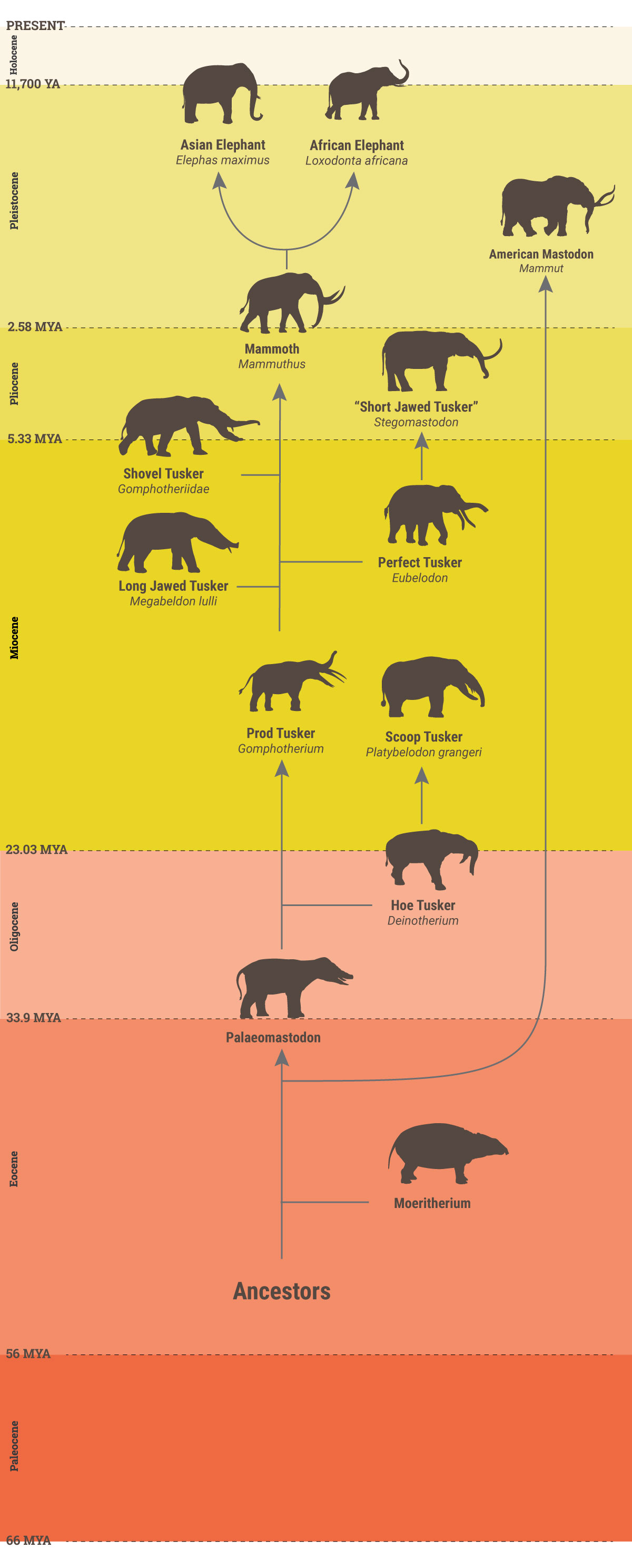
The elephant family, known as the Elephantidae, evolved from a group of small, forest-dwelling mammals that lived approximately 50 million years ago. These ancient elephants, known as proboscideans, were much smaller than their modern counterparts, with shorter legs and smaller bodies. They also had a more flexible spine, which allowed them to navigate through dense forests and climb trees to reach food.
Over time, the proboscideans began to adapt to new environments, developing longer legs and larger bodies in order to better survive in open grasslands. This allowed them to travel longer distances in search of food and water, and to defend themselves from predators. They also developed a trunk, which gave them increased flexibility and the ability to use their sense of smell to find food and water.
As the proboscideans continued to evolve, they became more specialized, with some species developing tusks and others developing a more streamlined body shape. This allowed them to better exploit different types of food sources and defend themselves from predators.
One of the most interesting adaptations of elephants is their social behavior. Elephants are highly intelligent and social animals, living in complex social groups known as herds. These herds are led by a dominant female, and all members of the herd work together to protect and care for the young. This social behavior has helped elephants to survive in a variety of environments, as they can rely on the support of their herd to find food and water, and to defend themselves from predators.
In conclusion, the evolution of elephants has been shaped by a variety of factors, including environmental changes, competition with other species, and the need to adapt to new environments. Through their adaptations, elephants have become one of the most successful and enduring species on the planet, and they continue to captivate and inspire people all over the world.
Elephant Evolution
How did elephants evolve over time? What features did mammoths have that were different from modern day elephants? Hence the elephant population is shrinking by every single year. They have to be able to reduce their body temperatures and to regulate them. Mastodon DNA was extracted from various different teeth, while straight-tusked-elephant DNA was taken from a petrous bone in the skull. By becoming the giant beasts we all know now, they protect themselves from predators. They are still considered to be on of the most adaptable animals in the world. That's why the elephant's nose gets longer? They are also distantly related to both dugongs, and hyraxes.
Next
Elephant Evolution: Phosphatherium to the Woolly Mammoth

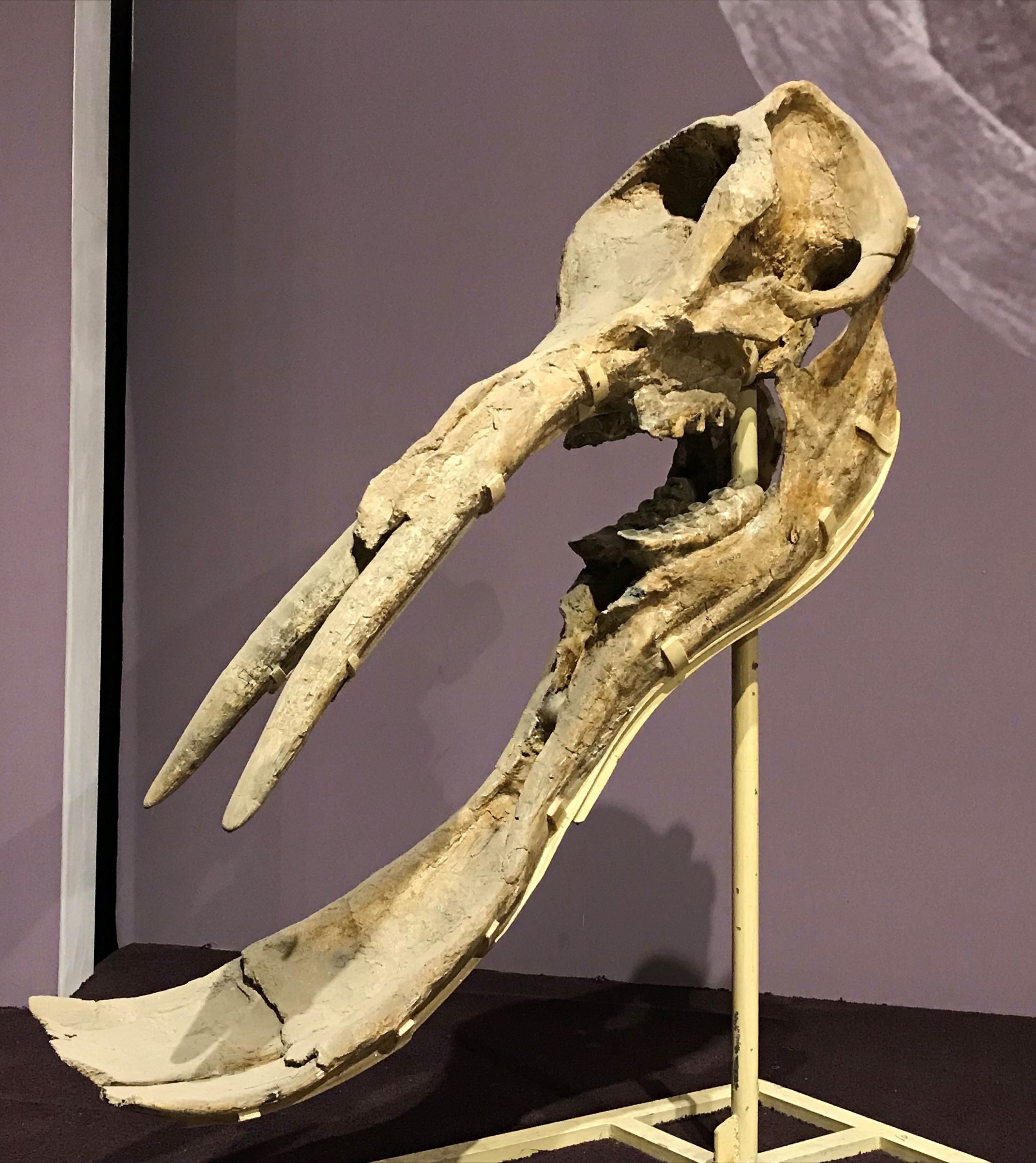
Their jaws are extremely long and its front has a pair of flat incisors in the lower jaw. It shows that the two modern African elephant species are heirs of a glorious and evolutionary successful past which still survives and speaks through their DNA. Moeritherium was named after Lake Moeris combined with Ancient Greek. They are very strange elephants that appeared in the Miocene era. What is the earliest ancestor of an elephant? With such a bizarre appearance, this species also has another name: elephant tooth shovel , their strange mouth resembles the combination of a duck and a muzzle of wild boars. Elephants - the largest land animals alive today - are the only remaining species of the family Elephantidae, which belongs to an ancient order of Proboscidea. The woolly mammoth was roughly the same size as modern African elephants.
Next
What did elephants evolve?

Researchers concluded in their study published in Researchers suggest that tumor suppression capabilities coincided with the evolution of exceptionally large body species to facilitate development. What is the common ancestor of elephants and manatees? DNA testing has proven beyond any doubt that they are indeed related to elephants. Did elephants live in the sea? Their last common ancestor with modern-day elephants lived somewhere in Africa about 6 million years ago. Elephant evolution is unfortunately in danger because of poaching. For this study, researchers extracted mammoth DNA from bone, molar teeth, tusk and fat tissue. Scientists speculate that their lower teeth structure is convenient for picking plants in the water when searching for food in the swamp. Long ago there were mega-armadillos, giant sloths, and RELATED STORY: Check out more news and information on.
Next
What is the ancestor of the elephant?

Then genetic analyses suggested that the African Elephant could be divided into Now a new elephant has been added to the mix. At that time African elephants branched off first. From the fossils discovered, paleontologists believe that they have a behavior similar to that of modern elephants and have fangs bent down to attach to the lower jaw. Blue whales are the largest animals ever to have lived. Could wooly mammoths be alive? Mammoths were slightly bigger and more widespread than mastodons, and had fatty humps on their necks, a much-needed source of nutrition in the harsh northern climates in which some species lived.
Next
Ancient DNA changes everything we know about the evolution of elephants

However, There are also some types of DNA that are, historically, easier to work with, such as mitochondrial DNA, which exists in multiple copies in each and every cell, and even in each and every mitochondria These copies of DNA are relatively small, compared to a chromosome, and due to their sheer abundance it becomes a much simpler task to reconstruct a whole mitochondrial genome - even from ancient material. Today, all but two members of the Elephantidae family of the order Probiscidea, meaning animals with trunks, have survived — African and Asian elephants. Scientists think woolly mammoths evolved about 700,000 years ago from populations of steppe mammoths living in Siberia. And they have become the most important authorities in elephants. The fossil evidence also adds to the exotic elephant evolutionary tale, which points towards morphological similarities between straight-tusked elephants and Asian elephants. Yet another northern African proboscid of this time was the confusingly named Palaeomastodon, which should not be confused with the Mastodon genus name Mammut that ruled the North American plains 20 million years later.
Next
Elephant Evolution

And this also makes the ancestors of the elephant skull thicker heavier and stronger, followed by a "lumpy" neck full of strong muscle. We all know that elephants use their noses to mess up almost everything, not just to breathe, this sedge is also flexible that can act as an arm and a device. That is why elephants are evolving to lose their tusks. Through generations of evolution, the head and chin of elephants have become shorter, while the nose continues to grow and change more flexibly. Recent morphological- and molecular-based classifications reveal the sirenians to be the closest living relatives of elephants.
Next
The ins and outs of elephant evolution

As members of the family Elephantidae, woolly mammoths were themselves elephants. The most important of these, from an evolutionary perspective, were the gomphotheres "bolted mammals" , but the most impressive were the deinotheres, typified by As terrifying as Deinotherium was, though, it represented a side branch in elephant evolution. However, with humans taking these areas away from them at an alarming rate there is a limit to what they are able to do and where they are able to survive today. Males reached shoulder heights between 2. Early ancestors in the Palaeocene and Eocene were small, semi-aquatic animals.
Next
Elephant Evolution: Why the Biggest Pachyderms are Big and Resistant to Cancer?
.jpg)
However, the reality is that many of the ancestors of these species mated with each other, leading to a patchwork genetic legacy of which interspecies hybridisation played a huge role. Importantly, until now only a mitochondrial genome was available for the American mastodon. But how are all these species related to one another, and what sort of events drove the evolution of elephants around the globe? However, poaching for ivory is reducing their population. Genome sequencing of elephants long extinct and those still walking the earth, along with the use of powerful computing techniques, tells a story of speciation, migration and repeated hybridisation. Modern day elephants are now only found in pockets of African savannah, in the tropical forests of West and Central Africa, or scattered around South-East Asia. These early hoofed mammals lived during the early Cenozoic age and were small, rodent-like creatures that lived on land. ALSO READ: Enhanced Cancer Protection of Elephants Despite many elephant relatives harboring extra copies of tumor suppression genes, scientists found that elephant genomes possess unique duplications that contribute to tumor suppression through genes involved in DNA repair, cellular growth, resistance to oxidative stress, aging, and death.
Next
Why did the elephant's nose evolve so long?

But the phenomenon isn't exclusive to elephants. This study changes everything we thought we knew about the evolutionary history and ancestry of modern elephants and their closest relatives. This can also account for the larger size of the ears; they use them as fans to cool down. Researchers searched for extra copies of the tumor suppressor gene in DNAs of the African savanna, Asian, and African forest elephants, and a number of following Afrotherians such as elephant shrews, Cape golden moles, rock hyraxes, extinct wooly mammoths, manatees, extinct mastodons, and more. Fossils show that the straight-tusked elephants arrived in Eurasia around 750 000 years ago and that they left Africa through the Middle East. Their natural habitat was simply changing faster than they could adapt and eventually the animals died off.
Next
The rise and fall of elephant ancestors

The mammoth was identified as an extinct species of elephant by Georges Cuvier in 1796. For this study, researchers focused on whether elephant genomes included more copies of tumor suppressors than expected whether it's a general trend among the species or if it's specific to one gene. The woolly mammoth Mammuthus primigenius is a species of mammoth that lived during the Pleistocene until its extinction in the Holocene epoch. How could the straight-tusked elephant be related to African elephants and its dwarf descendant be related to Asian elephants? Over the last 60 million years, proboscideans - the order of animals which includes elephants - changed dramatically as they expanded geographically and adjusted to various climate changes. Elephant Sense and Sensibility. From their evolution tree, scientists have discovered that elephants can adapt to climate change by becoming bigger in size and brain.
Next







.jpg)

