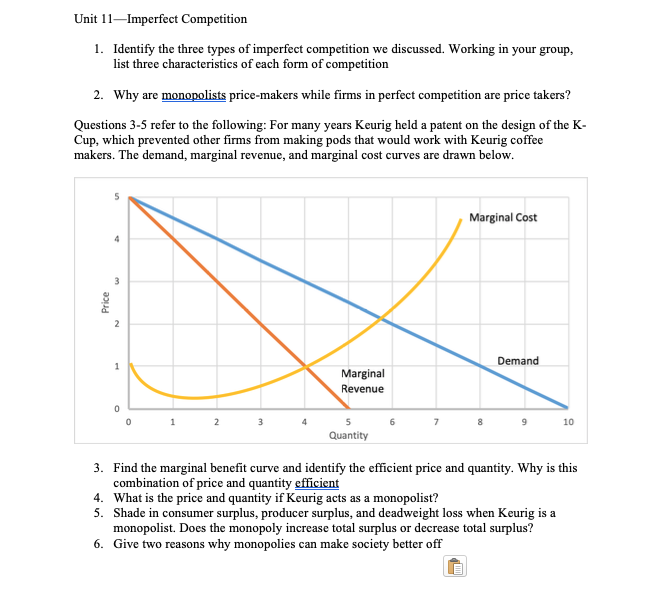
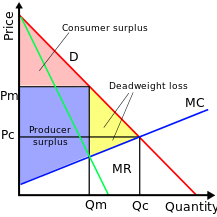
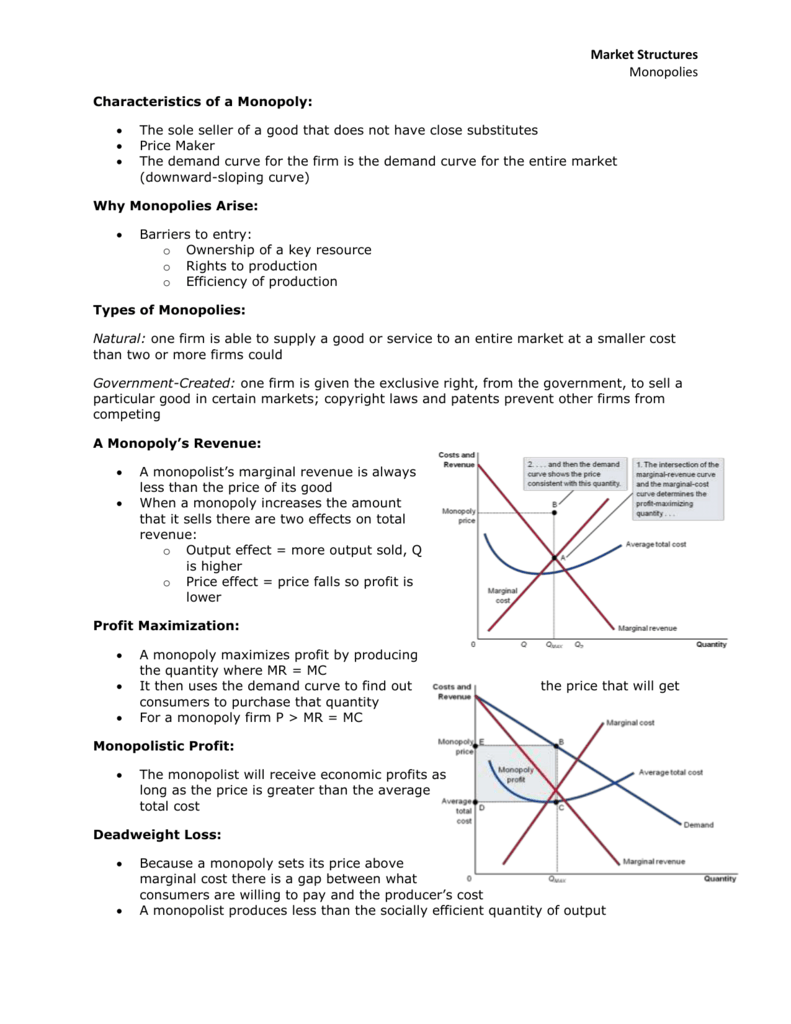
A monopolist is a price maker because they are the only seller in the market. This means that they have complete control over the price of their product or service, as there are no other competitors to offer alternatives or exert downward pressure on prices.
The ability to set prices is a key aspect of a monopolist's market power. Without competition, the monopolist can charge whatever price they want, as there is no incentive for them to lower their prices to attract customers. This can lead to higher prices for consumers, as the monopolist has no motivation to offer discounts or promotions to stay competitive.
There are several factors that can contribute to a monopolist's price-setting power. One is the presence of barriers to entry, which prevent new firms from entering the market and competing with the existing monopolist. These barriers can include high startup costs, government regulations, or patents and other intellectual property protections.
Another factor is the lack of substitutes for the monopolist's product or service. If there are no good substitutes available, consumers may be willing to pay a higher price for the monopolist's product, as they have no other options. This can allow the monopolist to charge a premium price for their product, further increasing their profits.
In addition to setting higher prices, a monopolist may also have the ability to engage in price discrimination, where they charge different prices to different groups of consumers based on their willingness to pay. This can further increase the monopolist's profits, as they are able to extract more money from consumers who are willing to pay higher prices.
Overall, a monopolist's ability to set prices is a key aspect of their market power. Without competition, they have complete control over the price of their product or service, which can lead to higher prices for consumers and higher profits for the monopolist.
Why are monopoly firms a price maker and not a price taker?

However, consumer debt can also include collateralized consumer loans like mortgage and car loans. What is the formula for maximum profit? There is a big difference between economic modeling of Price Maker models and legal determinations of whether Price Maker behavior is actionable. How do you find profit-maximizing price? Perfect Competition: It is opposite of Monopoly. Direct costs can include purchases like materials and staff wages. Assets that are commonly served in estate planning include money, properties, vehicles, investments, personal property artwork, jewelry, and other valuables , life insurance policies, and debt. If the objective of government is to achieve allocative efficiency, what kind of price should government establish for the monopolist? Long-run average total costs remain the same over a wide range of output. Produce an amount greater than 6 units.
Explain why a monopoly is a price maker

A UK Based online assignment help service offering writing and editing help for the students who are seeking homework help services, essay writing, assignment help, or help with assignment. Under perfect competition, there are very large number of firms producing homogeneous commodity. However in the present scenario when competition has reached heights, customers have tones of variety to choose from every genre- starting from daily soaps, eateries, clothes, electronics, etc. Which market is price taker? Select all that apply Which of the following are assumptions made in the model of pure monopoly? Produce an amount less than 4 units. In a monopoly, the price is set above marginal cost and the firm earns a positive economic profit. Not enough information is provided to determine the answer. In such a market, all firms determine the price of their own products.
SOLVED:Why is a monopolist a price maker rather than a price taker?

There is a lot of competition in the cell phone, tablet, and computer markets and there are lots of similar products on the market. . There was simply no viable way of incorporating competition into that industry until the advent of personal computers and, later, cellular phones. Buyers have only imperfect knowledge as to price, cost, and product quality. For sure, our Big 6 constitute an Oligopoly and they may be moving toward Monopoly Power as consolidation continues. A modern-day company with a monopoly is Monsanto, which sells genetically modified seeds.